Structure and Replication of DNA. OBJECTIVES Identify components of DNA, and describe how...
-
Upload
russell-norton -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Structure and Replication of DNA. OBJECTIVES Identify components of DNA, and describe how...

Structure and Replication of
DNA

OBJECTIVES
Identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA (TEKS 6A)
• Summarize the relationship between genes and DNA
• Relate DNA molecule to chromosome structure
• Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule
• Summarize the events of DNA replication
• Learn how to extract your own DNA

MAJOR DISCOVERIES FOR DNA
GriffithGenetic information could be transferred from one bacterium to another
Avery
Nucleic acid DNA stores and transmits genetic information from one generation to the next
Hershey-Chase
Genetic material was DNA, not protein
Chargaff
A=T G =C
Franklin, Watson, & Crick
DNA’s shape is a double helix

OBJECTIVES
Identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA (TEKS 6A)
• Summarize the relationship between genes and DNA
• Relate DNA molecule to chromosome structure
• Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule
• Summarize the events of DNA replication
• Learn how to extract your own DNA

MACROMOLECULES-POLYMERIZATION
Macromolecules are formed by a process known as polymerization in which large compounds are built by joining smaller ones together.
The smaller units, or monomers, join together to form polymers.
~”Mono” = one~”Poly” = many
Monomers may be identical ~like the links on a metal watch band
Monomers may be different~like the beads in a multicolored necklace

TYPES OF MACROMOLECULES
Four groups of organic compounds (macromolecules) found in living things are:
~carbohydrates~lipids~nucleic acids~proteins
Sometimes these organic compounds are referred to as biomolecules

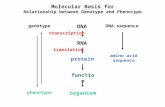
NUCLEIC ACIDS (GENETICS!!)
Nucleic acids are macromolecules/polymers containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus.
Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic, information
There are two kinds of nucleic acids: -ribonucleic acid (RNA)-deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).

NUCLEIC ACIDS-STRUCTURE
The monomers or “building blocks” of nucleic acids are called nucleotides
Nucleotides consist of three parts:-5-carbon sugar
-phosphate group
-nitrogenous base

DNA/RNA-STRUCTURE
Four nitrogenous bases for DNANucleotide
RNA has Uracil instead of Thymine
DNA = Deoxyribonucleic AcidRNA = Ribonucleic Acid

DNA/RNA STRUCTURE• A always pairs with T
(or U if RNA)• G always pairs with
C
• Connected by a hydrogen bond
RNA Structure


OBJECTIVES
Identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in the DNA (TEKS 6A)
• Summarize the relationship between genes and DNA
• Relate DNA molecule to chromosome structure
• Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule
• Summarize the events of DNA replication
• Learn how to extract your own DNA

DNA REPLICATION
EduSmart video – see pages 295-299