Accounting Elements, Accounting Equation and Double Entry Unit Two.
-
Upload
allen-barker -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
0
Transcript of Accounting Elements, Accounting Equation and Double Entry Unit Two.

Accounting Elements, Accounting Equation and
Double Entry
Unit Two

Learning Objectives Unit Two
to name elements of financial statements;
to describe relationship of elements of financial statements;
to analyze business transactions and determine their effects in elements of financial statements;
to record effects of business transactions on accounts in terms of debit and credit five different types of accounts;
to describe the rules of Double-entry Procedure.

If a company’s assets increase by $20,000 and its
liabilities decrease by $5,000, how much did the
owner’s equity increase or decrease?
Warming-up Unit Two

Text Skimming
Ask students to read the text quickly and then ask them to answer the following questions.
What are the accounting elements?Describe the accounting equation.Describe “T”account.

Vocabulary Unit Two
jargon sacrifice mortgage claim controversy
inflow enhancement outflow Peripheral double-entry bookkeeping
某一行业学科中专用的术语 损失 抵押 要求;索赔 论战,辩论;法律或财产价
值的诉讼 流入 增强,促进 流出 外围的;外部的 复式记账法

Vocabulary Unit Two
accounting equation fundamentalequilibrium
会计等式基础的,基本的平衡,均衡

Presentation
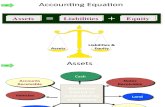
1. Elements of Financial Statements assets, liabilities, equity or net assets,
investments by owners, distributions to owners, comprehensive income, revenues, expenses, gains and losses.

Assets:probable future economic benefits
obtained or controlled by a particular entity as a result of past transactions or events.
Assets current assetsnon-current assets

current assets:cash, accounts receivable, inventories,
etc.non-current assets: long-term investments, plant and
equipment, and intangible assets.

Liabilities probable future sacrifices of economic
benefits arising from present obligations of a particular entity to transfer assets or provide services to other entities in the future as a result of past transactions or events.
Liabilities current liabilities non-current liabilities

current liabilities:accounts payable, notes payable, taxes
payable, salaries payable, etc.non-current liabilities: long-term note payable, mortgages
and bonds payable.

Equity or net assets: residual interest in the assets of an entity
that remains after deducting its liabilities. Investments by owners: increases in net assets of a particular
enterprise resulting from transfers to it from other entities of something of value to obtain or increase ownership interests (or equity) in it.

Distributions to owners: decreases in net assets of a particular enterprise
resulting from transferring assets, rendering services, or incurring liabilities by the enterprise to owners.
Comprehensive income: change in equity (net assets) of an entity during
a period from transactions and circumstances from non-owner sources.

Revenues: inflows or other enhancements of
assets of an entity or settlement of its liabilities (or a combination of both) during a period from delivering or producing goods, rendering services that constitute the entity’s ongoing major or central operations.

Expenses:outflows or other using up of assets
or incurrence of liabilities (or a combination of both) during a period from delivering or producing goods, rendering services, or carrying out other activities that constitute the entity’s ongoing major or central operations.

Gains: increases in equity (net assets) from
peripheral or incidental transactions of an entity and from all other transactions and other events and circumstances affecting the entity during a period except those that resulting from expenses or distributions to owners.

Losses: decreases in equity (net assets) from
peripheral or incidental transactions of an entity and from all other transactions and other events and circumstances affecting the entity during a period except those that resulting from expenses or distributions to owners.

Accounting Equation
Assets= Liabilities + Owners’ Equity
Analyze the example at P12-13.

Double-entry Bookkeeping
The basic principle of double-entry bookkeeping is that every transaction has a twofold effect. In other words, a value is received and a value is yielded or parted with. Both effects, which are equal in account, must be equal in amount, must be entered completely in the bookkeeping records.

