Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
-
Upload
tufail-ganaie -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 1/34
Double Entry System&
Accounting Equation
By -Mrs. Dilshad D. Jalnawalla
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 2/34
Accounting CyclePassing of Reverse Entries
Passing of Closing Entries
Preparation of Final Accounts
Passing of Adjustment Entries
Preparation of Trial Balance
Identification of Transaction
If not last transaction of theperiod
If last transaction of
the period
BusinessDocuments areprepared orreceived
Transactionsare recordedin books of
original entry
Transactionsare posted toledgers
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 3/34
Meaning of Transaction A transaction is a particular type of
external event, which can be expressedin terms of money and brings change inthe financial position of a business unit.
Transactions may be external (between
a business unit entity and a secondparty) or internal (not involving secondparty)
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 4/34
Meaning of Event Event is an occurrence, happening,
change or incident, which may or maynot bring any change in the financialposition of a business unit.
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 5/34
Identify whether events are
transactions or not:1. Mr. X started business with capital Rs.40,000/-2. Paid salaries to staff Rs.5,000/-3. Placed an order with Sen & Co. for goods for Rs.5,000/-4. Opened a bank account by depositing Rs.4000/-5. Received Pass book from bank.6. Received interest from bank Rs.500/-7. Received Free samples Rs.1,000/-
8. Sent peon to post office to bring the V.P.P. of Rs.600/-9. Appointed Mr.B As a manager on a salary of Rs.4,000 per
month.10. Purchased machinery for Rs.20,000/- in cash
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 6/34
Double Entry System
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 7/34
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 8/34
All transactions are supposed to havedual aspects a DEBIT ASPECT and aCREDIT ASPECT.
Accounts are maintained on accrual
basis under the system. A cost incurred (i.e.accrued) is dulyaccounted for irrespective of whetherit is paid or not during the period.
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 9/34
Features1. Records both aspects of each transaction.
2. Equal debit and credit entries are made for every
transaction in two different accounts.3. All transactions are recorded fully.
4. It is possible to prepare a Trial Balance and checkthe arithmetical accuracy of the books of account because it records all transactions in full.
5. Profit / Loss can be found out by showing in detailthe expenses and incomes.
6. Balance Sheet can be prepared in detail.
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 10/34
Debit and Credit The term debit is derived from the latin
base debere (to owe) which contractsto the form Dr. used in journal entriesto refer to debits.
Credit comes from the word credere
(that which one believes in, includingpersons, like a creditor), whichcontracts to the form Cr., used in
journal entries for a credit.
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 11/34
Debit and Credit are simply additions toor subtraction from an account. Inaccounting, debit refers to the left handside of any account and credit refers tothe right hand side. Assets, expenses
and losses accounts normally have debit balances; liability, income and capitalaccounts normally have credit balances.
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 12/34
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 13/34
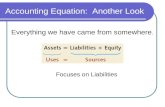
Accounting Equation
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 14/34
Accounting Equation is the foundationon which the Double Entry Bookkeepingsystem is build.
Accounting equation is expressed indifferent forms ranging from a summary
to a detailed equation.
Accounting Equation
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 15/34
Top most version Property = Property Rights
Assets=
Equities Property must be equal to the claims
against the property.
Basic requirement being tracking theproperties and how we acquired or got them and their source.
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 16/34
Expanded Equation
Property = Property Rights
Assets = Owners Equity + Outside Liabilities
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 17/34
Owners Equity is the right the owners haveon the property or assets of the business.
Components of Owners Equity
1. What they invested or put into the business(Capital).
2. What they took out (Drawings).3. Operations of the business which is called
as profits or losses; or Retained earnings.
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 18/34
Expanded Accounting
Equation
Assets = Liabilities+ Capital + Retained Earnings
Assets = Liabilities+ Capital+
(Income - Expenses)A = L + C + (I-E)
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 19/34
Assets= Liabilities + Capital
Liabilities=
Assets Capital Capital = Assets Liabilities
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 20/34
Illustration 1 If the liabilities of a business is Rs.
