Anemia-careplan for adult
Transcript of Anemia-careplan for adult
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
1/29
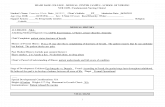
MIAMI DADE COLLEGE - MEDICAL CENTER CAMPUS - SCHOOL OF NURSINGNUR 1025L: Fundamentals Nursing Clinical
Students Name: Francisco J Ortiz Date:_07/15/13_ Clients Initials: ____ IH ___ Admission Date:_04/01/2013
Age: 91yr DOB: ______08/28/1921_____ Sex: Male X Female Race/Ethnicity: WHITE/______________Support System: _____son _________________________________________________________ Religion: _Catholic
MEDICAL HISTORYALLERGIES: _NKA_Admitting Medical Diagnosis (es): DMII; Fracture of humerus; dementia; hypertension; lipoidmetabolic disorder, iron deficiency; anemia
Chief Complaint: abnormal lab
History of Present Illness: Pt is a 91 yr old female historyfrom nursing home history of GI bleeding.Pt was sent back to the hospital because of low HH
Past Medical History (include past surgical history):Significant hypertension ,Dementia, asthma, DMII and hyperlipidemia; No alcohol abuse, no drugabuse
Clients (Parents)Understanding of Illness: patient has dementia and cannot recollect informationgiven
Stage of Development: Erickson Ego Integrity vs. Despair _ Freud: According to Freud, the genital
stage lasts throughout adulthood. He believed the goal is to develop a balance between all areas oflife. Piaget _ Formal Operational
____Special Developmental Considerations: N/AHeight: 162.56 cm Weight: 50 kg Placement in Growth Chart: _N/AImmunizations: Patient refused flu vaccine
VITAL SIGNSTime Taken: ______1000_________ Activity: ______________ Position: ____wheel chair__________
1
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
2/29
T_36.4 P96 R 19 BP _129/68Baseline (Normal Age for Age):T_ 36.137.8 P_60 -100 R_12-20_ BP120/80 _
NUTRITIONDiet: REGULAR Food Preferences:_EXTRA SYRUP IN BREAKFAST, COFFEE AFTER LUNCH, COOKIEAFTER DINNERNutritional Requirements: (Cal/Kg/Day): 2100 CAL/KG/DAY Total Calories per Day: _1900___________Fluid Requirements (Ml/Kg/Day): __________________________________ ________________Total Fluids per Day:_______________________________
Special Treatments: ____________N/AMedications atHome:_N/A_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
2
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
3/29
Medication(s) Worksheet
NAMECLASSIFICATI
ON
DOSE/ROUTE/FREQUENCY SAFE RANGE
MECHANISMOF ACTION
INDICATIONS SIDEEFFECTS
NURSINGCONSIDERATIONS
AND PATIENTEDUCATION
Prilosec 20mg daily by mouth Binds to anenzyme ongastric parietalcells in thepresence ofacidic gastricpH, preventingthe finaltransport ofhydrogen ionsinto the gastriclumen.
GERD/maintenance of healingin erosiveesopha- gitis.Duodenal ulcers(with or withoutanti-infec- tivesfor Helicobacter
pylori). Short-term treat-ment of activebenign gastriculcer.Pathologichypersecretoryconditions,includingZollinger-El-lison syndrome.Reduction ofrisk of GIbleeding incritically illpatients.
CNS:dizziness,drowsiness,fatigue,headache,weakness.CV: chestpain. GI:abdominalpain, acidregurgitation,constipation,diarrhea,flatu- lence,nausea,vomiting.Derm:itching,rash. Misc:allergicreactions.
A Assess patientroutinely forepigastricorabdominal pain anfrank or occult bloin the stool, emesor gastric aspirate
Monitor CBC withdifferentialperiodically duringtherapy.
3
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
4/29
Norvasc 10mg 1 tab PO Inhibits thetransport ofcalcium intomyocardialand vascularsmoothmuscle cells,resulting inin- hibition ofexcitation-contractioncoupling andsubsequentcontraction.
Indications:Aloneor with otheragents in themanagement ofhypertension,angina pectoris,and vasospastic(Prinzmetals)angina.
CNS:headache,dizziness,fatigue. CV:peripheraledema,angina,bradycardia,hypotension, palpita-tions. GI:gingivalhyperplasia,nausea.Derm:flushing.
