The Chemistry of Life - Delta Collegewebsites.delta.edu/mgrobert/PDFs/Biochemistry.pdf · ·...
Transcript of The Chemistry of Life - Delta Collegewebsites.delta.edu/mgrobert/PDFs/Biochemistry.pdf · ·...
Biochemistry The Chemistry of Life
Mark Robertson Professor of Biology
Delta College
The Chemistry of Carbon■ Molecules are either organic (contain
carbon) or inorganic (carbon is absent). ■ Organics contain carbon chains with
single, double, or triple-bonds.
C C C CC C
Common Organic Molecules■ Use monomers to produce polymers
(usually by dehydration synthesis). ■ Four major macromolecules:
– Carbohydrates (from monosaccharides) – Lipids (from fatty acids) – Proteins (from amino acids) – Nucleic Acids (from nucleotides)
Carbohydrates■ Made of chains or rings of
carbon with hydrogen and oxygen attached, their name ends in -ose
■ Monosaccharides (1 sugar) – 1) Glucose (C6H12O6) powdered
sugar – 2) Galactose (C6H12O6) – 3) Fructose (C6H12O6) plant sugar
(1)
(2)
(3)
Carbohydrates■ Disaccharides (consist of 2
linked monosaccharides) – 4) Sucrose (C12H22O11)
table sugar – 5) Lactose (C12H22O11)
milk sugar)
(4)
(5)
Carbohydrates■ Storage Polysaccharides
– Starch (plants) – Glycogen (liver of animals)
Glycogen
Metabolizing Saccharides
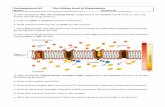
Lipids■ Generally large, nonpolar
(few charged ends), and hydrophobic (water fearing)
■ Contain long chains of carbon and hydrogen, but very little oxygen (-CH2CH2CH2-)
■ Grouped into fats, oils, steroids, phospholipids, and waxes
Lipids - Fatty Acids■ Many fats are used for energy storage and
based on glycerol backbone ■ Can attach fatty acids
-H
-HHO-
H2O H2O
What type of reaction was this? (note: water was released)
Lipids - Human Blood■ If no double bonds, saturated fat
(animal fats like lard and chicken fat) ■ Double bonds means unsaturated
(plant fats like olive oil and peanut oil) ■ Use triglycerides
to move fats in our blood
Triglyceride
Lipids - Phospholipids■ If take a glyceride molecule and add
2 fatty acids and a phosphate group, get a phospholipid (used in cell membranes)
■ Phosphate attracts water and the fatty acids repel water
Proteins - Amino Acids
■ Made from linked amino acids (with 20 used in organisms)
■ 10 essential amino acids ■ Functional vs. Structural uses
20 DifferentFunctional
Groups (-R)
CarboxylicAcid Group
(-COOH)
AminoGroup(-NH2)
AsparticAcid
Cysteine Glycine
Proteins - Forming Chains
■ Linkages are called peptide bonds ■ Dehydration synthesis forms links ■ Resulting molecule is called a polypeptide
+
PeptideBond
Proteins - Structural Levels■ Primary Structure
– Order of the Amino Acids ■ Secondary Structure
– Helix or sheet-like folding ■ Tertiary Structure
– 3-D folding to create shapes ■ Quaternary Structure
– Interaction of 2 or more chains
Nucleic Acids (DNA/RNA)
■ Built from nucleotides which have a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and 1 of 5 bases – Thymine (T) – Adenine (A) – Cytosine (C) – Guanine (G) – Uracil (U)
- D - P - D - P - D - P - D - P -
- D - P - D - P - D - P - D - P -
B B B B B B B B~ ~ ~ ~
One Nucleotide