Module: Blood &Lymphatic system Anat.Lect...reticular fibers which are arranged perpendicular to the...
Transcript of Module: Blood &Lymphatic system Anat.Lect...reticular fibers which are arranged perpendicular to the...

Module: Blood &Lymphatic
system
Anat.Lect.4
Dr. Mohamed FathiAss. Prof. Of Anatomy & human embryology
BMS department

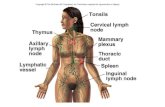
The lymphatic system
Definition: It is the system which returns the
lymph to the blood stream.
The lymph: is a clear colorless fluid which is
formed at the tissue spaces.
• It is composed of:
1-Blood plasma.
2- Proteins.
3- Lymphocytes.

The lymphatic system is composed of
A – Lymphatic tissues.
B – Lymphatic vessels.

A- Lymphatic tissue
• Is a type of connective tissue that contains
large numbers of lymphocytes.
• It is classified into:
• a- Lymphatic aggregations.
• b- Lymph nodes.

Lymphatic aggregations
• It is found in the following organs or structures:
• 1) Thymus.
• 2) Spleen.
• 3) Lymphatic nodules in close relation to epithelium of the alimentary canal e.g., tonsils, appendix, Peyer’s patches of the ileum.

Thymus gland• It is a bilobed organ
retrosternal in positionin the superiormediastinum.
• Large early in life(and involutes nearthe age of puberty.
• Secrete thymocinehormone whichpromote productionand maturation of T-Lymphocytes

• The thymus is formed of stroma and parenchyma.
A- Stroma of the Thymus:
1- Capsule: irregular collagenous connective tissue.
2- Trabeculae: delicate septa arise from the capsule dividing the lobes into incomplete lobules.

B- Parenchyma of theThymus:1-cortex 2-MedullaThe cortex of the Thymus• It is the site of maturation
of T lymphocytes.• Contains:1) Epithelial reticularcells (ERC)2) T-lymphoblasts3) T-lymphocytes4) Macrophages

The Medulla of the Thymus:
• -It is the central pale areaof the thymic lobule. ItContains:
• 1) Epithelial reticular cells(Types IV, V, VI). Theyappear larger and palerthan those of cortex.
• 2) Mature T-lymphocytes.
• 3) Hassal’s Corpuscles.
M
C

Hassal’s Corpuscle
• It is an acidophilic structure in themedulla of the thymus.
• It is formed of concentric layers ofepithelial reticular cells (type VI)around a central hyalineacidophilic mass.
• It is formed as a result ofdegeneration and calcification ofERC.
• They increase in number with age.
• Unknown function.

Blood-Thymus Barrier
• Exists in the cortex making it an immunologically protected region.
Formed of:
• 1. Endothelium of thymic capillaries (continuous type).
• 2. Complete thick basal lamina.
• 3. Perivascular C.T. and macrophages.
• 4. Basal lamina of ERC.
• 5. Complete layer of ERC.
Function: Protects the immature T cells from antigens in the blood.

Blood supply of the thymus
• Arteries enter the thymus through the
capsule to the trabeculae.
• At the corticomedullary junction the
arterioles leave the trabeculae to form
capillary beds that penetrate the cortex in
anastomosing archades to reach the medulla
to drain in small venules in the medulla.
• The thymus has No afferent lymphatics.

Lymph nodes
• These are localised bean like collections of lymphoid tissue which interrupt the course of the lymphatics ( act as a filter). They are present singly or in groups in specific locations in the body.
Functions:
• 1. Production of antibodies by the lymphocytes.
• 2. They pick up bacteria and antigens (by their phagocytic cells) preventing them from reaching the blood i.e., they act as filters.

Structures of lymph nodes
• The lymph node consists of stromaand parenchyma.
A- Stroma of the lymph node:
• 1. Capsule: dense irregular C.T.
• 2. Trabeculae: septa arising fromthe deep surface of the capsuledividing the node into incompletecompartments.
• 3. Reticular C.T: a network ofreticular cells and fibers whichsupport the parenchyma.
B- Parenchyma of the lymph node:
• Formed of: 1. Cortex 2. Paracortex3. Medulla
capsule
cortex
medulla
Ly.
follicles


1. Cortex: includes:
• a) Lymphoid nodules.
• b) Cortical lymphatic sinuses.

• Lymphoid nodules (Follicles):They are formed ofaggregation of lymphocytes.
Types of lymph nodules:1. Primary lymphatic nodules:
are present under the capsuleand appear oval, rounded orpyramidal. They arehomogenous in density andare formed of B lymphocytes.
2. Secondary lymphatic nodules:They have a dark periphery and apale central region called thegerminal center. Germinal centercontains: Activated Blymphocytes, T helper cells,macrophages, follicular dendriticcells and few plasma cells.

