Demystifying of Accounting Equation
-
date post
19-Oct-2014 -
Category
Education
-
view
587 -
download
26
description
Transcript of Demystifying of Accounting Equation

DEMYSTIFYING THE ACCOUNTING EQUATION

PRESENTED BY 1) AKASH 2) JAYA 3) NIKITA 4) SAYYAD 5) KANIK 6) JAYENDRA 7) SANTOSH

INTRODUCTION
Vidya is the qualified architect and a certified interior designer and decorator who initially was working with reputed consulted firm for almost a decade. But , later on April 2005 she started her own business under the name “ Sri Vidya Associates” for offering consultancy expertise in interior design and decoration.

AMOUNT BROUGHT IN BUSINESSINVESTMENT AMOUN
TEXPENDITUREFROM INVESTMENT
AMOUNT
OWN CONTRIBUTION
1,50,000 RENT 70,000
LOAN FROM BANK 1,50,000 PURCHASE OF COMPUTER 75,000
FURNITURE AND FIXTURES 10,000
PURCHASE OF SOFTWARES 60000
ADVANCE FOR EQUIPMENT 10,000
OFFICE SURPLUS 3000

After three month in june She received INR 280000 from billing (TDS25000) Outstanding Amount 95,000 Not recovered Amount 20,000
After some time when she found out that her bank balance had come down to RS 14750, she noted down the following expenditures from her bank A/c

Outgoing from bank A/c
Salary paid 3 months 12000*3 = 36000 Telephone and internet bill 1250*3 = 3750 Paid to welfare association 1000*3 = 3000 Insurance premium 6000*1 = 6000 Withdraw for personal use =10,000 Service tax payable during June =35,000 Paid freight for equipment = 5,000 Hotel charges = 5,200 Purchase of office supplies = 1800 Advanced income tax = 15000 Total exp. 1,20,750 Net Amt.available 14,750 Total bank amt. 1,35,500

PRINCIPLES OF BUSINESS
EMPLOYEESWorks for the system
BUSINESSMAN
SELF EMPLOYEDHates to work in the system
INVESTORSInvests in the system
OWN SYSTEM

EMPLOYEESA person who works to earn money• Works for the system• And earn money
Who makes money for following three entities• Employer• Government• Bank

SELF EMPLOYED (Skilled people)
A person who moves into the zone of independence
People who are ready to take calculated risks
Who works as• Doctors• Counselors

BUSINESSMENThese are the people who are having ability to lead people those are more talented than them.• Who can take high risk• And has great ideas to earn money
Owns control and the system• They run their own system• And keep control in their hands
They have the power to hire employees and even the self-skilled people• For accounting• marketing

INVESTORSThese are the most smart people amongst all the four quadrants• Smart income• More money in short time
They make money to work the system properly• functioning• planning
These are the people who are financially independent and do not have any time constraints• Own money• Self risk

Proper hierarchy of business principles
Investors
Businessmen
Employees/Self employed

Accounting is the art of recording, classifying and summarizing in a significant manner in terms of money, transactions and events which are, in part at least, of financial character and interpreting the results there of.
Accounting

Process Function of Accounting
1 Identifying the business transaction 2 Measuring the identified transaction 3 Recording the business transaction4 Classifying the Business Transaction5 Summarizing the business transaction6 Analyzing the business transaction 7 Interpreting the business transaction 8 Communicating the interpreted information to
the users

EQUITY It refers to total claims against the
enterprise. It can be divided into two parts:
(i) Owners Claim- Capital(ii) Outsiders Claim- Liability
Capital- the excess of assets over liabilities.
It is also known as net worth.
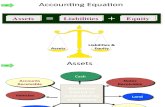
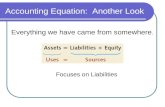
ASSETS= LIABILITIES + OWNER’S EQUITY

At the end of the accounting period, there may be expenses which have become due but have not yet been paid. The extent to which the amount belongs to the currents year but payable in the next year is called Outstanding Expenses.
Salaries a/c Dr
xxx To Outstanding salaries
a/c xxx(Being Salaries for the month of
Mar 2011 due but not yet paid accounted.)
WHAT IS THE MEANING OF OUTSTANDING EXPENSES

What is the relation between balance in hand and net profit?
The only relation is that both are the balancing figures i.e. balance in hand is the opening balance and net profit or loss is the closing figure...and balance in hand is the cash that you have & profit is the earning after your expenses. You might have profit without cash!!!

