Cellular Life History and Cellular...
Transcript of Cellular Life History and Cellular...

Cellular Life History and Cellular Organelles
Mark Robertson Professor of Biology Delta College
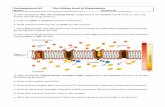
Cell FeaturesHuman cells have an outer plasma bilayer membrane, cytoplasm inside, and a nuclear membrane (forming a nucleus for us unlike bacteria).Our nucleus contains DNA.
When coiled (to move in cell division), DNA is called a chromosome. Uncoiled DNA is being read by the cell and is called chromatin. RNA is formed from DNA and it leaves the nucleus.
Membranous OrganellesEndoplasmic Reticulum
Rough form (RER) studded with ribosomes and creates proteins from amino acidsSmooth form (SER) creates lipids (fats) and detoxifies drugs
Golgi Apparatus (Body)Packages and ships products using vesicles
Golgi body also creates: Lysosomes (to destroy wastes with low pH and enzymes)Peroxisomes (to detoxify free radicals created from oxygen break-down)
Nucleus (cellular instructions housed in the DNA; encodes for cellular parts, repair, etc.)Mitochondria (uses O2 to burn sugars and release ATP for cellular use; Kreb’s Cycle)

Nonmembranous OrganellesRibosomes
Create proteins from ingested amino acidsFound in ALL living cells (free or attached to RER)
Microtubules/MicrofilamentsForm cellular cytoskeleton (to create cell shapes) and act as highways for cellular transport systems
Centrioles Create and destroy cytoskeleton and the spindle apparatus used during cellular reproduction Alters the shape of some cells (ex: WBCs)
Cilia/Flagella Less than 1/2 length if cilia, more than 1/2 if flagellaEither move items past the cell or move the cell itself
Inclusions (storage droplets, crystals, granules)
Stages of the Cell CycleDivision (2hrs)-mitosis (PMAT)-cytokinesis
Interphase (18hrs)-Gap 1 (4hrs)-Synthesis (10hrs)-Gap 2 (4hrs)
Differentiation into Adult Cells
Mitosis and CytokinesisInterphase (prepares the cell for replication)
Gap 1 (cell grows and makes more organelles) Synthesis (make copies of chromatin; nucleus darkens)Gap 2 (cell grows again and divides centrioles)
Mitosis (PMAT; divides up DNA)Prophase (dissolve nucleus; supercoil DNA)Metaphase (pull chromosomes to equator)Anaphase (pull copies apart; move to poles)Telophase (form nuclei; uncoil chromatin)
Cytokinesis (divides the cell itself)Cleavage furrow forms at equatorProtein bundles shrink and “pinch off” 2 new cells cell by binary fission

Potential Journal Critique Topics?Cancer (Cell Cycle Disorders)?
Mitochondrial Disorders?
Eve Hypothesis (Out of Africa)?
Lysosome Disorders?
Ribosomal Disorders?
Inclusions and Diseases?