Macromolecules, Water, and pH, · MACROMOLECULES •Macro = “Large” •Also known as polymers....
Transcript of Macromolecules, Water, and pH, · MACROMOLECULES •Macro = “Large” •Also known as polymers....

MACROMOLECULES, WATER, AND PH
Biology
Spring 2020

MACROMOLECULES

BIOLOGICAL MACROMOLECULES
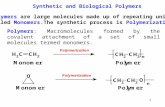
• Macro = “Large”
• Also known as polymers. Poly = “Many”
• Many what? Many monomers!
• Monomers are smaller repeating subunits that make up polymers
• Monomers are the building blocks of polymers!
• All biological macromolecules are organic molecules, meaning they contain the element CARBON.

CARBOHYDRATES
• Monomers: monosaccharides (simple sugars)
• If two monosaccharides join together, they form disaccharides
• If many monosaccharides join together, they form polysaccharides, or complex sugars
• Function: your body’s main source of energy
• Additional functions: structure and support
• Structure: Compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms for each carbon

LIPIDS
• FATS, oils and waxes!
• Monomer: No true monomer
• Function: to store energy
• Additional functions:
• Insulation
• Prevent water loss – lipids don’t mix with water!
• Additional information
• Hydrophobic: “water fearing”
• Lipids with only single bonds = saturated fats
• Lipids with at least one double bond = unsaturated fats

PROTEINS
• Monomer: Amino acids
• 20 different amino acids
• Function: involved in nearly every function of your body
• Structural support
• Build muscle
• Communicate signals between cells
• Speed up chemical reactions (ENZYMES)
• Control cell growth
• Additional information:
• Structure of a protein determines its function
• Made by the ribosome

NUCLEIC ACIDS
• Monomer: Nucleotides
• Three components: a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base
• Function: Store and transmit genetic information
• Additional Information:
• Composed of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous and hydrogen atoms
• DNA
• Double stranded
• Only in nucleus
• RNA
• Single stranded
• Anywhere in cell

WATER

PROPERTIES OF WATER: WATER IS A POLAR
MOLECULE
• Water is a polar molecule
• A water molecule has an overall positive
charge
• This makes it great for bonding!
• Water molecules form hydrogen bonds
easily with other water molecules
• A water molecule is held together with
covalent bonds
• Electrons are shared, but they are shared
unevenly

PROPERTIES OF WATER: WATER IS THE UNIVERSAL
SOLVENT
• Water is able to dissolve many substances, making it very useful!
• Water is the universal solvent
• Solvent: the substance that does the dissolving in a mixture.
• Solute: the substance that is dissolved in a mixture.

PROPERTIES OF WATER: PURE WATER HAS A PH OF 7
• Pure water has a pH of 7.
• There is an equal
concentration of OH- ions and
H+ ions.

PROPERTIES OF WATER: WATER IS BOTH COHESIVE AND ADHESIVE
• Cohesion: water’s ability to
form hydrogen bonds
with other water
molecules (water = water).
• Creates a high surface tension
• Adhesion: water’s ability to
form hydrogen bonds
with molecules other than
water (water = something
else).

PROPERTIES OF WATER: SOLID WATER IS LESS DENSE
• Liquid water becomes condenses
as it cools to freezing
• And yet…ice is less dense than
liquid water
• Fish can survive in the winter
because ice floats!

PH

PH… WHAT IS IT ACTUALLYMEASURING?
• The amount of
hydrogen ions or
hydroxide ions in
a solution
• If there are more
hydrogen ions (H+) ,
the solution will be
acidic.
• If there are more
hydroxide ions (OH-),
the solution will be
basic.

BIOLOGICAL PH
• Most biological
processes occur in
neutral pH or
weak acids/bases
• pH range of 6.5 to
7.5