Nucleic Acids Ch 12. Macromolecules n Macromolecules –“giant molecules” –Formed when...
-
Upload
avis-palmer -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
1
Transcript of Nucleic Acids Ch 12. Macromolecules n Macromolecules –“giant molecules” –Formed when...

Nucleic Acids Ch 12

Macromolecules Macromolecules
– “giant molecules”– Formed when monomers join together to form
polymers• Monomer = molecules, sm. Unit that can join to form
polymers• Polymer = multiple monomers (large molecules)
– There are 4 types of macromolecules• Carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids (we will be
talking about these today), and proteins

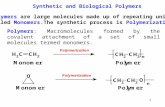
Monomers vs. Polymers
Think of monomers like blocks. Each monomer is one block.– How many monomers
are in this picture?
A polymer is what
you build from those monomers.
They are linked together by bonds.

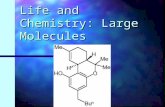
Nucleic Acids
Contain H, O, N, C, and P Polymers made from monomers known as
nucleotides Consist of: a nitrogenous base ( there are 4),
a phosphate group, and a 5-carbon sugar (ribose and deoxyribose)
Nucleotides join by covalent bonds (sharing of e-) to form a nucleic acid
These nucleotides form to create DNA or RNA

Nucleic Acids are complex macromolecules composed of nucleotides that store and transmit genetic information.

Searching for Genetic Material Mendel: modes of heredity in pea plants Morgan: genes located on chromosomes Griffith: bacterial work; transformation: change in genotype
and phenotype due to assimilation of external substance (DNA) by a cell
Avery: transformation agent was DNA

Searching for Genetic Material
Hershey and Chase√ bacteriophages (phages)
√ DNA, not protein, is the hereditary material √ Expt: sulfur(S) is in protein, phosphorus (P) is in DNA; only P was found in host cell

DNA Structure Chargaff
ratio of nucleotide bases (A=T; C=G)
Watson & Crick (Wilkins, Franklin)
The Double Helix (sometimes called a twisted ladder)
nucleotides: nitrogenous base (thymine, adenine, cytosine, guanine); sugar deoxyribose; phosphate group

Nucleotides are composed of:1. A sugar 2. A phosphate group3. A nitrogenous base

Types of Nucleic Acids DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid)

DNA Structure

DNA Bonding Purines: ‘A’ & ‘G’ Pyrimidines: ‘C’ & ‘T’
(Chargaff rules) ‘A’ H+ bonds (2) with ‘T’ ‘C’ H+ bonds (3) with
‘G’ Notice the number of H-bonds
between G-C and A-T. What do you think this means?

DNA Replication Watson & Crick strands are complementary; nucleotides line up
on template according to base pair rules (Watson)
Meselson & Stahl replication is semiconservative; Expt: varying densities of radioactive nitrogen

DNA Replication: a closer look Origin of replication (“bubbles”): beginning of replication Replication fork: ‘Y’-shaped region where new strands of DNA are
elongating Helicase:catalyzes the untwisting of the DNA at the replication fork DNA polymerase:catalyzes the elongation of new DNA

DNA Replication
Antiparallel nature: • sugar/phosphate backbone runs in opposite directions (Crick); • one strand runs 5’ to 3’, while the other runs 3’ to 5’; • DNA polymerase only adds nucleotides at the free 3’ end, forming new DNA strands in the 5’ to 3’
direction only

DNA Replication Leading strand:
synthesis toward the replication fork (only in a 5’ to 3’ direction from the 3’ to 5’ master strand)
Lagging strand: synthesis away from the replication fork (Okazaki fragments); joined by DNA ligase (must wait for 3’ end to open; again in a 5’ to 3’ direction)
Initiation: Primer (short RNA sequence~w/primase enzyme), begins the replication process

DNA Replication: the leading and lagging strands

DNA Repair
Mismatch repair: DNA polymerase
Excision repair:Nuclease
Telomere ends:telomerase

RNA
A messenger between DNA and ribosomes
“Decodes” the genetic message contained in the DNA molecule

3 Types of RNA:
Messenger RNA (mRNA) - copies information from DNA and carries it to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) - makes up the major part of the ribosomes
Transfer RNA (tRNA) - carries amino acids to the ribosomes where the amino acids are joined to form a polypeptide

Transcription
Information in a DNA molecule is transferred to an mRNA molecule (DNA RNA).
Guanine pairs with Cytosine Adenine pairs with Uracil Thymine pairs with Adenine

Practice Transcribing DNA
CUAGGA

Translation
Decoding mRNA into a chain of amino acids (RNA proteins)
Groups of 3 RNA nucleotides, called codons are “decoded” into amino acids

TranslationSection 12-3

TranslationSection 12-3

DNA RNA
Deoxyribose (sugar)
Double stranded Nitrogenous bases:
– Guanine– Cytosine– Adenine– Thymine
Ribose (sugar) Single stranded Nitrogenous bases:
– Guanine– Cytosine– Adenine– Uracil

Codon
Three-nucleotide sequence on mRNA that codes for a single amino acid

The Genetic Code

The Genetic Code

Mutation
Change in a DNA sequence that affects genetic information

Genetic Mutations
Point Mutations – change involving one or a few nucleotides– Substitution of one base for another– Insertion or deletion of a base
• Frameshift Mutations – shifts the reading of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a mucleotide

Substitution InsertionDeletion
Genetic Mutations: Substitutions, Insertions, Deletions
Section 12-4

Chromosomal Mutationsinvolve a change in the number or structure
Deletion – loss of chromosome Duplication – produce extra copies of
parts Inversions – reverse direction of parts Translocations – part breaks off and
attaches to another part

Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Translocation
Chromosomal MutationsSection 12-4