• Lymph Sinuses of the lymph node:
• They are spaces filled with lymph beneath the capsule and surrounding the lymphatic nodules and trabeculae.
• They are lined by discontinuous endothelial cells and partly by reticular cells and macrophages.
• They include:
a. Subcapsular sinus (between capsule and cortical nodule)
b. Cortical sinus (surrounds the cortical nodules)

2. Paracortical Zone (inner cortex):
• It is composed mainly of T lymphocytes and so known asthe Thymus-dependent area of the lymph node.
• It has many high endothelial post-capillary venules withlow cubical cells.
• It is the site where lymphocytes leave the blood to enterthe lymph node.
• B lymphocytes go to the outer cortex whereas Tlymphocytes remain in the paracortex.
• The paracortical zone contains: T lymphocytes, Blymphocytes, macrophages, antigen presenting cells,follicular dendritic cells and plasma cells.

3. Medulla:
• It is formed of medullary cords and medullary sinuses:
a. Medullary cords:
• -They branch and anastomose and are separated by medullary sinuses.
• -They are formed of lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages.
b. Medullary sinuses:
• -They are irregular spaces between the medullary cords.
• -They are lined by endothelial cells supported by reticular cells and fibers.

Site: In the left hypochondrium
Dimensions:Thickness= 1 inch
Breadth = 3 inches
Length = 5 inches
Weight: 7 ounces (150 gm)

Description: it has:
- 2 ends:
Posterior (medial) end: it is tapering
-2 surfaces:
Inner visceral surface which
contains the hilum
Anterior (lateral) end: it is broad
Outer diaphragmatic surface

RELATIONS OF THE SPLEEN
DIAPHRAGMATIC
SURFACE IS RELATED TO
DIAPHRAGM, LEFT
PLEURA AND LUNG, RIBS
FROM 9TH TO 11TH

Visceral surface:
It is related to the following organs:
A- fundus of stomach: at an area above the hilum
B- left kidney: at an area below the hilum
C- tail of pancreas: at an area just anterior to the hilum
D- left colic flexure: at an area near to the anterior end of the spleen

Blood supply:1- arterial blood supply: - From Splenic artery (branch of coeliac trunk)
- It is tortuous artery which runs along the upper border of the pancreas and in
leinorenal ligament
- It gives 5-6 terminal branches to the spleen
-These branches are end arteries, so infarction of the spleen is common
-2- venous drainage:by Splenic vein which passes behind the body of pancreas and joins the superior
mesenteric vein behind the neck of pancreas to form portal vein

Peritoneum of the spleen:Spleen is completely covered by peritoneum
It has the following peritoneal ligaments:
1- leinorenal ligament: extends between the hilum of the spleen and the left kidney
It contains Splenic artery and tail of pancreas
2- gastrosplenic ligament: it extends from the hilum to fundus of stomach
It contains the left gastroepiploic artery and short gastric arteries
Support of the spleen:- The main supporting factor of the spleen is phrenico-colic ligament which extends
from the diaphragm to the left colic flexure
- Other factors include intra-abdominal pressure, neighboring structures and
peritoneal ligaments

Structure of the spleen
• -The spleen is the largest lymphoid organ in
the body.
• -The spleen is formed of stroma and
parenchyma.

A. Stroma of the spleen
1. Capsule: formed of C.T. fibers,fibroblasts, and smooth muscle fibers. Itis covered by peritoneum.
The capsule is thickened at the region ofthe hilum where arteries and nervefibers enter and veins and lymphaticvessels leave the spleen.
2. Trabeculae: arise from the capsuleand are similar in structure to thecapsule. They divide the spleen intoirregular compartments.
3. Reticular C.T: formed of reticularfibers and reticular cells.

• B. Parenchyma of the spleen
• 1. The white pulp
• 2. The red pulp

• The white pulp: consists of Periarterial
lymphatic sheath and lymphoid nodules
(which are usually secondary with germinal
centers).

a) Periarterial lymphatic sheath (PALS):
• It is the lymphoid tissue immediately surrounding the central arteriole.
• It is formed of T lymphocytes, hence it is termed the Thymus dependent zone.
b) Lymph nodules:
• Rounded lymphoid tissue along the course of the PALS.
• Each nodule is traversed by the central arteriole (follicular artery) which occupies an eccentric position.
• The nodule is formed of B lymphocytes, macrophages and follicular dendritic cells.

