Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
Transcript of Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
1/30
MIAMI DADE COLLEGE - MEDICAL CENTER CAMPUS - SCHOOL OF NURSINGNUR 1025L: Fundamentals Nursing Clinical
Students Name: Francisco J Ortiz Date:_07/06/13_ Clients Initials: ____ER____ Admission Date:_05/20/2013
Age: 78yr DOB: ______06/15/1940_____ Sex: X Male Female Race/Ethnicity: WHITE/______________Support System: _____No living family membes _________________________________________________________
Religion: _Protestant__________
MEDICAL HISTORYALLERGIES: _NKA_Admitting Medical Diagnosis (es): Cardiac dysrthmias, CHF, hypertension, Constipation, seizure
disorder, dementia
Chief Complaint: patient right-side epitaxis
History of Present Illness: Pt is a 78 has history of pulmonary embolism and was anticoagulationbecause of this condition. Pt came back to hospital wih right-side epistaxis and currently at thebedside. Pt doesnot appear to have any acute bleeding.
Past Medical History (include past surgical history):Senile,Dementia, pulmonary embolism hypertension, asthma, Esophageal Reflux; No alcohol abuse,no drug abuse
Clients (Parents)Understanding of Illness: patient understands and full aware of condition
Stage of Development: Erickson Ego Integrity vs. Despair _ Freud: According to Freud, the genitalstage lasts throughout adulthood. He believed the goal is to develop a balance between all areas oflife. Piaget _ Formal Operational
____Special Developmental Considerations: N/AHeight: 170.18 cm Weight: 46.36 kg Placement in Growth Chart: _N/AImmunizations: Patient refused flu vaccine
1
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
2/30
VITAL SIGNSTime Taken: ______0930_________ Activity: ______________ Position: ____wheel chair__________
T_96.0 P65R 18 BP _145/60Baseline (Normal Age for Age):T_ 36.137.8 P_60 -100 R_12-20_ BP 120/80_
NUTRITIONDiet: Regular/Puree Food Preferences: coffee with 2 splenda, yogurt for LUNCH, N/A for DINNER
Nutritional Requirements: (Cal/Kg/Day): 1725CAL/KG/DAY Total Calories per Day: _1800___________
Fluid Requirements (Ml/Kg/Day): ____30-35 Ml/Kg/Day_____________ __Total Fluids per Day: _____1440-1680__________________________
Special Treatments: ____________N/AMedications atHome:_N/A_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
3/30
Medication(s) Worksheet
NAMECLASSIFICATI
ON
DOSE/ROUTE/FREQUENCY SAFE RANGE
MECHANISMOF ACTION
INDICATIONS SIDEEFFECTS
NURSINGCONSIDERATIONS
AND PATIENTEDUCATION
3
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
4/30
BUDESONIDE 0.5mg 1 tab Q12 bymouth
Potent, locallyacting anti-inflammatoryand immunemodifier.
Maintenancetreatment ofasthma asprophylactictherapy. Maydecrease theneed for oreliminate use ofsystemiccorticosteroidsin patients withasthma.
CNS:headache,agitation,depression,dizziness,fatigue,insomnia,restlessness. EENT:dysphonia,hoarseness,cataracts,nasalcongestion,pharyngi-tis, sinusitis.Resp:bronchospasm, cough,wheezing.GI: diarrhea,dry mouth
Monitor respiratorystatus and lungsounds. Assesspulmonary functiontests periodicallyduring and for severamonths after a transffrom systemic toinhalationcorticosteroids.
Assess patientschanging fromsystemic cortico-steroids to inhalationcorticosteroids forsigns of adrenalinsufficiency (anorexnausea, weakness,fatigue, hypotensionhypoglycemia) durininitial therapy andperiods of stress. Ifthese signs appear,
notify health careprofessionalimmediately; conditiomay be life-threatening
4
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
5/30
MEMANTINE 10mg 1 tab daily bymouth
Binds to CNSN-methyl-D-aspartate(NMDA) re-ceptor sites,preventingbinding ofglutamate, anexcitatoryneurotransmitter.
Moderate tosevereAlzheimersdementia.
CNS:dizziness,fatigue,headache,sedation.CV:hypertension. Derm:rash. GI:weight gain.GU: urinaryfrequency.Hemat:anemia.
