Present Continuous Tense - Voortrekker Afstandsleer
Transcript of Present Continuous Tense - Voortrekker Afstandsleer

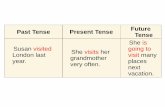
Present Continuous Tense

What is it?
Talk about an action that is still going on at a specific moment in the
present.

Time Words
at the moment, at present, now, while, still, right now, just now, currently, for the time being, this year, this term, etc.

What do we use?
be verb (is, am, are)
+
Verb+ing

Singular Form
1st 2nd 3rd
HE
I YOU SHE
IT
He
I am standing You are standing She is standing
It

Plural Form
1st 2nd 3rd
WE YOU THEY
We are standing You are standing They are standing

NEGATIVES
He is doing well.
to
He is not doing well

QUESTIONS
He is doing well.
to
Is he doing well?

QUESTION TAGS
REMEMBER: When the statement is positive your tag must be negative. When your statement is negative your tag must be
positive.
e.g. I am doing well, aren’t I? He is not doing well, is he?
A tag is there to confirm something. The speaker wants to make sure something is
correct.

REMEMBER:
•Verbs ending in -ie change to -ying lie = lying die = dying •Most verbs ending in -e lose the -e when -ing is added chase = chasing drive = driving BUT see = seeing dye = dyeing

Active and Passive •Find the verb •Who/What does it? = subject •To who/what is it done? = object •Change subject and object around •-ing becomes being •Use 3rd column verb •Therefore; be verb + being + 3rd column verb e.g. Jean is packing the backpack. (active) The backpack is being packed by Jean. (passive)

Reported Speech
•Present tense introductory verbs: says, asks, tells, wants to know, commands, enquires, recommends, etc.
•Past tense introductory verbs: said, asked, told, wanted to know, commanded, enquired, recommended, etc.

IMPORTANT
•NEVER change the introductory verb.
•If introductory verb is present tense: nouns; pronouns change all the rest stay the same.
•If introductory verb is past tense: nouns; pronouns change all the rest take one step back.

What is meant by “all the rest take one step back”?
Verbs go to the past tense.
is – was will go – would go
was – had been must go – had to go
are – were may go – might go
were – had been doesn’t go – didn’t go
see – saw don’t go – didn’t go
saw – had seen didn’t go – hadn’t gone
can go – could go
needn’t go – didn’t have to go

What is meant by “all the rest take one step back”?
Time words go one step back. •today – that day •tomorrow – the following day/the next day •yesterday – the day before/the previous day •the day before yesterday – two days before/two day ago/two days earlier •Last week – the week before/the previous week •next week – the following week •now – then •ago – before
OTHER CHANGES •here – there •this – that •these - those

GOLDEN RULES
•Find the introductory verb. •Decide on the tense it is in: present or past. •If the introductory verb is in present tense only change the nouns and pronouns, all the rest stay the same. •If the introductory verb is in the past tense change the nouns and pronouns, all the rest take one step back. •DO NOT chance the introductory verb. •Replace the inverted commas with that.

From direct to indirect:
DIRECT: Stephan says, “Tanya is working at the pet shop since last week.” (present) Stephen said, “Tanya is working at the pet shop since last week.” (past) INDIRECT: Stephen says that Tanya/she is working at the pet shop since last week. (present) Stephan said that Tanya/she was working at the pet shop since the previous week/the week before. (past)