Molecules of Life · Polymers are constructed using enzymes. A large number of polymers can be...
Transcript of Molecules of Life · Polymers are constructed using enzymes. A large number of polymers can be...

1/17/2020
1
Molecules of LifeLecture 4
At the end of this series of lectures you should be able to:
Define terms.
Explain why carbon is important in the formation of large molecules.
List and describe the macromolecules important for life.
Describe the structure, functions, and types of the macromolecules.
Objectives

1/17/2020
2
Organic compounds are carbon‐based.
Carbon is highly versatile Shares electrons (covalent bonds) with up to 4 different atoms.
Branch in up to 4 different directions.
Carbon bonds can be to Other carbon atoms
Other types of atoms
Double bonds
Hydrocarbons – Contain only hydrogen and carbon.
Organic Compounds
The properties of the organic molecule depend on:
The size and shape of the carbon skeleton
Functional groups attached to it.
Organic Compounds

1/17/2020
3
These tend to be large molecules They are also polymers – constructed from similar repeating
building blocks or pieces
The repeated blocks or pieces are called monomers.
Polymers are constructed using enzymes.
A large number of polymers can be constructed from a just a few monomers.
Length
Branching
Order of monomers
Macromoelcules
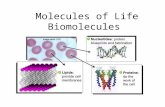
There are four types of macromolecules important for life:
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Proteins
Amino acids
Lipids
Fatty acid chains
Nucleic acids
Nucleotides
Macromolecules

1/17/2020
4
Monomers are monosaccharides
Carbon skeletons vary in length
Glucose is a six carbon sugar
Can have a ring shape
Fuel for cells and raw material for constructing other organic molecules.
Two linked monosaccharides are a disaccharides.
Sucrose (table sugar) is a disacharhide (glucose and fructose).
Carbohydrates
Figure 3.5_s2
NEUROtiker, Public Domain, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sucrose#mediaviewer/File:Saccharose2.svg

1/17/2020
5
Polysaccharides are long chains of monosaccahrides.
Storage molecules
Structural molecules
Carbohydrates
Starch Glucose monomers Energy storage in plants
Glycogen Glucose monomers Energy storage in animals
Cellulose Glucose monomers Plant cell walls – structural – Wood
Chitin Exoskeletons of arthropods
Carbohydrates

1/17/2020
6
Figure 3.7
Ben Mills, Public Domain, Glucose: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucose#mediaviewer/File:Alpha‐D‐glucose‐from‐xtal‐1979‐3D‐balls.pngCellulose: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cellulose#mediaviewer/File:Cellulose‐Ibeta‐from‐xtal‐2002‐3D‐balls.pngCeresVesta, Public Domain, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogen#mediaviewer/File:Glycogen_spacefilling_model.jpg
Cellulose
Glucose
Glycogen
Energy storage and structural moelcules Are water insoluble (hydrophobic) compounds Consist mainly of carbon and hydrogen atoms linked by
covalent bonds. Are not large molecules or they polymers (strictly
speaking)
Fats and oils Phospholipids Steroids
Lipids

1/17/2020
7
Fats and oils
Fats and oils are large lipids made from two kinds of smaller molecules:
glycerol
fatty acids
Fats are often called triglycerides because of their structure.
Lipids
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology by Stelios Kolomvounis, OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0

1/17/2020
8
If the fatty acid chains have as many hydrogen atoms as it could hold it is a saturated fatty acid – fat (solid at room temperature).
If the fatty acid chains contain double bonds (thus not as many hydrogen atoms as it could it is a unsaturated fatty acid – oil (liquid at room temperature).
Lipids
Phospholipids Important component of cell membranes.
Similar structure to fats – except one of the fatty acid chains has been replaced by a phosphate.
Head and tail shape develops
Phosphate head is hydrophilic (attracted to water)
Fatty acid tails are hydrophobic (repelled by water)
Forms a bilayer Heads facing out from the bilayer
Tails inside the bilayer
Lipids

1/17/2020
9
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology by Stelios Kolomvounis, OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology by Stelios Kolomvounis, OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0

1/17/2020
10
Steroids are lipids where the carbon skeleton contains four fused rings. Cell messengers
Cholesterol
Component in cell membranes – stabilizes the membrane
Used by the body to make steroids
Anabolic steroids
Increased muscle and bone mass
Health threats
Sex hormones
Lipids
Figure 3.2
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology by Stelios Kolomvounis, OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0

1/17/2020
11
Many uses in the body Functional (enzymes)
Catalysts
Structural proteins
Contractile proteins ‐‐muscle
Defensive proteins – antibodies
Signal proteins – some hormones
Receptor proteins – cell membranes
Transport proteins ‐‐ hemoglobin
Storage proteins – egg white
Proteins
Amino acids
Monomers (building blocks) for proteins
Structure
A central carbon bonded to
Hydrogen atom
An amino group
A carboxyl group.
Functional group symbolized by R
Determines the properties of the amino acid
Proteins

1/17/2020
12
Figure 3.11A
OpenStax College, CC BY 3.0, http://cnx.org/contents/6773536c‐3efb‐44c9‐8ace‐78fafdce27e1@4
Proteins are made by
Linking amino acids together
Dehydration reaction
Joins the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another amino acid
Creates a peptide bond.
More amino acids can be added by the same process to create a chain of amino acids
Polypeptide.
Proteins

1/17/2020
13
Figure 3.11C_s2
OpenStax College, CC BY 3.0, http://cnx.org/contents/6773536c‐3efb‐44c9‐8ace‐78fafdce27e1@4
Polypeptide chains contain hundreds or thousands of amino acids
The amino acid sequence causes the polypeptide to have a particular shape.
The shape of a protein determines its specific function.
If a protein’s shape is altered, it can no longer function.
Proteins

1/17/2020
14
A protein’s shape depends on four levels of structure. A protein can have four levels of structure: Primary structure – amino acid sequence
Determined by genes
Secondary structure – Coiling or folding of polypetide Coiling – alpha helix Folding – Pleated sheet Maintained by hydrogen bonds
Tertiary structure – Overall 3‐d structure of the polypetide Interactions between amino acid R‐groups Disulfide bonds
Quaternary structure – Combining two or more polypetide chains (subunits)
Protein
Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0

1/17/2020
15
In the process of denaturation, a polypeptide chain
Unravel
Changes shape
No longer functions
Proteins can be denatured by changes in salt concentration, pH, or by high temperatures.
Proteins
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) are composed of monomers called nucleotides.
Nucleotides have three parts:
Sugar
Ribose – sugar in RNA
Deoxyribose – sugar in DNA
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous base
Nucleic Acids

1/17/2020
16
Robert Bear and David Rintoul, CC BY‐SA 3.0, http://cnx.org/contents/efedfd3e‐01ef‐4c5f‐8265‐c7bf730161a4@5
Nucleotides DNA
Adenine – A Cytosine – C Guanine – G Thymine – T
RNA Adenine – A Cytosine – C Guanine – G Uracil – U
Nucleic Acids

1/17/2020
17
A polynucleotide (nucleic acid polymer) forms By dehydration reaction
The phosphate of one nucleotide bonds to the sugar of the next nucleotide
A repeating sugar‐phosphate backbone forms with protruding nitrogenous bases. Two polynucleotide strands wrap around each other to form a
DNA double helix. The two strands are associated because particular bases always
hydrogen bond to one another. A pairs with T, and C pairs with G, producing base pairs.
RNA is usually a single polynucleotide strand.
Nucleic Acids