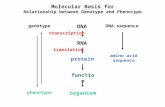
DNA sequencing: Importance The DNA sequences making up any organism comprise the basic blueprint for...
-
Upload
nigel-jonathan-melton -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of DNA sequencing: Importance The DNA sequences making up any organism comprise the basic blueprint for...

DNA sequencing: Importance
• The DNA sequences making up any organism comprise the basic blueprint for that organism

• Potential benefits• Molecular medicine
Improved diagnosis of disease – Disease gene identification will lead to more accurate diagnosis Earlier detection of genetic predispositions to disease – Will be able to assess risk for certain diseases, e.g. cancer, Type
II diabetes, heart disease Rational drug design – Drugs designed to target specific gene products that cause
disease Gene therapy and control systems for drugs – Replacement of defective genes for certain diseases Pharmacogenomics "custom drugs”– Drug therapy based on ones genotype…
The Human Genome Project (and others)

• Potential benefits– Bioarchaeology, anthropology, evolution, and
human migration • Study evolution through germline mutations in
lineages. • Study migration of different population groups
based on female genetic inheritance.• Study mutations on the Y chromosome to trace
lineage and migration of males. • Compare breakpoints in the evolution of mutations
with ages of populations and historical events.
The Human Genome Project (and others)

• Potential benefitsDNA forensics (identification) • Identify potential suspects whose DNA may match evidence
left at crime scenes. • Exonerate persons wrongly accused of crimes. • Identify crime and catastrophe victims. • Establish paternity and other family relationships. • Identify endangered and protected species as an aid to wildlife
officials (could be used for prosecuting poachers). • Detect bacteria and other organisms that may pollute air,
water, soil, and food.• Determine pedigree for seed or livestock breeds.
The Human Genome Project (and others)

• Potential benefitsAgriculture, livestock breeding, and
bioprocessing • Disease-, insect-, and drought-resistant crops.
• Healthier, more productive, disease-resistant farm animals.
• More nutritious produce .
• Biopesticides.
• Edible vaccines incorporated into food products
• New environmental cleanup uses for plants like tobacco.
The Human Genome Project (and others)

DNA sequencing methodologies: ca. 1977
• Maxam-Gilbert – base modification by
general and specific chemicals.
– depurination or depyrimidination.
– single-strand excision.
– not amenable to automation
• Sanger– DNA replication.
– substitution of substrate with chain-terminator chemical.
– more efficient
– automation??

Maxam-Gilbert ‘chemical’ method

versus “synthesis-based” methods
• Fred Sanger: Nobel Prize 1980• Instead of taking a complete sequence and
breaking it down, build DNA sequences up and analyze steps along the way
• They key to this process: dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs)

What to label for visualization?
• Primers?
• Disadvantages of primer-labels:
– four reactions
– tedious
– limited to certain regions, custom oligos or
– limited to cloned inserts behind ‘universal’ priming sites.
• Advantages: it works
• Solution:
– labeled “terminators” - ddNTPs

• ddNTPs are analagous to faulty LEGOs,
DNA Analysis: DNA Sequencing
Normal LEGOs have little pegs that allow them to stack
Faulty LEGOs lack the little pegs and nothing can stack on them – thus, they ‘terminate’ the stack









10_07_1_enzym.dideoxy.jpg

10_07_2_enzym.dideoxy.jpg

This is great but…
Wouldn’t it be great to run everything in one lane?Save space and time, more efficient
Fluorescently label the ddNTPs so that they each appear a different color

07_02.jpg

07_02_2.jpg

07_03.jpg

• http://www.dnai.org/b/index.html
DNA Analysis: DNA Sequencing

“virtual autorad” - real-time DNA sequence output from ABI 377
1. Trace files (dye signals) are analyzed and bases called to create chromatograms.
2. Chromatograms from opposite strands are reconciled with software to create double-stranded sequence data.





Alternatives to Dye Terminator Sequencing
• 454 Sequencing is a massively-parallel sequencing-by-synthesis (SBS) system
• capable of sequencing roughly 20 megabases (20,000,000 bp) of raw DNA sequence per 4.5-hour run
• Compare to best dye terminator sequencing rig today :ABI 3730xl
– (192 capillaries x ~1000 bp) in 5 hrs (2 2.5 hr runs) = 196,000 bp
• 454 sequencing relies on fixing nebulized and adapter-ligated DNA fragments to small DNA-capture beads in a water-in-oil emulsion.
• DNA is fixed to these beads is then amplified by PCR.
• Each DNA-bound bead is placed into a ~44 μm well on a PicoTiterPlate, a fiber optic chip. A mix of enzymes such as polymerase, ATP sulfurylase, and luciferase are also packed into the well.
• The four nucleotides (TAGC) are washed in series over the PicoTiterPlate.
• If a nucleotide complementary to the template strand flows into a well, the polymerase extends the existing DNA strand by adding nucleotide(s).
• Addition in a reaction that generates a light signal that is recorded by acamera in the instrument.

Pyrosequencing
Ronaghi M. Pyrosequencing sheds light on DNA sequencing. Genome Res 2001

Pyrosequencing - Solid Phase
Ronaghi M. Pyrosequencing sheds light on DNA sequencing. Genome Res 2001

Pyrogram
Ronaghi M. Pyrosequencing sheds light on DNA sequencing. Genome Res 2001

454 LifeSciences Sequencer

454 LifeSciences Sequencer
• Advantages– Fast, accurate– Great for small, simple genomes,
• Disadvantages– Reads only ~100 – 200 bp
– Crappy for large complex genomes (like ours)
– Homopolymer stretches (8+) are difficult to read

Alternatives to Dye Terminator Sequencing
• Others:– Microarray sequencing – aka sequencing by
hybridization

Alternatives to Dye Terminator Sequencing
• Others:– Nanopore sequencing