75,000 and the capital is Rs 85,000.Find out the total assets.
Total Assets = Capital + Liabilities
Total Assets = 85,000+75,000
Total Assets = Rs. 1,60,000/-
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 21/34
A business has assets of Rs. 54,321 andowners equity is Rs.34,215. What is theamount of liability?
Liabilities = Assets - Capital (Owners Equity)
Liabilities = 54,321 - 34,215
Liabilities = Rs.20,106/-
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 22/34
Cash Rs.10,000; Stock Rs.15,000;
Building Rs. 10,000; MachineryRs.1,80,000; Debtors Rs.45,000; andCreditors Rs.27,500. Ascertain the
capital.Capital = Assets Liabilities
Capital = (Cash+Stock+Building+Machinery+Debtors) Creditors
= (10,000+15,000+10,000+1,80,000+45,000) 27,500
= 2,60,000 27,500
= Rs.2,32,500/-
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 23/34
Illustration 2 If the assets of a business are
Rs.1,50,000 and Capital is Rs. 75,000,Calculate Creditors.
Answer : Creditors Rs. 75,000.
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 24/34
If the capital of a business is Rs. 80,000and the liabilities are Rs. 60,000,calculate the total assets of thebusiness.
Answer : Total Assets = Rs.1,40,000/-
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 25/34
Calculate total assets if (i) Capital isRs.50,000; (ii) Creditors Rs.30,000; (iii)
Revenue during the period Rs.52,000;(iv) Expenses during the same periodare Rs.38,000.
Answer: Total Assets = Rs.94,000/-
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 26/34
Illustration 3 Calculate Total Assets of the business when
Capital Rs.40,000; Creditors Rs.30,000; Revenue
earned during the period Rs.75,000; Expensesincurred during the period Rs.20,000. Value of Stock unsold Rs.20,000.
Answer :
Total Assets = Rs.1,25,000/-
(Includes Rs.20,000 closing stock)
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 27/34
Illustration 4
Prabhat has the following assets andLiabilities. Ascertain his Capital.
Cash Rs.2,500; Bank Rs.4,750; Debtors
Rs.1,800; Creditors Rs.2,200; Plant andMachinery Rs.8,000; BuildingRs.20,000, Furniture Rs.2,400; BillsReceivable Rs.5,650; Bills PayableRs.2,350.
Answer: Capital = Rs.40,550/-
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 28/34
Illustration 5 Show the accounting equations on the basis
of the following transactions.
1. Raghunath commenced business with cashRs.80,000/-
2. Purchased goods on credit Rs.20,000/-
3. Withdrew cash for private use Rs.2,000/-
4. Sold goods on credit (cost price Rs.15,000/-)Rs. 20,000/-
5. Purchased furniture Rs.1,500/-
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 29/34
Raghunath commenced business with cash
Rs.80,000/-
Assets - Liabilities = Capital
Cash 80,000 - 0 = 80,000
80,000 - 0 = 80,000
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 30/34
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 31/34
Withdrew cash for private use Rs.2,000/-
Assets - Liabilities = Capital
Cash 78,000 - 0 = 78,000
Stock 20,000 - Creditors 20,000 = 0
98,000 - 20,000 = 78,000
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 32/34
Sold goods on credit (cost price Rs.15,000/-)
Rs. 20,000/-
Assets - Liabilities = Capital
Cash 78,000 - 0 = 83,000
Stock 5,000 - Creditors 20,000= 0
Debtors 20,000 - 0 = 0
1,03,000 - 20,000 = 83,000
8/7/2019 Copy of Accounting Equation 1.3
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/copy-of-accounting-equation-13 33/34
Purchased furniture Rs.1,500/-
Assets - Liabilities = Capital
Cash 76,500 - 0=
83,000Stock 5,000 - Creditors 20,000 = 0Debtors 20,000 - 0 = 0Furniture 1,500 - 0 = 0
1,03,000 - 20,000 = 83,000