Pneumothorax
-
Upload
yassin-alsaleh -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
597 -
download
2
Transcript of Pneumothorax

Pneumothorax In the NeonateAlsaleh Y. M

objectives
• Introduction
• X-ray finding
• Case study
• Examples
• conclusion

Introduction• Pneumothorax refers to the presence of air in the
pleural cavity between the visceral and parietal pleura
• Pneumothorax represents the most commonly occurring air leak.
• it occurs spontaneously in 1 to 2 percent of term neonates without pulmonary disease.
• The rate of occurrence increases in ventilated neonates, where it ranges from 20 to 30 percent.
• Various mechanisms have been thought to be responsible for producing air leaks
• Pneumothorax is generally a clinical diagnosis that is confirmed with plain radiography and or Transillumination of the chest .

X-Ray Findings
• 1. Increased lucency on the affected side.
• 2. Decreased or absent pulmonary vascular markings.
• 3. Overall increase in the size of the affected hemithorax.
• 4. Widened intercostal spaces.
• 5. Flattened diaphragm on the affected side.
• 6. Sharp edge sign. The cardiac border and the diaphragm are seen in sharp contrast.

• 7. With tension pneumothorax, mediastinal shift with deviation of the trachea and heart to the opposite side.
• Decreased volume and increased opacity of the opposite lung.
• 8. With bilateral pneumothoraces, narrow cardiac silhouette.
X-Ray Findings cont.

CASE STUDY• A 27-week gestation, 1,000 gm female
born to a 19-year-old, Primi unbooked. The mother came to the emergency room complaining of increasingly severe abdominal cramping over the past six hours. On physical examination, labor were suspected, and the neonate delivered precipitously before any further testing could be done. Emergency room personnel provided 100 percent oxygen and bag and mask ventilation, called for pediatrician, patient intubated then transfered to NICU.

• Penetration
• Rotation
• Soft tissue
• Bony framework
• Trachea
• Hilum and heart
• Diaphragm
• Pleura
• Lung fields

impression
• A right tension pneumothorax is present.
• The shadow of the atelectatic right lung is visible.
• The heart and the mediastinum are shifted to the left.
• Decompression of the right chest is required.


EXAMPLES

The right lung has collapsed, and the mediastinum hasshifted to the left.

Right tension pneumothorax.

Left nontension pneumothorax with aircollecting anteromedially and laterally.

The tip of ETT is in the right bronchus


large right tension pneumothorax

Right tension pneumothorax

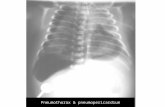
bilateral pneumothoraces


Left pnumothorax


Conclusion
• Always review all old films to properly assess the new one. Subtle findings can easily be missed when a single previous examination is reviewed.
• Obtaining a lateral x-ray can help to define the site and extent of the pneumothorax.
• High index of suspicion is necessary for diagnosis of pnuemothorax.

Thank you for your attention
انها رب يا األطفال ضحكة وصناعشبا الرمل موحش في غردت إذا

















![Carbon dioxide pneumothorax following retroperitoneal ... · tumor. Pneumothorax is a recognized complication of laparoscopic surgery [3, 4]. Although the incidence of pneumothorax](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/609aa5997fa83a720d634fe1/carbon-dioxide-pneumothorax-following-retroperitoneal-tumor-pneumothorax-is.jpg)