Monitor blood pressureand pulse before therapy,during dose titration, andperiodically duringtherapy. Monitor ECGperiodically duingprolonged therapy.
Celexa 10mg 1 tab PO Selectivelyinhibits thereuptake ofserotonin inthe CNS.
Depression. CNS:NEUROLEPTICMALIGNANTSYNDROME,SUICIDAL
THOUGHTS,
apathy,
confusion,drowsiness,insomnia,weakness,agitation,amnesia,anxiety.
Assess for suicidaltendencies, especiallyduring early therapy anddose changes. Restrictamount of drug availableto patient. Risk may be
increased in children,adolescents, and mayminimize dry mouth. If drymouth persists for morethan 2 wk, consult healthcare professionalregarding use of salivasubstitute
4
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
5/29
Namenda 10mg 1 tab PO Binds to CNSN-methyl-D-aspartate(NMDA) re-ceptor sites,preventingbinding ofglutamate,an excitatoryneurotransmitter.
Moderate tosevereAlzheimersdementia.
CNS:dizziness,fatigue,headache,sedation.CV:hypertension. Derm:rash. GI:weight gain.GU: urinaryfrequency.Hemat:anemia.
Assess cognitive function(memory, attention,reasoning, language,ability to perform simpletasks) periodically duringtherapy.
5
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
6/29
Amaryl 4mg 1 tab PO (with
breakfast)Lower bloodglucose bystimulatingthe releaseof insulinfrom thepancreasandincreasingthesensitivity toinsulin atreceptorsites. Mayalso de-creasehepaticglucoseproduction.
Control of bloodglucose in type2 diabetesmellitus whendiet therapyfails. Requiresomepancreaticfunction.
CNS:dizziness,drowsiness,headache,weakness.GI:constipation, cramps,diarrhea,drug-inducedhepatitis,heartburn, qappetite,nausea,vomit- ing.Derm:photosensitivity, rashes.
Observe for signs andsymptoms ofhypoglycemic reactions(sweating, hunger,weakness, dizziness,tremor, tachycardia,anxiety).
6
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
7/29
Zestril 10mg 1 tab PO ACEinhibitorsblock theconversionofangiotensin Ito thevasoconstrictorangiotensinII. ACEinhibitorsalso preventthedegradationofbradykininand othervasodilatoryprostaglandins. ACEinhibitorsalso qplasma reninlevels and pal-dosteronelevels. Netresult issystemicvasodilation.
Alone or withother agents inthemanagement ofhypertension.
CNS:dizziness,drowsiness,fatigue,headache,insomnia,vertigo,weakness.Resp:cough,dyspnea.CV:hypotension,chest pain,edema,tachycardia.Endo:hyperuricemia
Hypertension: Monitorbloodpressure and pulsefrequently during initialdose adjustment andperiodically duringtherapy. Notify healthcare professional ofsignificant changes.
7
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
8/29
Ferrous sulfate 65mg tab with breakfast An essentialmineralfound inhemoglobin,myo- globin,and manyenzymes.Enters theblood-stream andistransportedto theorgans ofthe re-ticuloendothelial system(liver,spleen, bonemarrow),where it isseparatedout andbecomes
part of ironstores.
Prevention/treatment of iron-deficiencyanemia
CNS: IM, IVSEIZURES,dizziness,headache,syn- cope.CV: IM, IVhypotension,hypertension,tachycardia.GI: nausea;PO,constipation,dark stools,diarrhea,epigastricpain, GIbleeding;
Assess nutritional statusand dietary history todetermine possible causeof anemia and need forpatient teaching.
Assess bowel function forconstipation or diarrhea.Notify health careprofessional and use
appropriate nursingmeasures should theseoc- cur.
8
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
9/29
Zocor 20mg 1 tab PO nightly Inhibit anenzyme, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-co-enzyme A(HMG-CoA)reductase,which isrespon- sibleforcatalyzingan earlystep in thesynthesis ofcholesterol.
Adjunctivemanagement ofprimaryhypercholes-terolemia andmixeddyslipidemias.
CNS:dizziness,headache,insomnia,weakness.CV: chestpain,peripheraledema.EENT:rhinitis;lovastatin,blurredvision.Resp:bronchitis.
