Life and Chemistry: Large Molecules. Macromolecules monomers are linked together to form polymers...
Transcript of Life and Chemistry: Large Molecules. Macromolecules monomers are linked together to form polymers...
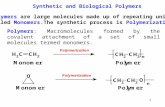
MacromoleculesMacromolecules
monomers are linked together to monomers are linked together to form polymersform polymers dehydration synthesis (condensation)dehydration synthesis (condensation) broken apart via hydrolysisbroken apart via hydrolysis
function is related to structurefunction is related to structure
MacromoleculesMacromolecules
4 classes of biological 4 classes of biological macromoleculesmacromolecules proteinsproteins carbohydratescarbohydrates nucleic acidsnucleic acids lipidslipids
ProteinsProteins
polymers of amino acidspolymers of amino acids
functions include functions include structural supportstructural support catalysiscatalysis transporttransport defensedefense movementmovement regulationregulation
Proteins Proteins
each amino acid contains the each amino acid contains the followingfollowing carboncarbon H atomH atom amino groupamino group carboxyl groupcarboxyl group side chainside chain
provides unique chemical propertiesprovides unique chemical properties
Amino Acids to ProteinsAmino Acids to Proteins
peptide bondpeptide bond joins two amino acids joins two amino acids carboxyl group of one bonds with carboxyl group of one bonds with
amino group of anotheramino group of another
20 used to make every protein20 used to make every protein each distinguished by its side chaineach distinguished by its side chain
Protein StructureProtein Structure
4 structural levels4 structural levels type, position, and number of amino type, position, and number of amino
acids determine function and acids determine function and structurestructure
1.1. primary structureprimary structure sequence of amino acids comprising sequence of amino acids comprising
the proteinthe protein huge variation possiblehuge variation possible
Protein StructureProtein Structure
2.2. secondary structuresecondary structure regular, repeating patterns as a result of regular, repeating patterns as a result of
H-bondsH-bonds helix helix pleated sheet pleated sheet
Protein StructureProtein Structure
3.3. tertiary structure tertiary structure results from interactions between R results from interactions between R
groupsgroups final 3-D structure of a single proteinfinal 3-D structure of a single protein
4.4. quaternary structure quaternary structure arrangement of protein subunits into arrangement of protein subunits into
a large macromoleculea large macromolecule
Environmental Effects on Environmental Effects on ProteinsProteins
structure affected by:structure affected by: pHpH temperaturetemperature
denaturationdenaturation
CarbohydratesCarbohydrates
primarily C, H, and Oprimarily C, H, and O 1:2:1 (CH1:2:1 (CH22O)O)
functionsfunctions energy sourceenergy source structurestructure
CarbohydratesCarbohydrates
4 categories:4 categories: monosaccharidesmonosaccharides disaccharidesdisaccharides oligosaccharidesoligosaccharides polysaccharidespolysaccharides
LipidsLipids
no polymersno polymers nonpolar hydrocarbons nonpolar hydrocarbons hydrophobichydrophobic
Fats and oilsFats and oils
triglyceridestriglycerides composed of fatty acids and glycerolcomposed of fatty acids and glycerol fats vs. oilsfats vs. oils saturated vs. unsaturatedsaturated vs. unsaturated energy storageenergy storage
PhospholipidsPhospholipids
compositioncomposition 2 fatty acids2 fatty acids phosphate containing polar headphosphate containing polar head
forms biological membranesforms biological membranes
SteroidsSteroids
composed of 4 fused carbon ringscomposed of 4 fused carbon rings
functionsfunctions part of membranespart of membranes hormoneshormones developmentdevelopment ion balanceion balance
Nucleic AcidsNucleic Acids
nucleotide structure nucleotide structure 5-C sugar5-C sugar phosphate groupphosphate group nitrogenous basenitrogenous base
functionfunction storage, transmission, and use of storage, transmission, and use of
genetic materialgenetic material
Nucleic AcidsNucleic Acids
2 types2 types DNADNA
information storageinformation storage RNARNA
transmission transmission