Ovarian borderline tumors
description
Transcript of Ovarian borderline tumors
Serous ovarian borderline tumorsa clinicopathologic review
Ovarian borderline tumorsNadeem R. Abu-Rustum, MDMemorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
Key PointsSerous LMPMucinous LMP
Favorable outcomeFertility consequences
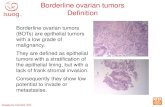
Borderline tumorsSynonyms:Tumor of borderline malignancyBorderline tumor (BT)Tumor of low malignant potential (LMP)Atypical proliferative tumorBorderline tumorsBorderline: Neither clinically benign nor malignantRecurrence can occur, but death is uncommon
Borderline tumorsBorderline: Neither clinically benign nor malignantRecurrence is common, but death is uncommon Borderline: Neither morphologically benign nor malignantArchitectural complexity without malignant cytologic features & NO invasionBorderline tumorsSerous BTs and seromucinous BTs are both pathologically borderline and clinically borderline.
Borderline tumorsSerous BTs and seromucinous BTs are both histopathologically borderline and clinically borderline.
Gastrointestinal mucinous, endometrioid & transitional BTs are only pathologically borderlineThey are clinically BENIGN.Serous LMP
Serous LMP
Serous LMP
Serous LMP
Serous Carcinoma: PathogenesisFimbria?
Dysplasia
High Grade Serous CarcinomaBRCA-1mutationTP53 mutationFamilialSporadicTP53 mutationSerous Epithelium
Borderline tumor (BT)
Micropapillary BT
Low Grade Serous CarcinomaKRASBRAFCourtesy: Rob Soslow, MSKCCCystadenoma15This is an overview of serous carcinogenesis. As you can see, in familial cases, BRCA-1 mutations give rise to dysplastic inclusion cysts. Full fledged carcinomas arise after the acquisition of p53 mutations. Sporadic high grade cancers arise by a similar mechanism, but BRCA-1 mutation per se is not seen. Notice now that the low grade carcinomas do not feature in the familial arm of this illustration. They are thought to arise almost exclusively in the sporadic setting. BRAF or KRAS mutations lead to development of serous borderline tumors, which become proliferative (ie micropapillary) and then invasive. The molecular alterations leading to proliferation in a borderline tumor and then invasion are not well understood.Low grade serous carcinoma: pathogenesis
16These illustrations depict stepwise changes in serous borderline tumor leading to a sporadic, invasive low grade serous carcinoma.Ovarian LMP Tumors10-15% of epithelial tumorsMedian age in mid-40s50% of serous tumors & 90% of mucinous tumors are unilateral60% of serous tumors & 90% of mucinous tumors are stage IFertility-sparing surgery possible in majority of young patients10-yr. survival ~90% for both tumor types17Risk factors for recurrence of ovarian serous borderline tumorsAge Elevated preoperative CA-125Micropapillary histologyInvasive implantsResidual peritoneal disease
Shih KK, et al. (MSKCC) Gynecol Oncol 2011Evaluation of peritoneum & omentum much more important than lymph nodesSerous Borderline Tumors:10-20 year Follow-upSerous BT70% Stage I30% > Stage I90-95% Non-Inv5-10% Inv56% No Rec44% Recur83% Inv**17% Non-Inv**75% of patients diedSilva EG, et al. Am J Surg Pathol 2006;30:1367-1371Serous Carcinoma: PathogenesisFimbria?
Dysplasia
High Grade Serous CarcinomaBRCA-1mutationTP53 mutationFamilialSporadicTP53 mutationSerous Epithelium
Borderline tumor (BT)
Micropapillary BT
Low Grade Serous CarcinomaKRASBRAFCourtesy: Rob Soslow, MSKCCCystadenoma20This is an overview of serous carcinogenesis. As you can see, in familial cases, BRCA-1 mutations give rise to dysplastic inclusion cysts. Full fledged carcinomas arise after the acquisition of p53 mutations. Sporadic high grade cancers arise by a similar mechanism, but BRCA-1 mutation per se is not seen. Notice now that the low grade carcinomas do not feature in the familial arm of this illustration. They are thought to arise almost exclusively in the sporadic setting. BRAF or KRAS mutations lead to development of serous borderline tumors, which become proliferative (ie micropapillary) and then invasive. The molecular alterations leading to proliferation in a borderline tumor and then invasion are not well understood.
