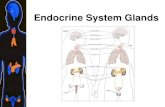
TOPIC : Regulation Aim : Explain the function the different endocrine glands.
-
Upload
blake-ramirez -
Category
Documents
-
view
20 -
download
0
description
Transcript of TOPIC : Regulation Aim : Explain the function the different endocrine glands.
TOPIC: RegulationAim: Explain the function the different
endocrine glands.
Do Now: Ditto – Human Nervous System Mapping Review
HW: Ditto – Did you Know?
X
A B C
1.Which cells are target cells for hormone A? Explain why.
2.Which cells are target cells for hormone B? Explain why.
14-year old Khagendra Thapa Magar shown in the picture with another boy is only 50 centimetres (20 inches) tall and has been submitted to the Guinness world record as the world's smallest person. The previous world record holder was a Jordanian boy at 25.5 inches tall. Weighing only 4.5 kilograms, he is shown in exhibitions to collect fund for his education.
This X-ray shows how an enlarged right lobe of the thyroid has moved the trachea to the patient's left. The trachea (outlined in light yellow) should be straight from the mouth down to the lungs, but in this patient it is compressed and displaced far to the left.
Temperature goes above set
value
Thermostat turns heat off
Temperature falls below set temperature
Thermostat turns on heat
Thermostat
(cells absorb some glucose and liver converts glucose to glycogen)
and more glucagon
(liver converts glycogen to glucose)
Maintaining blood sugar level
Homeostasis: Maindex
Thyroxine LevelThyroxine level too
low
Pituitary gland secretes TSH
TSH stimulates thyroid to produce thyroxin
Thyroxine level increases
Thyroxine level too high
Pituitary gland stops TSH production
Thyroid decreases thyroxine production
Thyroxine level decreases