Unit 3: Cells & Tissues - Badger Anatomy & Physiology€¦ · Unit 3: Cells ... II. Cellular...
Transcript of Unit 3: Cells & Tissues - Badger Anatomy & Physiology€¦ · Unit 3: Cells ... II. Cellular...
-
1
Unit3:Cells&TissuesChapter3CellsChapter4Tissues
1.Nucleus:> Controlcenter> Housesgeneticmaterial
*3distinctregionsofthenucleus:> Nuclearmembranecontrolswhat
enters&leavesnucleus> Chromatingeneticmaterial> Nucleolussynthesisofribosomes
I.AnatomyofaCell(3regions)
2.PlasmaMembrane:controlswhatenters&leavesthecellStructure:> 2Lipidlayers(phospholipids)&cholesterol
hydrophobic & hydrophyllic ends
> Proteins(receptors,channels,carriers,enzymes,anchors,identifiers) Createporesinwhichmaterialcanpassthroughfreely Carrier/transportproteins(bindingsites) Glycoproteins
Determinebloodtype
> Microvilli Helpsurfacearea Found on cells that function in absorption
3.Cytoplasm> Areabetweennucleus&plasmamembranewheremost
cellularactivitieshappens
-
2
-
3
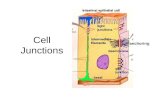
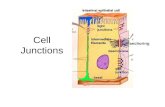
Connectionsbetweenadjacentcells...1.TightJunctions
Anatomy: Plasmamembranefusedtogetherlikea"zipper"
Function: Leakproof,preventssubstancesfrompassingthroughextra
cellularspace Found in small intestine - keep enzymes from "seeping" into our
bloodstream
II.CellularJunctions
2.Desmosomes Anatomy:
Adhesionjunctions(anchoring)connectedtogetherbyproteinfilaments
Function: Preventcellsfrombeingpulledapartwhensubjectedtostress Holds skin together
II.CellularJunctionscont'd
-
4
3.GapJunctions Anatomy:
Membranesheldtogetherwithhollowproteinfilaments
Function: Communicationbetweencells Nutrients&ionspassdirectlyfromcelltocell Found in Cardiac muscle tissue ------
II.CellularJunctionscont'd
III.Cytoplasm
> 3Majorelementsofthecytoplasm:
1.Cytosol:liquidportionsuspendsotherelements
2.Inclusions:chemicalsubstancesfoundincells Stored nutrients Pigments in skin
3.Organelles:metabolicmachineryofthecell
-
5
IV.CellTransport
> Solutionhomogenousmixtureof2ormorecomponents solute vs solvent (universal solvent = H2O)
> Intracellularfluidcytoplasm&nucleoplasm
> Interstitialfluidexterior(thousandsofingredients) aminoacids,vitamins,fattyacids,sugars
being dissolved doing the dissolving
V.MovementofSubstances:Passive or Active Transport
PassiveTransport:nocellularenergyisrequired,gowiththeconcentrationgradient
A.Diffusionprocessinwhichmoleculesmovefromanareaofhigherconcentrationtoanareaoflowerconcentration
*speed of diffusion depends on concentration, size, & temperature
> SimpleDiffusion Moleculesaresmallenoughtopassdirectlythroughporesin
membrane Moleculesarelipidsoluble
> Osmosisdiffusionofwater(aquaporins)
> FacilitatedDiffusion Moleculeistoolargetopassthroughpores Notlipidsoluble Transportprotein(specific)neededtobringitacrosscellmembrane
-O2, CO2, fatty acids, steroids
-glucose, amino acids, ions
-
6
-
7
B.Tonicity:compare[solute]of2solutions
> Hypertonic:
> Hypotonic:
> Isotonic
V.MovementofSubstancescont'd
-
8
Beaker Cell
Solute "A" Solute "A"
Solute "B" Solute "B"
Solute "A" = NaClSolute "B" = Glucose
Scenarios:1. What environment is the cell in?2. Explain osmosis.3. How would NaCl diffuse if it was impermeable?4. How would NaCl diffuse if it was permeable?5. How would Glucose diffuse if it was permeable?
-
Attachments
CellOrganelle&TransportQuiz2015162.docx
Anatomy & PhysiologyName/Hr:__________________________
Match the following functions with the corresponding organelle:
____1. Functions in ATP production (powerhouse)a. Golgi
____2. Assembles & packages materials to be secretedb. Lysosomes
____3. Uses digestive enzymes to break down materials in the cellc. Mitochondria
____4. Synthesize ribosomesd. Nucleolus
____5. Site of protein synthesise. Ribosomes
Multiple Choice:
6. Which of the following junctions allows cells to communicate by allowing nutrients and ions to pass from cell to cell?
a. gap junctionsb. Golgi junctionsc. desmosomes d. tight junctions
7. The plasma membrane consists primarily of
a. sugars and starchc. lipids and proteins
b. proteins and starchd. lipids and sugars
8. Microvilli
a. are responsible for protein synthesis
b. are found in cells that do not function in absorption
c. function in movement
d. help increase the surface area of the plasma membrane
9. Osmosis
a. does not require any cellular energyd. both a and b
b. moves water up the concentration gradiente. both a and c
c. is the diffusion of water
10. In the figure below, which of the following environments is the red blood cell in?
a. isotonicc. hypertonic
b. hypotonicd. at equilibrium
For questions 11 & 12, use the diagram to the right.
11. The solution outside the bag would be referred to as
a. hypotonicc. isotonic
b. hypertonicd. idontknowtonic
12. Which of the following statements below is NOT true?
a. The glucose will move into the bag
Beaker
10% NaCl
15% Glucose
Bag
5% NaCl
35% Glucose
b. Water will travel out of the bag
c. The NaCl will travel out of the bag
d. Water will travel into the bag
Organic Compound
Monomer(s)
XC: Unit 2 - List the 4 organic compounds we discussed in class. What are the building blocks/monomers for each compound?
SMART Notebook
Page 1Page 2Page 3Page 4Page 5Page 6Page 7Page 8Attachments Page 1