Serous LMP
Bilaterality common in Serous = Loss of Fertility
Significance ofMicropapillary (MP) ArchitectureAssociated with invasive implantsMore aggressive because of invasive implantsRecur more frequently
More bilateral (70% vs. 20%)More involve surface (60% vs. 30%)
Implant TerminologyOvarian borderline tumor + peritoneal disease = borderline tumor with implants
Ovarian carcinoma + peritoneal disease = metastatic ovarian carcinomaImplant TerminologyOvarian borderline tumor + noninvasive peritoneal disease = borderline tumor with noninvasive implants
Ovarian borderline tumor + invasive peritoneal disease = low grade serous carcinoma
Significance of Implant TypeNon-invasive implant 10 year survival:95%
Invasive implant 10 year survival:33-50%
Stage III low-grade serous ca 10 yr survival:25-50%No invasion AND no diffuse high-grade cytologic atypia or micropapillary architecture: non-invasive epithelial implant
Fat or muscle invasion: invasive implant
YesYesNoNoYesNoImplant AssessmentCourtesy of Rob Soslow, MSKCCImpact of ImplantsSerous LMPRecurrence non-InvasiveRecurrence InvasiveDeath non-InvasiveDeath Invasive18%36%6%25%Evaluation of peritoneum & omentum much more important than lymph nodesLymph Nodes30% of stage III SBTs have involved LNsNO Prognostic implicationDifferential diagnosis:CarcinomaNodular aggregates > 1mmBenign Mullerian inclusions (endosalpingiosis)Mesothelial hyperplasia
McKenney JK, Balzer BL, Longacre TA. Am J Surg Pathol , 2006 Therapy of LMP & Low-Grade Serous CarcinomaSurgery is the main treatmentHormonal therapy (90% or SBT are ER+)Cytotoxic chemotherapy4% complete response to platinum and taxol*Targeted therapyMEK inhibitors for invasive implants/low grade serous carcinoma
*Schmeler KM, et al. Gynecol Oncol. 2008Serous Carcinoma: PathogenesisFimbria?
Dysplasia
High Grade Serous CarcinomaBRCA-1mutationTP53 mutationFamilialSporadicTP53 mutationSerous Epithelium
Borderline tumor (BT)
Micropapillary BT
Low Grade Serous CarcinomaKRASBRAFCourtesy: Rob Soslow, MSKCCCystadenoma37This is an overview of serous carcinogenesis. As you can see, in familial cases, BRCA-1 mutations give rise to dysplastic inclusion cysts. Full fledged carcinomas arise after the acquisition of p53 mutations. Sporadic high grade cancers arise by a similar mechanism, but BRCA-1 mutation per se is not seen. Notice now that the low grade carcinomas do not feature in the familial arm of this illustration. They are thought to arise almost exclusively in the sporadic setting. BRAF or KRAS mutations lead to development of serous borderline tumors, which become proliferative (ie micropapillary) and then invasive. The molecular alterations leading to proliferation in a borderline tumor and then invasion are not well understood.Well staged Ovary-confined SBT (with or without MP) = Benign
Unstaged SBT+MP = uncertain malignant potential
SBT with non-invasive implants = slow malignant potential
SBT with invasive implants = carcinoma
Behavior of Serous Borderline TumorsMucinous Borderline Ovarian TumorsEndocervical or seromucinous (15%)Gastrointestinal (85%)Metastasis from GI primaryMucinous Borderline: PathogenesisRule out GI Primary
Mucinous BT
SporadicCystadenoma
Gastrointestinal Mucinous BT
Endometriosis
Endocervical Mucinous BTSeromucinous BTKRASARID1A mutationIn 33%40This is an overview of serous carcinogenesis. As you can see, in familial cases, BRCA-1 mutations give rise to dysplastic inclusion cysts. Full fledged carcinomas arise after the acquisition of p53 mutations. Sporadic high grade cancers arise by a similar mechanism, but BRCA-1 mutation per se is not seen. Notice now that the low grade carcinomas do not feature in the familial arm of this illustration. They are thought to arise almost exclusively in the sporadic setting. BRAF or KRAS mutations lead to development of serous borderline tumors, which become proliferative (ie micropapillary) and then invasive. The molecular alterations leading to proliferation in a borderline tumor and then invasion are not well understood.Seromucinous Borderline Tumors(15% of Mucinous LMP)SynonymsEndocervical-type mucinous borderline tumorMixed epithelial borderline tumor
True borderline tumor, like serous borderline tumor
Seromucinous Borderline
Seromucinous Borderline
Seromucinous
Seromucinous Borderline TumorsSimilarities with serous borderline tumorAssessment of micropapillary architecture
Association with implants
Possibility of malignant behavior (very rare!)