At the end of the
accounting period, there may be expenses which have been paid in advance. These are expenses which are paid in advance and would be adjusted in the relevant expenditure during the subsequent accounting periods.
PREPAID EXPENSES

WHAT IS ACCRUED INCOME?
Income that is earned in a fund or by company by providing a service or selling a product, but has yet to be received. Mutual funds or other pooled assets that accumulate income over a period of time but only pay it out to shareholders once a year are, by definition, accruing their income. Individual companies can also accrue income without actually receiving it, which is the basis of the accrual accounting system.

MEANING OF PROVISION FOR DEPRECIATION?
For calculating depreciation over assets we make an account known as depreciation.
In this particular case there is no amount for depreciation but we calculate it on the basis of accounting standard that we have to take 10% depreciation on furniture that would be Rs. 250 for three months.

Why is her own contribution shown under liabilities?
Because that contribution is treated as the capital for the business and the business is liable to pay back to vidya’s contribution at the time of dissolution of firm.
according to law business is treated separate and the people who work for them also treated as separate entity

Actual rent and Realistic rent
Definition of actual rent: The actual rental rate that the landlord achieves after deducting the concession value from the base rental rate a tenant pays
Definition of realistic rent. The realistic rent is that the landlord achieves before deducting the concession tax, and municipal charges from the actual rent

Meaning of “Current Liability”
LIABILITIES These denote the money which a businessman owes to
outsider who have supplied goods or rendered services to the business.
Long term liability- which are repaid after one year.
Current liability- which are repaid within a period of one year.

ASSETS : Fixed And Current Assets
Assets: Economic resources employed by an enterprise or
valuable things having a money value. Assets may be of various types:-
Fixed Assets- are of permanent nature and are acquired for use in the business and not for resale. Ex- land & building, Plant & Machinery, furniture.
Current Assets- are those which can be converted into cash within a period of 12 months. Ex- closing stock, debtors, cash in hand.

PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT
It is prepared to know the net profit or loss. It includes indirect expenses other than manufacturing
expenses All the balances of nominal account are transferred to
profit and loss account Incomes and expenses are shown Helpful in preparation of balance sheet Income tax is levied on the basis of net income

Payments Amount (Rs.) ReceiptsAmount (Rs.)
To Rent 30,000By Salary Received 4,800
To Salary Paid 60,000By Sales 280,000
To Tel. Bill 3,750
To Maintenance 3,000
To Insurance 1,000
To Office Supply 1,800
To Bad Debts 20,000
To Freight 5,000
To Int. Paid 4,500
To Service tax 35,000
To Membership 1,000
To Depriciation 250
To Sundry Expenses 5,200
To Net Profit 114,300
Total 284,800Total 284,800
To Net Profit added to Capital 114,300
Profit & Loss Account of Vidya Associates as on June 2005

BALANCE SHEET
Statement containing the balances of assets and liabilities on a particular date
It has two sides i.e. on left side liability is shown and on right side asset is shown
It shows the financial position of the business

Capital + Liability Amount (Rs.) Assets Amount (Rs.)
Capital 1,50,000 Current Assets :-
(+) Net Profit 1,14,300 Bank 134,350
(-) Depreciation 10,000 254,300 Bills Recievable 95,000
P.P. for Equipment 50,000Liability :- Prepaid Inc. Tax 15,000Creditors 75,000 Tax Deducted at Source 25,000
Loan @ 12% p.a. 150,000 Security Deposit 60,000 Adv. Insurance 5,000 Fixed Assets :- Office Stock 1,200
Furniture
10,000
(-) 10% Dep.
250 9,750 Computer 75,000 Intangible Assets :- Membership (Lifetime) 9,000
Total 479,300 Total 479,300
Foot Note :-
(a) Bank balance calculated at Rs. 1,34,350
Balance Sheet of Vidya Associates as on June 2005

CONCLUSION First of all Vidya needs to appoint an
accountant for handling her business accounts as she is unable to understand the accounting jargons.
Secondly, as we have seen that she is earning the profit more than her previous salary that means her decision for starting her own business is justified.