Circulatory System Delivery of oxygen, hormones and nutrients to an organism’s cells.
-
Upload
herbert-burke -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of Circulatory System Delivery of oxygen, hormones and nutrients to an organism’s cells.
No Circulatory System
• Sponges, cnidarians, flat and roundworms
• Uses diffusion to provide cells with oxygen, nutrients and disposal of wastes
Open Circulatory System
• Arthropods and mollusks• Heart pumps blood into vessels with open ends
• Blood and interstitial fluid is called hemolymph
Closed Circulatory System
• Cephalopods, annelids, echnoderms & all vertebrates
• Vessels don’t have open ends; blood circulates through vessels that branch into smaller and smaller ones in a continuous loop
• Hemoglobin is used for oxygen transport
• 8 functions
8 functions are:
1. Transport nutrients2. Transport oxygen3. Help maintain fluid balance4. Help defend body5. Transport cell waste to excretory organs6. Transport hormones7. Help distribute heat8. Help maintain pH
Components of Blood
• Plasma
• Erythrocytes (red blood cells, RBC’s)
• Leukocytes (white blood cells, WBC’s)
• Thrombocytes (platelets)
Plasma
• Pale yellow liquid that makes up about 55% of blood
• Contains many proteins that help with clotting, hormone transport, and fat transport
• Helps maintain blood pressure and pH
• Made up of 90% water and 10% solute
Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
• Have a flexible, biconcave shape• produced in red bone marrow• filled with hemoglobin – a protein that binds to
oxygen in the lungs to transport it to tissues of body
• has no nucleus• only lives 4 months• produced constantly by stem cells; if production
slows down, anemia develops
Leukocytes (white blood cells)• Help fight bacteria
• Made in red bone marrow
• Primary cells of immune system
• 2 types– Lymphocytes – produce antibodies– Macrophages – eat foreign cells by phagocytosis
(also called phagocytes)
• Cancer of white blood cells is called leukemia
• Larger than RBC’s and have a nucleus (add)
Thrombocytes (platelets)
• not whole cells, but rather bits of cytoplasm covered by membrane
• If a blood vessel gets a HOLE, it must be plugged right away, and this is what platelets do!
• When a blood vessel gets DAMAGED, chemicals are released and platelets recognize this. It then releases a clotting PROTEIN that initiates chemical reactions resulting in the formation of a protein called a FIBRIN
– Fibrin traps blood cells and CLOT forms
Arteries
• carry blood away from heart• smaller divisions of them
are called arterioles• have ability to relax/constrict
to control blood pressure and volume of blood transported
• Largest artery is the aorta coming out of the heart
Capillaries
• Smallest blood vessel division
• Point at which materials can diffuse into the interstial fluid
• They connect arteries to veins
Veins
• Veins – take blood from the body back to the heart
• smaller divisions are called venules• largest vein is the vena cava which
leads to the heart• Metaarterioles – they directly
connect arterioles to venules
Blood Types • Red blood cells are coated with a protein called an
antigen• Your blood cells have either A antigens, B
antigens, both A and B antigens or none• The kinds of antigens present determine blood
type• Antibodies seeks out foreign antigens and kill them• So if a person with type B blood receives type A or AB
blood, the antibodies will react with the donor’s blood and cause the blood to CLUMP.
Type Antigen of RBC
Antibodies in plasma
Can receive from
Can donate to
A A B O,A A, AB
B B A O.B B, AB
AB A,B None O, A, B, AB
AB
O None A,B O O, A, B, AB
Rh Factors
• Rh factors are another antigen on the surface of the RBC’s• If you have this antigen/protein, you are said to be Rh+
and if you don’t have it you are Rh-• Dangerous in pregnant women who are Rh- carrying a
Rh+ child• During delivery, the blood mixes, so the mother will
produce antibodies and the first child is unharmed• But if the second child is also Rh+, then those antibodies
will attack the child’s blood cells causing severe complications– Can be treated in early pregnancy– Otherwise child will not be able to produce RBC’s and that makes
oxygen levels low and death could result.
