Chapter 8 Cellular Energy *Photosynthesis *Cellular Respiration Cellular Energy Cellular Energy.
PreAssignment #3 The Cellular Level of Organization Name...
Transcript of PreAssignment #3 The Cellular Level of Organization Name...

PreAssignment #3 The Cellular Level of Organization Name: _______________________________ Section #: _______ 1) After visiting the “Na+ /K+ Exchange Pump” assignment in the content area of my D-2-L class site, answer the following questions: a. Is this an active or passive transport mechanism? b. What chemical molecule acts as power for this process? c. What ions (number and type) bind to the protein to change its conformation (shape)? Do they then get pumped in or out of the cell? d. Once the bound phosphate is lost from the pump, which ions (number and type) are then released? Do they enter or exit the cell?
2) After visiting the “Active/Passive Transport Video” assignment in the content area of D-2-L, answer the following questions: a. What is the smallest unit of life? b. Since passive transport does not require ATP, what drives their molecular movement of materials? c. What are three good examples of passive cellular processes? Which one also uses a carrier protein? d. What does the term “passive” mean in this context? e. What two items must be present if active transport is going to occur through a membrane?

f. What process is needed by the cell if particles are too large to use a membrane protein channel? g. Why are lysosomes still needed after either phagocytosis or pinocyctosis has occurred?
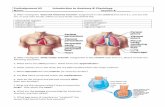
3) After visiting the “Organelles And Their Function” assignment in the content area of D-2-L, answer the following questions: All living cells share three characteristics: _____________, ____________, and ____________. The two main groups of cells are the ______________ (like plants and animals) and the ____________ (like bacteria). Organelles inside the cell include the nucleus. Spread out (or open) DNA in the nucleus is called ____________, but it condenses during cellular division to form _______________. Ribosomes have the job of making _____________. Like all organelles, they may float around in the jelly-like _____________. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is either _____________ or ______________. Vesicles of products leave the ER and join the highly folded ________________ for processing. Here, proteins are customized by adding either ____________ or ____________ to the folded protein. Worn out cell parts are destroyed by enzymes in the _______________. Mitochondria create _____________ during cellular respiration. The cytoskeleton is made of threadlike ______________ and hollow _____________. Plant cells have _______________, but animal cells do not. In our trachea, _____________ help expel debris. Male _____________ , however, have flagella to move. 4) After visiting the “DNA vs. RNA” assignment in the content area of D-2-L, tell me how the two molecules differ from one-another in regards to their:

Characteristic DNA RNA a) general jobs that they have
b) relative resistance to UV radiation
c) type of helix geometry used
d) bases and sugars that they use
e) number of strands and relative length
f) actual base pairing sequences
g) relative reactivity of their sugars
h) relative resistance to enzyme attack
5) Describe the four main functions of cellular membranes: a. b. c. d. 6) Membrane proteins have many different functions. Which type of protein specifically:
Require energy (ATP) to transport small solutes across. Allow us to identify “self” versus “non-self” in immune responses Attach to molecules like insulin to control cellular uptake of glucose. Allow passage of important ions so muscle and nervous tissues can function. Attach a sperm to an ovum (egg) cell during reproduction.

Internally, they bind to the cytoskeleton to stabilize cell shapes. Operate by binding to extracellular ligands as triggers. Allows small solutes and water to pass through.
7) List 4 membranous organelles and then describe their functions: a. b. c. d. 8) List 4 non-membranous organelles and then describe their functions: a. b. c. d. 9) Describe 4 main ways that rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum differ from one-another: a. b. c. d. 10) Which specific organelle:
Ingests pyruvate and oxygen, and then expels CO2, water, and ATP (energy)? Break down food, cellular debris, even or the cell itself with digestive enzymes? Using basal bodies, they wave rhythmically to remove debris in our trachea? Protects all of the instructions for the cell, and connects to the RER with pores? Using kinesin and dynein, these large proteins move products like a highway? Produced from a small and a large subunit, they produce proteins for the cell? Create spindle fibers during cellular reproduction and also form basal bodies? Digest fatty acids and protect the cell from free radicals by using catalase?