Assess cognitivefunction (memory,attention, reasoning,language, ability toperform simple tasksperiodically duringtherapy.
Lab TestConsiderations: May
cause anemia
5
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
6/30
CEPHALEXIN 500MG TAB Q8 bymouth
Bind tobacterial cellwallmembrane,causing celldeath. T
Treatment ofthe followinginfectionscaused bysusceptibleorganisms: Skinand skinstructureinfections(including burnwounds),Pneumonia
CNS:SEIZURES
(highdoses). GI:PSEUDOMEM-BRANOUSCOLITIS,
diarrhea,nausea,vomiting,cramps.Derm:STEVENS-
JOHNSONSYNDROME,
Assess for infection(vital signs;appearance of woundsputum, urine, andstool; WBC) at be-ginning and duringtherapy.
Before initiatingtherapy, obtaina
history to determineprevious use of andreactions to pencillinor cephalosporins.Persons with anegative history ofpenicillin sensitivitymay still have anallergic response.
6
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
7/30
CLONIDINE 0.2MG TAB Q12 BYMOUTH
Stimulatesalpha-adrenergicreceptors inthe CNS, whichresults indecreasedsympatheticoutflowinhibitingcardioacceleration andvasoconstric-tion centers.Prevents painsignaltransmissionto the CNS bystimulatingalpha-adrenergicreceptors inthe spinalcord.
PO,Transdermal:Management ofmild tomoderatehypertension.
CNS:drowsiness,depression,dizziness,nervous-ness,nightmares.CV:
bradycardia,hypotension(q withepidural),palpitations.GI: drymouth,constipation,nausea,vomiting.
Monitor intake andoutput ratios and daiweight, and assess foedema daily, especiaat beginning oftherapy.
Monitor blood pressuand pulse frequentlyduring initial dose
adjustment andperiodically throughotherapy. Reportsignificant changes.
7
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
8/30
ARICEPT 5MG TAB ONCE DAILYBY MOUTH
Inhibitsacetylcholinesterase thusimprovingcholinergicfunction bymaking moreacetylcholineavailable
Mild tomoderatedementiaassociated withAlzheimersdisease.
CNS:headache,abnormaldreams,depression,dizziness,drowsiness,fatigue,insomnia,syncope,sedation(unusual).CV: atrialfibrillation,hyper-tension,hypotension,vasodilation.
Assess cognitivefunction(memory,attention, reasoning,language, ability toperform simple tasksperiodically duringtherapy.
Administer Mini-MenStatus Exam(MMSE)
initially andperiodically as ascreening tool to ratecognitive functioning
Administer ClockDrawing Test initiallyand periodically as ascreening tool tomeasure severity ofdementia.
8
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
9/30
Medication(s) Worksheet
CLASSIFICATION NAME
DOSE/ROUTE/FREQUENCY SAFE RANGE
MECHANISM
OF ACTION
INDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS NURSINGCONSIDERATIO
NS ANDPATIENT
EDUCATIONFERROUS
SULFATE325MG DAILY BY
MOUTHAn essentialmineral foundinhemoglobin,myoglobin,and manyenzymes.Enters theblood- streamand istransportedto the organsof thereticuloendothelial system(liver, spleen,bonemarrow),where it isseparated outand becomespart of ironstores.
PO:Prevention/treatment of iron-deficiencyanemia.
CNS: IM, IVSEIZURES,dizziness,headache,syncope. CV:IM, IVhypotension,hypertension,tachycardia.GI: nausea;PO,constipation,dark stools,diarrhea,epigastric pain,GI bleeding;IM, IV, tastedisorder,vomiting.
Assess nutritionalstatus and dietaryhistory todeterminepossible cause ofanemia and needfor patientteaching.
Assess bowelfunction forconstipation ordiarrhea. Notifyhealth careprofessional anduse appropriatenursing measures
should theseoccur.
9
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
10/30
ATROVENTSAN
EVERY 4 TO 6 HOURS Inhaln:Inhibitscholinergicreceptors inbronchialsmoothmuscle,resulting indecreasedconcentrations of cyclicguanosinemonophosphate (cGMP).Decreasedlevels ofcGMPproduce localbronchodilation
Inhaln:Maintenancetherapy ofreversibleairwayobstruction dueto COPD,includingchronicbronchitis andemphysema.