Obtain a dietary history,especially with regard tofat consumption.
9
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
10/29
Aspirin 81mg daily PO Inhibits thesynthesis ofprostaglandins that mayserve asmediators ofpain andfever,primarily inthe CNS.Has nosignificantanti-inflammatory propertiesor GItoxicity.
Mild pain. Fever. GI: HEPATICFAILURE,HEPATOTOXICITY
(overdose).GU: renalfailure (highdoses/chronic use). He-mat:neutropenia,
pancytopenia,leukopenia.Derm: rash,urticaria.
Assess overall healthstatus and alcohol usagebefore administeringacetaminophen. Patientswho are malnourished orchronically abuse alcoholare at higher risk ofdeveloping hepato-toxicity with chronic useof usual doses of thisdrug.
Assess amount,frequency, and type ofdrugs taken in patientsself-medicating,especially with OTCdrugs. Prolonged use ofacetaminophen increasesthe risk of adverse renaleffects. For short-termuse, combined doses ofacetaminophen andsalicylates should not
exceed therecommended dose ofeither drug given alone.
10
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
11/29
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY-BRIEF TEXTBOOK PICTURE WITH CLIENT COMPARISONDefinition, Etiology, Incidence, Pathophysiology, Diagnostic tests, Signs & symptoms, Medical
treatments
Textbook Client
Pathology- Incidence of anemia reflect the presence of bone
marrow failure or excessive loss of red blood cells or both.Bone marrow failure can occur due to nutritionaldeficiencies, toxic exposures, tumor, or mostly due to
unknown causes. Red blood cells can be lost through
hemorrhage or hemolysis (destruction) in the latter case, theproblem can be caused by the effects of red blood cells that
do not correspond to the resistance of normal red blood cellsor due to several factors outside the red blood cells that
causes red blood cell destruction.Red blood cell lysis (dissolution) occurs mainly in the
phagocytic system or in the reticuloendothelial system,
especially in the liver and spleen. As a byproduct of this
Patient has lab levels indicative of Low Iron anemia
11
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
12/29
process the bilirubin that is formed in phagocytes will enter
the bloodstream. Any increase in red blood cell destruction(hemolysis) immediately reflected by increasing plasma
bilirubin (normal concentration of 1 mg / dl or less; levels of1.5 mg / dl result in jaundice in the sclera.
Anemia is a blood disease characterized less low levels of
hemoglobin (Hb) and red blood cells (erythrocytes). Thefunction of the blood is carrying food and oxygen to all
organs of the body. If the supply is less, then the intake ofoxygen will be less. As a result, can inhibit the work of the
vital organs, the brain One. The brain consists of 2.5 billionbioneuron cells. If capacity is lacking, then the brain will belike computer memory is weak, slow catch. And if it is
damaged, can not be repaired (Sjaifoellah, 1998).
Classification- Anemias can be classified by cytometric
schemes (i.e., those that depend on cell size and hemoglobin-content parameters, such as MCV and MCHC),
erythrokinetic schemes (those that take into account the ratesof rbc production and destruction), and
biochemical/molecular schemes (those that consider the
etiology of the anemia at the molecular level.
Etiology- The most common cause of anemia is deficiency of
nutrients required for the synthesis of red blood cells, such asiron, vitamin B12 and folic acid. The rest is the result of a
variety of conditions such as hemorrhage, geneticabnormalities, chronic disease, drug toxicity, and so on.