Lymphatic System
• Consists of the heart & lymphatic blood vessels• Circulatory system is very leaky because fluids
are forced out of thin walls of capillaries by the pressure of the heart pumping
• This loss of fluid must be made up so the Lymphatic system saves the day!– It collects and recycles this fluid by letting it diffuse
into lymphatic capillaries, then the lymph passes into lymphatic ducts that drain into veins in the lower part of the neck
The Heart
• Consists of Cardiac tissue• Encased by pericardium• 2 chambers divided by septum
1. atrium – get blood from the veins
2. ventricles – pump blood into the arteries
SA Node – tissue that starts impulse of heart beat (pacemaker)-Sinoatrial nodeAV Node –conducts impulse from atria into the ventricles- Atrioventricular node
Specific Blood Vessels
• Aorta – biggest artery; pumps blood from LV to the body
• Vena Cavas – biggest veins– Superior – returns blood from upper parts of
body to the heart– Inferior – returns blood from lower parts of
body
** Both join together to deliver the blood to the RA
Other Arteries and Veins
• Coronary – heart
• Pulmonary – lungs
• Carotid – Brain
• Subclavian – shoulder/ arm region
• Mesenteric – intestine
• Renal – kidneys
• Iliac - legs
Valves
• Prevent backflow of blood
• Close automatically
• Valves between chambers
• Valves at exits to hearts
• Types of Valves– Mitral valve – prevents
blood from going back into the atrium (also called bicuspid)
– Aortic Valve – prevents blood from reentering the left ventricle
– Tricuspid Valve – separates the right atrium and right ventricle
2 Circulatory Circuits
1. Pulmonary
• Deoxygenated blood from body enters RA-RV then goes to the lungs by pulmonary artery – pulmonary capillaries and “picks up” oxygen by diffusion then returns back to the heart via pulmonary veins into LA so it can then go to the systematic circuit
• Gas exchange occurs – CO2 is released and O2 is picked up by blood
2. Systematic Circuit• Pumps oxygen rich blood from left
atrium/left ventricle out through aorta to all the capillaries in the organs and the tissues of the body
• The deoxygenated blood is then returned to the right side of the heart by veins entering the right atrium
General Flow to Remember
•Right atrium Right ventricle Lungs Left Atrium Left Ventricle Body Right Atrium
General flow with Valves
• Pulmonary veins – left atrium – mitral valve – left ventricle – aortic valve – aorta – arteries – cells of the body – vena cavas – right atrium – tricuspid valve – right ventricle – pulmonary artery – lung – pulmonary vein – left atrium
Cardiac Cycle
• Cardiac cycle is each heartbeat and is started by the pacemaker
• The pacemaker is on the backside of the RA and is made of special muscle tissue
• 2 phases1. systole phase – pd. Of contraction
upper number of blood pressure reading 2. diastole phase – pd. Of relaxation
lower number of blood pressureNormal Blood Pressure is from 100-130 for systolic and 70-
90 for diastolic, so a good reading is 120/80
Diseases of Circulatory System
• Cardiovascular disease - #1 killer in U.S.; caused by artherosclerosis – narrowing of the arteries. This is caused by lipids sticking to artery walls, then Ca sticks to it and it hardens into plaque.
• Heart attacks – artherosclerosis of coronary artery; blood to heart slows or stops; very often is fatal
• High blood pressure = hypertension and if its left untreated it leads to heart damage, stroke or kidney failure
Continued…
• Strokes – artherosclerosis of cerebral arteries; blood flow to brain is suddenly decreased
• Anemia – deficiency in hemoglobin caused by hemorrhaging, lack of iron or Vitamin B12 or by sickle cell anemia (faster than normal destruction of RBC’s)
• Leukemia – form of cancer in which WBC’s rapidly multiply taking over RBC’s causing anemia, death by hemorrhaging or infection
Continued…
• Hemophilia – one factors needed for blood clotting is missing thus person cannot stop bleeding
• Heart Murmur – caused by problem with heart valves causing irregular heart sounds
• Gangrene – death of cells/tissue caused by lack of circulation to the area
Fun Facts…
•8% of ones body weight is blood•Average adult has 5-6 liters of
blood•Your heart will beat
approximately 2.5 billion times in your lifetime
•Bp is highest in arteries and lowest in veins
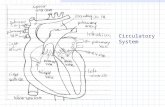
Lets label the heart1. Artery to body
2. Vein from body
3. Upper Vena Cava (from body)
4. Pulmonary artery (to lungs)
5. Pulmonary vein (from veins)
6. Tricuspid Valve
7. Right Atrium
8. Lower Vena Cava (from body)
9. Right ventricle
10. Septum
11.Left ventricle
12.Aortic Valve
13.Bicuspid Valve (mitral)
14.Left Atrium
15.Pulmonary vein (from lungs)
16.Pulmonary Artery (to lungs)
17.Aorta
18.Vein from body
19.Artery to body





























































![Circulatory System. Figure 24.01 Transports materials throughout body: Nutrients Metabolic wastes Gases (O 2 & CO 2 ) Hormones [regulate body processes]](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/56649f285503460f94c4148f/circulatory-system-figure-2401-transports-materials-throughout-body-nutrients.jpg)