CNS: dizziness,headache,nervousness.EENT: blurredvision, sorethroat; nasalonly, epistaxis,nasal
dryness/irritation. Resp:bronchospasm,cough. CV:hypotension,palpitations.GI: GI irri-tation, nausea.Derm: rash
Assess forallergy to atropineand belladonnaalkaloids; patientswith theseallergies may alsobe sensitive toipratropium.Atrovent HFA MDIdoes not containCFC or soy andmay be usedsafely in soy orCFC-allergicpatients.However,Combivent MDIshould be avoidedin soy or peanut-allergic patients.
10
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
11/30
Aspirin 81mg daily PO Inhibits thesynthesis ofprostaglandins that mayserve asmediators ofpain andfever,primarily inthe CNS. Hasno significantanti-inflammatoryproperties orGI toxicity.
Mild pain. Fever. GI: HEPATICFAILURE,HEPATOTOXICI
TY (overdose).GU: renalfailure (highdoses/chronicuse). He- mat:neutropenia,pancytopenia,leukopenia.Derm: rash,urticaria.
Assess overallhealth status andalcohol usagebeforeadministeringacetaminophen.Patients who aremalnourished orchronically abusealcohol are athigher risk ofdevelopinghepato- toxicitywith chronic useof usual doses ofthis drug.
Assess amount,frequency, andtype of drugstaken in patientsself-medicating,especially withOTC drugs.
Prolonged use ofacetaminophenincreases the riskof adverse renaleffects. For short-term use,combined dosesof acetaminophenand salicylatesshould not exceedthe recommendeddose of eitherdrug given alone.
11
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
12/30
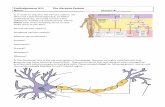
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY-BRIEF TEXTBOOK PICTURE WITH CLIENT COMPARISONDefinition, Etiology, Incidence, Pathophysiology, Diagnostic tests, Signs & symptoms, Medical
treatments
Textbook Client
Pathology-Nosebleeds are due to the rupture of a bloodvessel within the richly perfused nasal mucosa. Rupture may
be spontaneous or initiated by trauma. Nosebleeds arereported in up to 60% of the population with peak incidences
in those under the age of ten and over the age of 50 and
Patient has rupture of a blood vessel within the richly perfused nasalmucosa
12
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
13/30
appear to occur in males more than females.[3] An increase in
blood pressure (e.g. due to general hypertension) tends toincrease the duration of spontaneous epistaxis.[4]
Anticoagulant medication and disorders of blood clotting can
promote and prolong bleeding. Spontaneous epistaxis is morecommon in the elderly as the nasal mucosa (lining) becomes
dry and thin and blood pressure tends to be higher. Theelderly are also more prone to prolonged nose bleeds as their
blood vessels are less able to constrict and control thebleeding.
Classification- Commonly used classification according to
site of bleeding source
Anterior epistaxis:
Accounts for approximately 90% of nosebleeds
Usually originates from the Kiesselbach plexus, a rich
vascular anastomosis located at the anterior nasal
septum; this region is called Little's area.
Posterior epistaxis:
Originates from the posterior nasal cavity ornasopharynx [3] [4]
Posterior nasal and nasopharyngeal vessels often have
a larger calibre and may produce more active
bleeding.
Patient has anterior epitaxis that originates from the Kiesselbachplexus, a rich vascular anastomosis located at the anterior nasal septum;
Etiology- etiology of epistaxis is multi factorialbut can be divided into two broad groups Localand systemic. It must be noted that most casesof epistaxis do not have an easily identifiable
Patient epitaxis appears local
13
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nosebleed#cite_note-AAFP-3http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nosebleed#cite_note-4http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anticoagulanthttp://bestpractice.bmj.com/best-practice/monograph/421/resources/references.html#ref-3http://bestpractice.bmj.com/best-practice/monograph/421/resources/references.html#ref-4http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nosebleed#cite_note-AAFP-3http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nosebleed#cite_note-4http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anticoagulanthttp://bestpractice.bmj.com/best-practice/monograph/421/resources/references.html#ref-3http://bestpractice.bmj.com/best-practice/monograph/421/resources/references.html#ref-4 -
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
14/30
cause.
Statistics-
Epistaxis that occurs in children younger than 10years usually is mild and originates in theanterior nose, whereas epistaxis that occurs inindividuals older than 50 years is more likely tobe severe and to originate posteriorly [9].