• The red bulb consists of Formed of splenicsinusoids and splenic cords.
a) Splenic sinusoids:
• - They have wide lumena.
• - They are surrounded by discontinuousbasement membrane and are supported byreticular fibers which are arrangedperpendicular to the longitudinal axis ofthe sinusoids.
• - They are lined by fusiform endothelialcells which are separated by wide spaces(resembling staves of a barrel).
• - The slit-like spaces between theendothelial cells permit extensive exchangeof fluids, and passage of cells between thesinusoids and cords.
• - Macrophages are associated with the wallof the sinusoids.

b) Splenic cords (Cords of Billroth):
• It is the tissue between the white pulp and the blood sinusoids.
• They are formed of a network of reticular cells and fibers and they are filled with:
1. All elements of blood (RBCs, WBCs and platelets)
2. Macrophages
3. Plasma cells
4. Dendritic cells
5. Lymphocytes

• The Marginal Zone
• It represents the border betweenthe white and red pulps.
• It is composed of B lymphocytes,
• many macrophages, plasma cells
• and dendritic cells.
• It contains numerous wide blood
• sinuses called marginal sinuses.
• It is the first site of contact betweenthe blood and the splenicparenchyma.
• Circulating T and B lymphocytesleave the blood to enter to the whitepulp

Comparison between the structure of LN and spleen

Development of spleen
Time: 5th week
Origin: from the mesodermal cells of the left layer of thedorsal mesogastrium. The cells proliferate formingseparate nodules which fuse later forming a lobulatedspleen. Lobulation is evidenced by the presence of notcheson the upper border of the mature spleen.
*After development of the spleen, the dorsalmesogastrium becomes differentiated into:
a. Part cranial to the spleen: gastro-phrenic lig.
b. Part ventral to the spleen:[between it & the stomach] :gastro-splenic lig.
c. Part dorsal to the spleen:[between it & the left.Kidney]:lieno-renal lig.
d. Part caudal to the spleen :greater omentum.
Anomalies:
• 1. Persistent fetal lobulation. 2. Accessory splenicnodules.

THE PALATINE TONSILS• A large lymphoid mass situated in
lateral wall of oropharynx.
• - Represents the lateral part ofWaldeyer’s ring that encirclesthe entry of the digestive system& respiratory system.
• - This ring is formed bypharyngeal tonsils superiorly,palatine & tubal tonsils laterally& lingual tonsils inferiorly.
• Site: Tonsillar fossa (sinus)between palatoglossal &palatopharyngeal arches.
• Shape: oval or almond shape. Ithas 2 borders, 2poles, 2 surfaces.

• The borders:-
1) Anterior border: related to palatoglossal arch.
2) Posterior border: related to palatopharyngeal arch. The poles:-
1) Upper pole: related to soft palate.
2) Lower pole: related to the tongue

The surfaces:-
1) Medial surface: free surface contains12-15 crypts to trap bacterial debris.(The largest crypt is called intratonsillarcleft).
2) Lateral surface: has outer fibrouscapsule derived from pharyngeobasilarfascia. Capsule is loose at thepharyngeal muscular wall but firmlyattached to the side of tongue to keepthe tonsil in place during deglutition.
• - Capsule rests on tonsillar bedwhich is formed of:
• i - Pharyrngeobasilar fascia.
• ii - Superior constrictor pierced bytonsillar artery.
• iii - Styloglossus & 9th cranial nerve.

Blood Supply
* I) Arterial supply:-
• 1- The main source: tonsillarbranch of facial artery.
• 2- Additional sources:
• - Ascending palatine of facial artery.
• - Ascending pharyngeal artery, a branch of EC.
• -Tonsillar branch of greater palatine artery.
• - Dorsal lingual artery.
*Venous drainage: accompanythe arteries to end in paratonsillarvein, pharyngeal vein or facialvein.
*Lymphatic drainage:jugulodigasrtic L.N.
*Nerve supply: glossopharyngeal& lesser palatine nerves.
* Function: trapping the foreignmaterials & bacteria by theircrypts then initiate the formationof antibodies against them

B-Lymphatic vessels
Organ
Lymph drain by
Lymphatic capillaries
units Small lymphatic
vessels
Large lymphatic
vessels
Lymph drains into the blood
stream
N.B:1-The lymphatic vessels drain lymphfrom the organ called Afferentlymphatic vessels.
2-The lymphatic vessels drain lymphinto blood called Efferent lymphaticvessels.
3-the lymph of the right side reachblood through right lymphatic duct.4-the lymph of the left side reachblood through thoracic duct.

Sites without lymphatics
• 1-The central nervous system( brain and spinal cord).
• 2- Bone marrow.
• 3- Spleen.
• 4- Avascular structures (epidermis, articular cartilages).

Sites rich with lymphatics
• 1-Dermis.
• 2- Mucous membranes.
• 3- Serous membranes.
• 4- Glands.