Patient anemias related to poor nutrition
Statistics-
7% of children aged 1-2 had anemia in the US 1999-2000
(MMWR, NCHS, CDC)
12% of women aged 12-49 had anemia in the US 1999-
2000 (MMWR, NCHS, CDC)
174,600 nursing home residents had anemia in the US
1999 (National Nursing Home Survey, NCHS, CDC)
10.7% of nursing home residents had anemia in the US1999 (National Nursing Home Survey, NCHS, CDC)
Patient lies within the range of those 23% of females havinganemia
12
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
13/29
3.4 million cases in the US (Mayo Clinic)
1.3% of population self-reported having anemia inAustralia 2001 (ABS 2001 National Health Survey,
Australias Health 2004, AIHW)
0.3% of male population self-reported having anemia in
Australia 2001 (ABS 2001 National Health Survey,
Australias Health 2004, AIHW)
2.3% of female population self-reported having anemia in
Australia 2001 (ABS 2001 National Health Survey,Australias Health 2004, AIHW)
217,000 women self-reported having anemia in Australia2001 (ABS 2001 National Health Survey, Australias Health2004, AIHW)
13
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
14/29
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
Test(i.e. X-Ray, MRI, EEG, EKG)
RESULTSDate, Result, Significance
N/A
14
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
15/29
15
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
16/29
Laboratory values
CHEMISTRYPROFILE
NORMALVALUES
CLIENTSVALUES
HEMOTOLOGY
NORMALVALUES
CLIENTS VALUES
DATE DATE
DATE DATE DATE
DATE
SODIUM 135-145
Meq/L
142
5/10/13
WBC 3.8-10.8
K/uL
4.82
5/10/13
POTASSIUM 3.5- 5.1mEq/L
4.55/10/13
RBC 3.80-5.20 2.06*L5/10/13
CHLORIDE 98-108mEq/L
1095/10/13
HGB 11.8-15.4g/dl
12.15/10/13
CO2 19-34 23.05/10/13
HCT 41-50 38*L5/10/13
CALCIUM 8.2-10.3mg/dL
7.75/10/13
MCV 79.4-94.8fL
90.75/10/13
GLUCOSE 70-105mg/dL
110(H)**5/10/13
MCH
BUN 7-25 mg/
Dl
36 (H)**
5/10/13
MCHC 25.6-32.2
pg
27.8
5/10/13CREATININE 0.6-1.2
mg/dL1.15/10/13
PLATELETS 11.5-15.0%
16.65/10/13
PHOSPHORUSCHOLESTEROL
DIFFERENTIAL
TOTALPROTEIN
6.4-8.9g/dL
6.45/10/13
NEUTROPHILS
ALBUMIN 3.5-5.0g/dL
3.485/10/13
SEGMENTS
ALBUMIN/GLOBULIN RATIO
2.975/10/13
BANDS
16
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
17/29
AST (SGOT) 13-39 U/L 235/10/13
LYMPHOCYTES
ALT (SGPT) 7-52 U/L 155/10/13
EOSINOPHILS
TOTALBILIRUBIN
0.3-1.0mg/dL
BASOPHILS
AMYLASE MONOCYTES
LIPASECOAGULATION
STUDIESPTT
SODIUM 135-145Meq/L
1425/10/13
WBC 3.8-10.8 K/uL 4.825/10/13
POTASSIUM 3.5- 5.5mEq/L
4.55/10/13
RBC 3.80-5.20 2.06*L5/10/13
CHLORIDE 98-108mEq/L
1095/10/13
HGB 11.8-15.4g/dl 12.15/10/13
CO2 19-34 23.05/10/13
HCT 38*L5/10/13
CALCIUM 8.2-10.3mg/dL
7.75/10/13
MCV 90.75/10/13
GLUCOSE 70-105mg/dL 110(H)**5/10/13
MCH
BUN 7-25 mg/Dl
36 (H)**5/10/13
MCHC 27.85/10/13
CBC BMP
Hgb Na+
Cl-
BUNWBC Plts Glucose
Hct K+ HCO3 Creatinine
17
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
18/29
URINALYSISCOLOR YELLOWAPPEARANCE CLEARSP. GRAVITY 1.010 MISCELLANEOUS
TESTPH 4.8 TEST NORMAL
VALUESCLIENTS VALUES
DATE DATE DATEGLUCOSE NORMA
L
URINE
CULTURE
PENDI
NG
07/17/1
3KETONE NEGATIVE
OCCULT BLOODPROTEIN NEGATI
VEBILRUBIN NEGATI
VEUROBILINOGEN NORMA
LNITRITE NEGATI
VELEUCOCYTE NEGATI
VE
CASTWBCRBCCRYSTALSSQUAMOUSCELLS/ EPITHELIALCELLS
Relate the clinical significance of abnormal lab values above:
GLUCOSE(HIGH)- INDICATIONS:- Symptoms of elevated glucose levels include abdominal pain, fatigue, muscle cramps,nausea, vomiting, polyuria, and thirst. Possible interventions include sub- cutaneous or IV injection of insulin with continuous glucose
18
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
19/29
monitoring.