Data from the National Hospital AmbulatoryMedical Care Survey indicate that epistaxisaccounted for
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
15/30
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
Test(i.e. X-Ray, MRI, EEG, EKG)
RESULTSDate, Result, Significance
CHEST XRAY REVEALS EMPHYSEMATOUS CHANGES
15
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
16/30
16
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
17/30
Laboratory values
CHEMISTRYPROFILE
NORMALVALUES
CLIENTSVALUES
HEMOTOLOGY
NORMALVALUES
CLIENTS VALUES
DATE DATE
DATE DATE DATE
DATE
SODIUM 135-145
Meq/L
137
4/20/13
WBC 3.8-10.8
K/uL
6.1
4/20/13
POTASSIUM 3.5- 5.1mEq/L
4.44/20/13
RBC 3.80-5.20 3.12*L4/20/13
CHLORIDE 98-108mEq/L
1014/20/13
HGB 11.8-15.4g/dl
9.8*L4/20/13
CO2 19-34 274/20/13
HCT 41-50 29.7*L4/20/13
CALCIUM 8.2-10.3mg/dL
8.34/20/13
MCV 79.4-94.8fL
95.34/20/13
GLUCOSE 70-105mg/dL
154 *H4/20/13
MCH 31.34/20/13
BUN 7-25 mg/
Dl
9.2
4/20/13
MCHC 25.6-32.2
pg
32.8
4/20/13CREATININE 0.6-1.2
mg/dL1.14/20/13
PLATELETS 11.5-15.0%
124/20/13
PHOSPHORUSCHOLESTEROL
DIFFERENTIAL
TOTALPROTEIN
6.4-8.9g/dL
6.74/20/13
NEUTROPHILS
ALBUMIN 3.5-5.0g/dL
3.774/20/13
SEGMENTS
ALBUMIN/GLOBULIN RATIO
2.974/20/13
BANDS
17
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
18/30
AST (SGOT) 13-39 U/L 272/21/13
LYMPHOCYTES
ALT (SGPT) 7-52 U/L 152/21/13
EOSINOPHILS
TOTALBILIRUBIN
0.3-1.0mg/dL
BASOPHILS
AMYLASE MONOCYTES
LIPASECOAGULATION
STUDIESPTT
SODIUM 135-145Meq/L
1374/20/13
WBC 3.8-10.8 K/uL 6.14/20/13
POTASSIUM 3.5- 5.5mEq/L
4.44/20/13
RBC 3.80-5.20 3.12*L4/20/13
CHLORIDE 98-108mEq/L
1014/20/13
HGB 11.8-15.4g/dl 9.8*L4/20/13
CO2 19-34 274/20/13
HCT 29.7*L4/20/13
CALCIUM 8.2-10.3mg/dL
8.34/20/13
MCV 95.34/20/13
GLUCOSE 70-105mg/dL 154 *H4/20/13 MCH 31.34/20/13
BUN 7-25 mg/Dl
9.24/20/13
MCHC 32.84/20/13
CBC BMP
Hgb Na+
Cl-
BUNWBC Plts Glucose
Hct K+ HCO3 Creatinine
18
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
19/30
URINALYSISCOLOR YELLOWAPPEARANCE CLEARSP. GRAVITY 1.04 MISCELLANEOUS
TESTPH 5 TEST NORMAL
VALUESCLIENTS VALUES
DATE DATE DATEGLUCOSE NORMA
L
URINE
CULTURE
PENDI
NG
06/17/1
3KETONE NEGATIVE
OCCULT BLOODPROTEIN NEGATI
VEBILRUBIN NEGATI
VEUROBILINOGEN NORMA
LNITRITE NEGATI
VELEUCOCYTE NEGATI
VE
CASTWBCRBCCRYSTALSSQUAMOUSCELLS/ EPITHELIALCELLS
Relate the clinical significance of abnormal lab values above:
GLUCOSE(LOW)- INDICATIONS:-Symptoms of elevated glucose levels include abdominal pain, fatigue, muscle cramps,nausea, vomiting, polyuria, and thirst. Possible interventions include sub- cutaneous or IV injection of insulin with continuous glucose
19
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
20/30
monitoring.
