Accounting Equation -1
-
Upload
pradeep-gupta -
Category
Documents
-
view
236 -
download
0
Transcript of Accounting Equation -1
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
1/36
Use the accounting equation to
analyze business transactions.
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
2/36
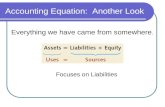
Assets
Liabilities &
Equity
Accounting Equation
Liabilities
Liabilities Equity
EquityAssets
Assets = +
A1
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
3/36
Land
Equipment
Buildings
Cash
Vehicles
Store
Supplies
Notes
Receivable
Accounts
Receivable
Resources
owned or
controlled by
a company
AssetsA1
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
4/36
Taxes
Payable
Wages
Payable
Notes
Payable
Accounts
Payable
Creditors
claims on
assets
LiabilitiesA1
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
5/36
Owners
claim on
assets
Dividends
Contributed
Capital
Retained
Earnings
EquityA1
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
6/36
Liabilities EquityAssets = +
Expanded Accounting Equation
Revenues ExpensesCommon
StockDividends
__++
__
Retained Earnings
Liabilities
Liabilities Equity
EquityAssets
Assets = +
A1
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
7/36
Transaction Analysis Equation
The accounting equation MUST remain in
balance after each transaction.
LiabilitiesLiabilities EquityEquityAssetsAssets = +
A2
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
8/36
The Accounting EquationThe Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Owners Equity
The resourcesThe resources
owned by aowned by a
businessbusiness
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
9/36
The Accounting EquationThe Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Owners Equity
The rights of theThe rights of the
creditors, whichcreditors, which
represent debtsrepresent debtsof the businessof the business
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
10/36
The Accounting EquationThe Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Owners Equity
The rights of theThe rights of the
ownersowners
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
11/36
ASSETS
FIXED FLOATING(CURRENT) FICTITIOUS LIQUID WASTING TANGIBLE INTANGIBLE
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
12/36
FIXED ASSET
LAND BUILDINGPLANT
MACHINERY FIXTURESVEHICLE
MACHINERY
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
13/36
FLOATING(CURRENT ASSETS)
STOCK CASH BANK
DEBTOR PREPAID EXPB/R
MARKEATABLE SECURITIES
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
14/36
FICTITIOUS ASSET
LOSS ON ISSUE OF
SHARESPRELIMINARY
EXPENSES
UNDERWRITING COMMISSION
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
15/36
LIQUID ASSET=CA-STOCK-PREPAID EXP
CASH BANKDEBTORS
B/R
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
16/36
WASTING ASSET=PATENTS, ASSETS TAKEN ON
LEASE,MINES ETC
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
17/36
LIABILITY
FIXED LIABILITY
(CAPITAL, LONG TERM LOANS)
FLOTING LIABILITY(CREDITORS)
CONTINGENT
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
18/36
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
19/36
What is a business
transaction?
Abusiness transaction is an economic event orcondition that directly changes an entitys financial
condition or directly affects its results of operations.
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
20/36
On November1,
2005, Chris
Clark begins abusiness that will
be known as
NetSolutions.
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
21/36
a. Chris Clark deposits $25,000 in a banka. Chris Clark deposits $25,000 in a bank
account in the name of NetSolutions.account in the name of NetSolutions.
Chris Clark, Capital
25,000 Investment
by Chris
Clark
Cash
25,000a.
Assets Owners Equity=
=
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
22/36
b. NetSolutions exchanged $20,000 for land.b. NetSolutions exchanged $20,000 for land.
Chris Clark, Capital
25,000
Cash + Land
25,000Bal.
Assets Owners Equity=
=b. 20,000 +20,000
Bal. 5,000 20,000 25,000
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
23/36
Accounts Chris Clark,Cash + Supplies + Land Payable Capital
Assets
c. During the month, NetSolutions purchasedc. During the month, NetSolutions purchased
supplies for $1,350 and agreed to pay thesupplies for $1,350 and agreed to pay the
supplier in the near future (supplier in the near future (on accounton account).).
Owners
Liabilities + Equity=
Bal. 5,000 20,000 25,000c. + 1,350 + 1,350
Bal. 5,000 1,350 20,000 1,350 25,000
=
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
24/36
d. NetSolutions provided services tod. NetSolutions provided services to
customers, earning fees of $7,500 andcustomers, earning fees of $7,500 andreceived the amount in cash.received the amount in cash.