BUN(HIGH)- INDICATIONS:-A patient with a grossly elevated BUN may have signs and symptoms including acidemia,agitation, confusion, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and coma. Possible interventions include treatment of the cause, administration of
intravenous bicarbonate, a low-protein diet, hemodialysis, and caution with respect to prescribing and continuing nephrotoxic
medications.
RBC(LOW)- INDICATIONS:-Low RBC count leads to anemia. Anemia can be caused by blood loss,
decreased blood cell production, increased blood cell destruction, or hemodilution.
HCT (LOW)- INDICATIONS:- High Hct leads to polycythemia. Polycythemia can be caused bydehydration, decreased oxygen levels in the body, and an overproduction of RBCs by the bonemarrow. Dehydration from diuretic use, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, severe burns, ordecreased fluid intake decreases the plasma component of whole blood, thereby increasing the ratioof RBCs to plasma, and leads to a higher than nor- mal Hct. Causes of decreased oxygen includesmoking, exposure to carbon monoxide, high altitude, and chronic lung disease, which leads to amild hemoconcentration of blood
Head to Toe AssessmentGeneral Appearance:The pt is resting comfortably in no acute distress. No weight loss or gain. No feverHead & Hair: Norm cephalic and atraumatic
Face: Norm cephalic and atraumatic
Eyes: Norm cephalic and atraumaticEars: Norm cephalic and atraumaticNose: Turbinates bright red and swollen, mucous pink, no swellingLips/Mouth/Throat: No cracking/ lesions on lips, mouth is clean and free from debris, mild breath odor.
19
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
20/29
Neck:Chest/Breast:Clear to palpation and auscultation lateral chest is larger than anterior/posterior diameter.Lungs:Clear to auscultation; no abnormal sounds heard.Heart:Normal rhythm sounds heart at the fine precordial points.Abdomen/Kidneys:Normal bowel sounds, no masses, lumps, or tenderness found.Genitalia (Internal Exam Deferred): N/ARectum (Internal Exam Deferred): N/AExtremities:No edema clubbing or cyanosisBack: no deformities
R.O.M.: Limited range of motion. Patient is in the wheelchair bound.Document findings on next page
20
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
21/29
21
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
22/29
Plan of Care
Priority Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Diagnosis: Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body Requirements
Risk Nursing Diagnosis: Risk of Enhance tissue perfusionSupporting Data: Patient reports of decreased exercise or activity tolerance
Subjective: Patient states I am tiredObjective: patient labs show abnormal lab levels after analysis
Expected Outcome (Goals)
Long Term: Provide patient nutritional/fluid needs to avoid further complication before discharge.
Short Term: After 1hr disease process/prognosis and therapeutic regimen will be understood by patient.
Nursing InterventionsNursing Actions Scientific Principle
and/or RationaleEvaluation Modification of Plan of
CareMonitor vital signs:Auscultate breath sounds,
heart rate and rhythm,respirations q 4 hours.
Respiratory systemmay become
decompensated.Tachycardia andchanges in bloodpressure may bepresent because ofpain, anxiety andreduced cardiacoutput.
BP is 129/68 Lungsounds are clear to
auscultation, respiratoryrate is between 20 to 24breaths per minute andpulse is at 96
Assess peripheral pulses,capillary refill, skin turgor,and mucous membranes q
Indicators of level ofhydration andadequacy of circulating
Mucous membrane aremoist, capillary refill isless than 2 seconds and
If skin turgor +2 call doctorfor order of IV fluids forhydration.
22
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
23/29
4 hours. volume. skin turgor has increased
Monitor laboratory studies, e.g.,Hb/Hct and RBC count, arterial
blood gases (ABGs).
Identifies deficiencies inRBC components affecting
oxygen transport and
treatment needs/response totherapy.
Pt labs will showimprovement if othertreatments are workinge.g. iron supplement
Note changes in balance,gait disturbance, andmuscle
weakness.
May indicate
neurological changesassociated withvitamin B12 deficiency,affecting client safetyand increasing risk ofinjury.
Patient showed signs of
improved musclestrength after consumingmeals
Elevate head of bed, as
tolerated.
Enhances lungexpansion to maximizeoxygenation forcellular uptake. Note:May be contraindicated
if hypotension ispresent.
