· Web viewStep 5: The ribosome continues to match the _____ in the mRNA with _____ in tRNA until...
Transcript of · Web viewStep 5: The ribosome continues to match the _____ in the mRNA with _____ in tRNA until...

8-5 Translation(In the ___________________)
The mRNA made during transcription is used to make a protein mRNA _________________
_____________________________ are coded by mRNA base sequences.
______________________________ converts mRNA messages into polypeptides. A ____________________is a sequence of _____________ nucleotides that codes for an amino acid.
ProteinsRemember that proteins, which are sometimes called polypeptides,are macromolecules made of monomers called amino acids.
During translation, ribosomes decode the ___________________message (made of nucleotides) to make polypeptide chains (made of amino acids).
Step 1: Two subunits of the ribosome attach to the ________________________.
Step 2: __________________________ read the mRNA ______________’ _____________. As each codon of the mRNA moves through the ribosome, the correct amino acid is brought to the ribosome by ______________________.
The Genetic CodeIn RNA, the nucleotides are read in “words” made of 3 nucleotide “letters”. Each “word” is called a ______________________ and contains the genetic code for one _____________________.
The first “word” or start codon is always the same for every protein. It is always _____________.
What amino acid is associated with the codon AUG? ____________________
There are a total of ________different amino acids that can be arranged in different ways to make different proteins.
Step 3

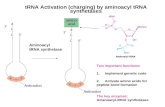
Each___________________ molecule has a group of __________________ nucleotides called the _______________________. These three nucleotides pair with the nucleotides in the codon. The tRNA molecule also has an ________________________ attached.
Step 4: _______________________ bonds form between amino acids to form the _______________________ chain in a process called elongation (it makes the polypeptide chain longer.)
Step 5: The ribosome continues to match the _____________________ in the mRNA with ________________ in tRNA until it reads a codon in the mRNA that says “stop.” A tRNA for “stop” does not carry an amino acid. No peptide bond will form, so the ribosome releases the mRNA and the protein.
Step 6: The newly formed polypeptide will start to coil and bend, forming the 3-D shape of proteins (recall the 4 levels of protein structure)
Why are proteins important?
Each protein has a specific function within living cells. Some functions of proteins are:acting as enzymes, to speed up and regulate chemical reactions. making pigments determining your blood type. regulating cell growth and development.