“T” account
the name of the account and the account number
the debit side (left side)
the credit side (right side)

Assets and Expenses Dr. Cr. + _ (Increases) (Decreases) Liabilities, Owner’s equity and Income Dr. Cr. _ + (Decreases) (Increases)

Notes Unit Two
The relationship between the accounting elements can be expressed in a simple mathematical form known as the accounting equation: assets = liabilities + owners’ equity. This equation shows that the assets of a business are equal to the liabilities and owners’ equity, it is the framework for the entire accounting process.
会计要素之间的关系用一个简单的数学等式,也就是我们所说的会计等式,可以表达为:资产 = 负债 + 所有者权益。这个等式表明了企业的资产等于负债和所有者权益的总和 ,这是整个会计程序中的基本框架。

Notes Unit Two
The basic principle of double-entry bookkeeping is that very transaction has a twofold effect. In other words, a value is received and a value is yielded or parted with. Both effects, which are equal in amount, must be entered completely in the bookkeeping records.
复式记账的基本原理是每一项交易活动都有双重的影响。换言之,有一项金额收入就必然有一项金额支出,两者金额相等必然完整记入账簿。
double-entry accounting system 复式记账会计制度。即从两个方面反映一项经济业务,在借贷两方记录相等的金额。在公元 1300 年,意大利北部城市首先使用复式记账方法, 1494 年 L·Pacioli 所著的《算术、几何和比例概要》一书,是阐述复式记账法的第一本著作。复式记账技术的产生在会计发展史上具有重大意义。复式记账规则可以用会计恒等式来说明,即资产 = 负债 + 所有者权益。

Notes Unit Two
accounting conventions
会计惯例。会计惯例指在长期的会计实践中逐渐形成的,为大 家所 接 受的 观 念、 方 法和 程序。有时可与 principles, concepts, postulates, assumptions 通用。
accounting practice
会计实务。会计实务是指会计人员在日常工作中所使用的会计程序和方法;或指会计人员在其日常工作中的习惯做法,有时可能有悖于理论。
accounting equation
会计等式,会计平衡式,也称 balance-sheet equation , 即资产 = 负债 + 所有者权益,是复式记账方法的理论依据。

Accounting Elements,
Accounting Equation and Double Entry
Unit Two

Review
1. Ask students to read all the new words and phrases.
2. Review the language points.

Exercises Unit Two
II. Term Study. Match the terms in column A with the definitions in column B.
A B
1. assets
2. liabilities
3. equity or net assets
4. investments by owners
5. distributions to owners
6. comprehensive income
7. revenues
8. expenses
9. gains
10. losses
A. landB. losses from incidental transactions of an entityC. change in equity of an entity from transactions
and circumstances from non-owner sourcesD. residual interest in the assets of an entityE. increases in equity from peripheral transactions
of an entityF. notes payableG. salesH. interest paid to bankI. distributions of Cash dividends to ownersJ. services received as investments by owners

Exercises Unit Two
III.Supply the missing information in the following statements and translate it into Chinese.
(1) Double-entry bookkeeping is a system by which each _______ has two sides, a _____ side and a _____ side, ① ② ③
and each _________ is entered twice, as a debit in one ④account and as a credit in another. The rule is: debit the receiver, credit the _____. Every debit must have a ⑤corresponding credit and every credit a _____. If all the ⑥
_______ have been correctly made, the total of all the debits ⑦must at any time equal ______.⑧
(2) An accounting equation is an expression of the relationship between the _____ and _______ and ① ②
___________ of an enterprise. It is stated as Assets = ③______ + ________. The two sides must always _____.④ ⑤ ⑥
account debit credit
transaction
sender debit
accounts credits
assets
liabilities owners’ equity
Liabilities Owners’ equity balance

Exercises Unit Two
(3) A balance sheet is a statement that shows the _____, ________ and ___________ at a specific date, ① ② ③
usually at the end of the financial year.
(4) An income statement, also known as profit and loss statement, is a summary of the _______, _______ and ① ②
_________ of a business for a specific period f time.③
assets
liabilities
owners’ equity
revenue expenses net income

Case Study
1. Prepare the entry required for each of the following transactions.
1) Shares of capital stock were issued for $24,000 cash.
2) Issued convertible bonds for cash up to $150,000 due within three years.
3) Purchased $2,300 of land on account. 4) Sold merchandise to a customer who agreed
to pay within two months amount to $18,000.

5) Converts a bond payable $80,000 into common stock.
6) Paid salaries of $4,000 for this month.
7) Purchased a truck for cash $5,000.8) Declared a cash dividend of $7,000

9) Paid off the accounts payable $9,300 arising from the purchase of supplies.
10) Cash was received for sales of goods, $851,000.
11) Collected the account receivable of $23,000
12) Paid advertising for this quarter, $10,000.

Assignments
Do Ex.IV in the exercise books.