Pt tolerated head rest at
45 degrees and 90
degress
May have to be discontinued if
hypotension is present or noted
Assist client to prioritizeADLs and desiredactivities. Alternate restperiods with activityperiods.
Promotes adequaterest, maintains energylevel, and alleviatesstrain on the cardiacand respiratorysystems.
The patientverbalizes understandingof priority learning needs.
Change environment towhere pt will have
23
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
24/29
Review nutritional history,including food preferences.
Identifies deficienciesand suggests possibleinterventions. Note:Daily meal diary overperiod of time may benecessary to identify
anemia related tonutrient deficienciessuch as no meat in dietiron and vitamin B12deficiency, or few leafyvegetables in dietfolic acid deficiency.
Patient toleratedambulating from chair tobed after a short rest
Encourage questionsbefore and after eachteaching.
Questions facilitateopen communicationbetween patient andhealth careprofessionals, andallow verification ofunderstanding of giveninformation and theopportunity to correctmisconceptions
The patient askedquestions regarding herregimen, diet andconcerns when injectingherself.
Suggest bland diet, low inroughage, avoiding hot,spicy, or very acidic foods,as indicated
When oral lesions arepresent, pain mayrestrict type of foodsclient can tolerate.
Pt ate puree food thatwas tolerate forconsumption
Ask doctor if TPN is apossible suggestion for I/O
24
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
25/29
Encourage or assist withgood oral hygiene beforeand after meals; use soft-bristled toothbrush forgentle brushing. Providedilute, alcohol-free
mouthwash if oral mucosais ulcerated.
Enhances appetite andoral intake. Diminishesbacterial growth,minimizing possibilityof infection. Specialmouth-care techniques
may be needed iftissue is fragile,ulcerated, or bleedingand pain is severe
Pt demostrated use oforal hygiene after Iperformed task
Review individuals targetblood glucose levels assoon as possible.
Although this rangevaries per person, theideal range for theadult diabetic isconsidered to be 80 to120 mg/dL. (Doengespg 418)
Patient understood thattheir normal blood sugarlevels are between 70 to100 milligrams perdeciliter.
Monitor laboratory studies,such as Hgb/Hct, bloodurea nitrogen
(BUN), prealbumin andalbumin, protein,transferrin, serum
iron, vitamin B12, folicacid, TIBC, and serum
Aids in establishingdietary plan to meetindividual needs.Evaluateseffectiveness oftreatment regimen,including dietary
sources of needed
Pt BUN level becamestable after treatment
If level are still low aftertreatment consult withdoctor for other treatment
25
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
26/29
electrolytes. nutrients.
Review clients dietaryprogram; compare withrecent intake before end ofshift.
Identifies deficits anddeviations fromtherapeutic plan, whichmay precipitate
unstable glucose anduncontrolledhyperglycemia.(Doenges pg 412)
The patient complieswith the new way ofteaching nutritionalintake and insulin
pattern.
Monitor laboratory studies, e.g.,
Hb/Hct and RBC count, arterialblood gases (ABGs).
Identifies deficiencies inRBC components affectingoxygen transport and
treatment needs/response totherapy.
CARE PLAN RUBRICStudent: ___________________________________ Date: ______________________
26
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
27/29
CATEGORIES POSSIBLE POINTS
YOURPOINTS
COMMENTS
SUBJECTIVE DATA(Relevant and timely and quotedfrom patient)
10
OBJECTIVE DATA(Includes vital signs, physicalassessment findings, diagnostictests and procedures, relevantmedications, etc.)
10
NURSING DIAGNOSIS(NANDA, R/T, AEB)
20
GOAL(Condition, Time Frame,Parameters, and must be realistic)
20
INTERVENTIONS ANDRATIONALES(Assess, Assist, and Teach)
20
EVALUATION OF CARE PLAN(Evaluate each nursing action foreffectiveness)
10
MODIFICATION OF CARE PLAN(Modify patient care plan based onpatients response to interventions)
10
27
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
28/29
*TOTAL SCORE:
*Student must obtain score of > 77% in order to obtain a grade of S on the weekly care plan.
Reviewed with student: ______________________________ Date: ___________________Signature
28
-
7/29/2019 Anemia-careplan for adult
29/29