Bal. 12,500 1,350 20,000 1,350 32,500
d. + 7,500 + 7,500
Accounts Chris Clark,Cash + Supplies + Land Payable Capital
AssetsOwners
Liabilities + Equity
Bal. 5,000 1,350 20,000 1,350 25,000Fees
earned
=
=
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
25/36
e. 3,650 2,125
800
450
275
Wages
Rent
Util.
Misc.
Accounts Chris Clark,Cash + Supplies + Land Payable Capital
Assets
e. NetSolutions paid the followinge. NetSolutions paid the following
expenses: wages, $2,125; rent, $800;expenses: wages, $2,125; rent, $800;
utilities, $450; and miscellaneous, $275.utilities, $450; and miscellaneous, $275.
Owners
Liabilities + Equity=
Bal. 12,500 1,350 20,000 1,350 32,500
=
Bal.8,850 1,350 20,000 1,350 28,850
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
26/36
Accounts Chris Clark,Cash + Supplies + Land Payable Capital
Assets
f. NetSolutions paid $950 tof. NetSolutions paid $950 to
creditors during the month.creditors during the month.
Owners
Liabilities + Equity=
Bal. 8,850 1,350 20,000 1,350 28,850
f. 950 950
=
Bal. 7,900 1,350 20,000 400 28,850
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
27/36
Accounts Chris Clark,Cash + Supplies + Land Payable Capital
Assets
g. At the end of the month, the costg. At the end of the month, the cost
of supplies on hand is $550, soof supplies on hand is $550, so$800 of supplies were used.$800 of supplies were used.
Owners
Liabilities + Equity=
Bal. 7,900 1,350 20,000 400 28,850
g. 800 800
=
Bal. 7,900 550 20,000 400 28,050
Supplies
expense
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
28/36
Accounts Chris Clark,Cash + Supplies + Land Payable Capital
Assets
h. At the end of the month, Chrish. At the end of the month, Chris
withdrew $2,000 in cash from thewithdrew $2,000 in cash from the
business for personal use.business for personal use.
Owners
Liabilities + Equity
Bal. 7,900 550 20,000 400 28,050
h. 2,000 2,000
Bal. 5,900 550 20,000 400 26,050
With-
drawal
=
=
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
29/36
Owners
withdrawals
Expenses
Decreased byDecreased by
Owners Equity
Effects ofTransactions on Owners EquityEffects ofTransactions on Owners Equity
Increased byIncreased by
Owners
investments
Revenues
Net
income
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
30/36
ACCOUNTING EQUATION
Economic resources=Claims
Asset=Liability+Capital
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
31/36
Accounting for Business Transactions
What is a transaction?
It is any event that both affects the financial
position of the business and can be reliablyrecorded.
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
32/36
Accounting for Business Transactions
1 Gay Gillen invests $30,000 to begin Gay Gillen
eTravel.
2 Gillen purchases an office location, paying$20,000 in cash.
3 She buys office supplies, agreeing to pay $500
in 30 days.
4 She earns and collects $5,500 revenues.
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
33/36
Accounting for Business Transactions
5 Gillen performs services, and the client agrees
to pay $3,000 within one month.
6 During the month, she pays $3,100 forexpenses incurred.
7 Gillen pays $300 to the store from which she
purchased $500 worth of supplies.
What is the effect of these transactions on the
accounting equation?
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
34/36
OwnersAssets = Liabilities + Equity
1) Cash + $30,000 + $30,000
2) Cash 20,000Land + 20,000
3) Supplies + 500 + 500
4) Cash + 5,500 + 5,500
5) Receivable + 3,000 + 3,0006) Cash 3,100 3,100
7) Cash 300 300
Totals + $35,600 + 200 + $35,400
Accounting for Business Transactions
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
35/36
Accounting for Business Transactions
Notice that the equation always stays in
balance.
Each transaction affects at least two accounts,sometimes more.
Some transactions affect only one side of the
equation; some affect both sides.
-
8/8/2019 Accounting Equation -1
36/36
Accounting for Business Transactions
Other transactions that took place were as
follows:
The business collected $1,000 from the client. She sold some land at cost for $9,000.
She withdrew $2,100 from the business.