RBC(LOW)- INDICATIONS:-Low RBC count leads to anemia. Anemia can be caused by blood loss,decreased blood cell production, increased blood cell destruction, or hemodilution.
HGB(LOW)- INDICATIONS:- Low Hct leads to anemia. Anemia can be caused by blood loss, decreasedblood cell production, increased blood cell destruction, and hemodilution. Causes of blood lossinclude menstrual excess or frequency, gastrointestinal bleeding, inflammatory bowel disease, and
hematuria. Decreased blood cell production can be caused by folic acid deficiency, vitamin B12deficiency.
HCT (LOW)- INDICATIONS:- High Hct leads to polycythemia. Polycythemia can be caused bydehydration, decreased oxygen levels in the body, and an overproduction of RBCs by the bonemarrow. Dehydration from diuretic use, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, severe burns, ordecreased fluid intake decreases the plasma component of whole blood, thereby increasing the ratioof RBCs to plasma, and leads to a higher than nor- mal Hct. Causes of decreased oxygen includesmoking, exposure to carbon monoxide, high altitude, and chronic lung disease, which leads to amild hemoconcentration of blood
Head to Toe AssessmentGeneral Appearance:
The pt is resting comfortably in no acute distress. No weight loss or gain. No feverHead & Hair: Norm cephalic and atraumatic
Face: Norm cephalic and atraumatic
Eyes: Norm cephalic and atraumaticEars: Norm cephalic and atraumatic
20
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
21/30
Nose: Turbinates bright red and swollen, mucous pink, no swellingLips/Mouth/Throat: No cracking/ lesions on lips, mouth is clean and free from debris, mild breath odor.Neck:Chest/Breast:Clear to palpation and auscultation lateral chest is larger than anterior/posterior diameter.Lungs:Clear to auscultation; no abnormal sounds heard.Heart:Normal rhythm sounds heart at the fine precordial points.Abdomen/Kidneys:Normal bowel sounds, no masses, lumps, or tenderness found.Genitalia (Internal Exam Deferred): N/ARectum (Internal Exam Deferred): N/AExtremities:No edema clubbing or cyanosisBack: no deformities
R.O.M.: Limited range of motion. Patient is in the wheelchair bound.Document findings on next page
21
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
22/30
22
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
23/30
Plan of Care
Priority Nursing Diagnosis: Ineffective airway clearance related to epitaxis
Risk Nursing Diagnosis: Risk of bleeding as evidence by patient showing signs of right-sidebleeding:Supporting Data: Patient came in with right-sided epitaxis
Subjective:Patient states I am bleeding from my noseObjective:patient shows obvious signs of bleeding
Expected Outcome (Goals)
Long Term: Patients right-side epitaxis will be minimized by discharge
Short Term: After 1 hrs. Of nursing interventions, the client epitaxis will be managed
Nursing InterventionsNursing Actions Scientific Principle
and/or RationaleEvaluation Modification of Plan of
CareMonitor vital signs:
Auscultate breath sounds,heart rate and rhythm,respirations q 4 hours.
Respiratory system
may becomedecompensated.Tachycardia andchanges in bloodpressure may bepresent because ofpain, anxiety andreduced cardiacoutput.
BP is 145/60 Lung
sounds are clear toauscultation, respiratoryrate is between 20 to 24breaths per minute andpulse is at 65
Assess peripheral pulses,capillary refill, skin turgor,
Indicators of level ofhydration and
Mucous membrane aremoist, capillary refill is
23
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
24/30
and mucous membranes q4 hours.
adequacy of circulatingvolume.
less than 2 seconds andskin turgor has increased
Clean secretions from themouth and trachea
To preventobstruction /aspiration.
Clean patient and assessfor any continuousbleeding
Continue to monitor patientand assess for any bleeding
Give Fowler's or semi-Fowler position.
Positioning helpsmaximize lung
expansion and reducerespiratory effort.
Patient will remain insemi fowler to manage
nose bleed
Maintain a fluid inclusion at least
as much as 250 ml / day unless
contraindicated.
Helping dilution of
secretions.
Patient will intake atleast
250ml daily
Ask doctor if intake can be
increase if improvements are shown
Identify priority of learning needswithin the overall care plan as
soon as possible.
Teaching standardizedcontent that the patient
already knows wastesvaluable time and hinders
critical learning. Adults learn
material that is important tothem
The patientverbalizes understandingof priority learning needs.
