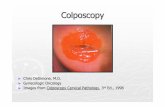
Colposcopy of cevicovaginitis
-
Upload
aboubakr-mohamed-elnashar -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
249 -
download
0
Transcript of Colposcopy of cevicovaginitis
The colposcope is basically low power stereoscopic
microscope with a focal length between 20 & 30 cm &
magnification between 6 & 40
Colposcopy mainly evaluates the changes in:
•Terminal vascular network of the cervix &
•Surface epithelium after application of acetic acid.
2 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
The most common indications of colposcopy
are evaluating patients with
1. Abnormal cytology.
2. Clinically suspicious cervix
It locates the site of the lesion.
It confirms or rule out invasive cancer.
3 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
Recent recommendations of FIGO for management of abnormal smear( Benedet,2000)
Persistent inflam., persistent ASCUS, LSIL, HSIL, AGCUS,Invasive
Colposcopy±biopsy
Normal or LSIL HGSIL Invasive
6 mo smear x 2 LEEP Appropriate TT
Normal Persistent
Annual screening
4 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
Cervicovaginitis is the most common gynecological
disorder, affecting half of women some time during
adult life.
Cervicitis represents a problem of considerable
complexity, because
1. Inflammation is not always of primary origin in the
cervix
2. It is often associated with other cervical
pathological states e.g. lacerations, erosion or
ectropion.
5 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
3. Cervicitis, erosion, ectropion are terms which are
used without any real attempts at accurate
diagnosis.
Thanks to Colposcopy, now, we can diagnose the
different cervical changes very accurately
6 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
A. Primary inflammation (10%)
I. Vaginitis:
1. Red punctate:
T.V(50%), Candida (25%), B. V.(20%)
2. White punctate
Candida (95%), T.V (4%), B.V. (1%)
3. Focal
T.V (98%)
4. Mixed:
8 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
5. Rare:
Vesicular: HSV, febrile illness
Follicular: CT
Hypertrophic (Granular): secondary to focal vaginitis
Emphysematous: metabolic or toxic factors
Desquamating: viral
II. Erosion: Specific Non specific
III. Ulceration: specific Non specific
9 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
B. Secondary inflammation (20%)
1. Infected TTZ
2. Infected ectopy
3. Infected ATZ
4. Infected polyp
10 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
Colposcopy of Chlamydia trachomatis
Follicular (hypertrophic) cervicitis
Lymphoid follicles: creamy white, raised rounded
swellings
Not altered after application of actic acid or Shiller s
iodine
12 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
Colposcopy of HPV
1. Florid
2. Spiked
3. Flat: Subclinical HPV
4. Condylomatous cervicitisa
13 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
Colposcopy of HSV
seen only if the patient has vulval HSV & vulval pain
1. One or more vesicles: short duration (24-36 hr),
ulcers
2. Sometimes ulcers coalesce to form one large ulcer
with some appearance of invasive cancer
3. Increased surface vacularity
14 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
Colposcopy of TV
1. Red punctate vaginitis
2. Tiny non-staining areas
3. Focal vaginitis
4. Speckeled appearance
15 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
1. Colposcopy is useful in diagnosing some kinds of
infections on the first visit:
T. vaginalis HPV
2. There are many other cases in which we must
treat the acute inflammation first in order to perform
satisfactory colposcopy at a second opportunity
17 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
3. Areas of true erosion can be easily recognized, &
the visualization of the free connective tissue is a
very important diagnostic element
4. Colposcopy is very useful for determining the
origin of menopausal spotting in cases of atrophic
vaginitis.
18 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
5. Also, in cervicitis of pregnancy complicated by
cervical bleeding from little capillaries, colposcopy
establishes the nature of the spotting
6. Traumatic lesions (f. bodies or decubitus) can be
recognized.
19 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR
7. In chronic cervicitis
any abnormalities in vascular net distribution make a
biopsy mandatory.
8. In some cases of chronic cervicitis, the vascularity
& the proliferative tendency is so marked that it leads
to suspicion of cancer. Biopsy under colposcopic
direction is an accurate method of determining the
cervical pathology.
20 ABOUBAKR ELNASHAR