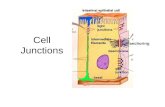
Cell Junctions. “serve to anchor cells to one another or to provide a passageway for cellular...
-
Upload
godwin-cole -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
2
Transcript of Cell Junctions. “serve to anchor cells to one another or to provide a passageway for cellular...

Cell Junctions

“serve to anchor cells to one another or to provide a passageway for cellular exchange.”
Three major types: Desmosomes Tight junctions Gap junctions
Cell Junctions


Desmosomes Hold two cells together Intermediate filaments (made of protein
keratin) Provide mechanical stability and strength Like rivets fastening cells into strong
sheets Tissues: skin, uterus, heart

Desmosomes

Tight Junctions Create impermeable seals around cells Example: digestive tract tube does not
allow enzymes from digestive tract to pass through bloodstream
Animal cells only Prevents leakage of molecules

Tight Junctions


Communication junctions “passageways between cells that allow
transfer of chemical or electrical signals” Two kinds:
plasmodesmata gap junctions

Gap Junctions Narrow tunnels made of protein connexins Prevents cytoplasm of each cell from
mixing Allows passage of ions/small molecules Tunnels-1.5 nm diameter Gap between cells- 2-3 nm Pattern of channel formation determines
permeability



Endocytosis (endo = inside, cyto = cell)
Capture of substances outside the cell when the plasma membrane merges to engulf it.
***There are three types of endocytosis1. phagocytosis2. pinocytosis3. receptor-mediated

Pinocytosis (pino = to drink, cyto = cell)
Pinocytosis occurs when dissolved materials enter a
cell. The plasma membrane folds inward to form a channel allowing the liquid to enter. The
plasma membrane closes off the channel, encircling the liquid inside a vesicle.
Oils enter cells through pinocytosis

Phagocytosis (phago = to eat, cyto = cell)
Phagocytosis occurs when undissolved solids enter a
cell. The plasma membrane wraps around
the solid material and engulfs it, forming a
vesicle. Phagocytic cells, such as white blood cells, attack and engulf bacteria
in the manner.

Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Occurs when specific molecules bind to specialized “receptors”
(proteins) in the plasma membrane. The membrane, the
receptors, and the specific molecules, called ligands, fold
inward forming vesicles. Hormones target special “target
cells” by receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Ligand
Receptor Protein
Molecule being ingested

Exocytosis (exo = outside, Cyto = cell)moving substances outside the cell
Process of vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing their content to the outside
of the cell.

Passive Transport No energy expended by the
cell Goes “downhill” with the
concentration gradient Substances move from [HI] [LOW] Examples: diffusion, osmosis,
facilitated diffusion

Diffusion
Solution = solute + solvent Solute- substance that is dissolved Solvent- substance that does the dissolving
(fluid) Solute particles dissolved in a solvent are
constantly in motion. Temperature motion
This constant motion causes DIFFUSION Diffusion- movement of particles from areas of
high concentration to areas of low concentration



Osmosis and Tonicity Hypertonic- the solution that has [solute]
Water flows toward the hypertonic environment
Hypotonic- the solution that has [solute]
Water flows away from a hypotonic environment
Isotonic- the solutions have equal concentrations of solute (no net osmosis)

Osmosis and Tonicity

Facilitated Diffusion
• Down gradient• No ATP used
Carrier – Mediated Transport

Carrier – Mediated Transport
Active Transport (Sodium-Potassium Pump)
• Needed because Na+ and K+ constantly leak through membrane
• One ATP utilized to exchange three Na+ pushed out for two K+ brought in to cell

Carrier – Mediated Transport
Secondary Active Transport
Sodium-Potassium Pump
CYTOPLASM
Glucosemolecule
Sodiumion
Na+–K+
pump
+
+
• Regulation of cell volume• Heat production • Maintenance of a membrane potential
• Secondary active transport (No ATP used)

Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels

Voltage-Gated Potassium Channel