Biological Macromolecules – Polymers (The Importance of Carbon) Honors Biology Monkemeier.
-
Upload
lucinda-matthews -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
4
Transcript of Biological Macromolecules – Polymers (The Importance of Carbon) Honors Biology Monkemeier.

Biological Macromolecules – Biological Macromolecules – PolymersPolymers
(The Importance of Carbon)(The Importance of Carbon)
Honors BiologyHonors Biology
MonkemeierMonkemeier

CarbonCarbon
Carbon can bond with itself to form Carbon can bond with itself to form chains, branched chains and rings.chains, branched chains and rings.

Carbon SkeletonsCarbon Skeletons
When carbon bonds with itself to form the When carbon bonds with itself to form the chains, branched chains and rings, the chains, branched chains and rings, the structures are known as carbon skeletons.structures are known as carbon skeletons.
Carbon skeletons provide the “backbone” Carbon skeletons provide the “backbone” for biological molecules.for biological molecules.
Carbon skeletons are formed during Carbon skeletons are formed during photosynthesis.photosynthesis.

HydrocarbonsHydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are Hydrocarbons are molecules molecules composed of just composed of just carbon and carbon and hydrogen.hydrogen.
The carbon – The carbon – hydrogen bonds hydrogen bonds are HIGH in are HIGH in ENERGY.ENERGY.

Other Elements Important to Other Elements Important to Biology and Functional groups.Biology and Functional groups. Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen,
Phosphorus, Sulfur.Phosphorus, Sulfur. These elements are part of functional These elements are part of functional
groups. Functional groups are groups of groups. Functional groups are groups of atoms covalently bonded to each other atoms covalently bonded to each other and when attached to a “carbon and when attached to a “carbon skeleton” or molecule, the molecule skeleton” or molecule, the molecule gains their chemical and physical gains their chemical and physical properties.properties.

Functional GroupsFunctional Groups

Biological MoleculesBiological Molecules

Biological MacromoleculesBiological Macromolecules
Some molecules in biology are extremely Some molecules in biology are extremely large and are made by putting together large and are made by putting together smaller subunits.smaller subunits.
Biological Macromolecules are also known Biological Macromolecules are also known as POLYMERS. Poly = many and as POLYMERS. Poly = many and mer = pieces. mer = pieces.
Starch, Cellulose, DNA, Enzymes are all Starch, Cellulose, DNA, Enzymes are all examples of biological macromolecules examples of biological macromolecules a.k.a. polymers.a.k.a. polymers.

Building Biological Building Biological MacromoleculesMacromolecules
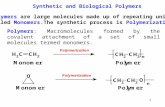
The chemical reaction that The chemical reaction that attaches the “mers” or attaches the “mers” or subunits together to form subunits together to form biological macromolecules is biological macromolecules is known as dehydration known as dehydration synthesis a.k.a. condensation.synthesis a.k.a. condensation.

Dehydration SynthesisDehydration Synthesis

Dehydration SynthesisDehydration Synthesis
How is water How is water involved?involved?
Why is it called Why is it called dehydration dehydration synthesis?synthesis?
Examine the Examine the diagram to see.diagram to see.

Hydrolysis a.k.a. Hydrolysis a.k.a. DecompositionDecomposition The chemical reaction that The chemical reaction that
breaks apart biological breaks apart biological macromolecules into their macromolecules into their subunits is known as subunits is known as hydrolysis or decomposition.hydrolysis or decomposition.

Hydrolysis a.k.a. Hydrolysis a.k.a. DecompositionDecomposition

Hydrolysis (Decomposition)Hydrolysis (Decomposition)
Why is it called Why is it called hydrolysis?hydrolysis?
Hydro refers to Hydro refers to water – why?water – why?
Lysis means split – Lysis means split – how does this how does this relate?relate?










![Surface induced self-organization of comb-like macromolecules · plex polymers [1-3]. Among these polymers are comb or brush copolymers, i.e., macromolecules which consist of a backbone](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/5f511c3b124f6372f46cee28/surface-induced-self-organization-of-comb-like-macromolecules-plex-polymers-1-3.jpg)