Evaluate level of activitytolerance. Provide calm,quiet environment. Limitpatients activity orencourage bed/chair restduring acute phase. Havepatient resume activitygradually and increase asindividually tolerated.
Duringsevere/acute/refractoryrespiratory distress,patient may be totallyunable to performbasic self-careactivities because ofhypoxemia anddyspnea. Restinterspersed with careactivities remains an
Patient toleratedambulating from chair tobed after a short rest
24
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
25/30
important part oftreatment regimen. Anexercise program isaimed at increasingendurance andstrength withoutcausing severedyspnea and canenhance sense of well-being.
Encourage questions before andafter each teaching.
Questions facilitate opencommunication between
patient and health careprofessionals, and allow
verification of understandingof given information and the
opportunity to correct
misconceptions
The patient askedquestions regarding herregimen, diet andconcerns when injectingherself.
Pt will maintain clear lungfields and remain free ofsigns of respiratorydistress throughout
hospital stay
Auscultate breathsounds Q1- 2 .
Presence of crackles,
wheezes maysignify airwayobstruction, leading toor exacerbatingexisting hypoxia.
Pt demonstrated effectivecoughing techniques for student
nurse
Elevate head of bed,assist patient to assumeposition to ease work ofbreathing. Include periods
Oxygen delivery maybe improved by uprightposition and breathingexercises to decrease
The patient tolerateddeep breathing exercises
25
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
26/30
of time in prone positionas tolerated.
airway collapse,dyspnea, and work ofbreathing. Note: Recentresearch supports useof prone position toincrease Pao2.
after showing correcttechniques
Review individuals target blood
glucose levels as soon as possible.
Although this range varies
per person, the ideal range
for the adult diabetic is
considered to be 80 to 120
mg/dL. (Doenges pg 418)
Patient understood that their
normal blood sugar levels are
between 70 to 100 milligrams
per deciliter.
Pt will maintain a patent airway atall time
Monitor resp. rate,depth, and effort, useof accessory muscles,nasal flaring, andabnormal breathingpatterns. respiratory rate, useof accessory muscles,nasal flaring,
and abdominalbreathing may indicatehypoxia.
Pts airway remained open
Review clients dietary program;
compare with recent intake before
end of shift.
Identifies deficits and
deviations from therapeutic
plan, which may precipitate
unstable glucose and
The patient complies with the
new way of teaching nutritional
intake and insulin pattern.
26
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
27/30
uncontrolled hyperglycemia.
(Doenges pg 412)
Administer glucose solution 5%
dextrose and half-normal saline to
1000ml in 24 hours.
Glucose solutions may be
added after insulin and fluids
have brought the blood
glucose to approximately
400 mg/dL.
Patients blood glucose level
was at 450mg/dL after
administration of IV.
Encourage deep-slow orpursed-lip breathing asindividually needed/tolerated.
Oxygen delivery maybe improved by uprightposition and breathingexercises to decreaseairway collapse,dyspnea, and work ofbreathing. Note: Recentresearch supports useof prone position toincrease Pao2.
The patient tolerateddeep breathing exercisesafter showing correcttechniques
CARE PLAN RUBRICStudent: ___________________________________ Date: ______________________
CATEGORIES POSSIBLE POINTS
YOURPOINTS
COMMENTS
27
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
28/30
SUBJECTIVE DATA(Relevant and timely and quotedfrom patient)
10
OBJECTIVE DATA(Includes vital signs, physicalassessment findings, diagnostictests and procedures, relevantmedications, etc.)
10
NURSING DIAGNOSIS(NANDA, R/T, AEB)
20
GOAL(Condition, Time Frame,Parameters, and must be realistic)
20
INTERVENTIONS ANDRATIONALES(Assess, Assist, and Teach)
20
EVALUATION OF CARE PLAN(Evaluate each nursing action foreffectiveness)
10
MODIFICATION OF CARE PLAN(Modify patient care plan based onpatients response to interventions)
10
*TOTAL SCORE:
28
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
29/30
*Student must obtain score of > 77% in order to obtain a grade of S on the weekly care plan.
Reviewed with student: ______________________________ Date: ___________________Signature
29
-
7/29/2019 Preassignment Work-Careplan #3
30/30