Shappell HW, et al. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002 Seromucinous Borderline TumorsDifferences with serous borderline tumorAssociation with Precursor EndometriosisMalignant potential is lower
Seromucinous BT: Evidence Supporting Relation to Endometrioid NeoplasiaLack or paucity of WT1 stainingPresence of ARID1A mutation in approximately 1/3 of casesVang R, et al. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2006Wu DH, et al. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2012
(Gastro)intestinal mucinous borderline tumorGastrointestinal Mucinous Borderline TumorsProblems with accurate diagnosisLarge, unilateral, heterogeneous tumorsMany metastases to the ovary have a borderline appearanceLow-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasmsPancreatobiliary carcinomaEndocervical adenocarcinomaIntestinal-Type Mucinous Tumors:Features Favoring MetastasisBilateral diseaseSurface involvementDestructive stromal invasionNodular growth patternSignet ring cellsVascular invasion
Lee KR, Young RH. Am J Surg Pathol. 2003
52Classic Mucinous Borderline Tumor
Mucinous BT
Mucinous borderline tumors very large technically limits ovarian preservation
Mucinous BT
Mucinous Borderline TumorsMucinous intestinal type virtually always limited to ovary & behaves benignData on endocervical seromucinous type are limited, but benign behavior commonMucinous PMP almost invariably derived from GI tract, usually appendix
57Algorithm for distinguishing primary vs. metastatic mucinous carcinoma(and borderline tumors)Bilateral mucinous carcinomas = metastaticUnilateral mucinous ca & 12 cm = primary ovarian Yemelyanova AV, et al. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008 Metastatic carcinoma may look benign or borderlinePseudomyxoma-associated tumors are notoriousMetastatic pancreatobiliary carcinomas frequently mimic the appearance of primary ovarian tumors
Meriden Z, et al. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011 Feb;35(2):276-88.
Metastatic mucinous carcinoma may look benign or borderlineBilateral in 90% of casesNodularity in 63% and surface involvement in 40% Infiltrative growth pattern in 80%, accompanied by borderline-like and/or cystadenomatous areas in 50% Meriden Z, et al. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011 Feb;35(2):276-88.
Borderline tumors at frozen-sectionWhen and why do you perform staging operations?Detect extra ovarian SURFACE diseaseSerous and seromucinous BT
Concern that the diagnosis will be upgraded to carcinoma on permanent sectionsMicropapillary serous
Ovarian cancer: distinct disease entities: Genotypep53PIK3CAKRAS/BRAFHigh-Grade Serous+++ +-Low-Grade Serous- - ++Endometrioid- +++ Clear cell-+++-Mucinous-- KRAS+++ SummarySerous BT Prognosis depends on surgery, stage, implant type, and micropapillary architecture
Tumors with NON-invasive implants may recur as invasive implants/low-grade serous carcinoma
Tumors with invasive implants are similar to low-grade serous carcinoma
SummaryLow-grade serous carcinomas are clinically, biologically and morphologically distinct from High-Grade serous carcinoma
Many LG serous ca might represent progression from SBT and SBT with micropapillary features
They rarely progress to a high-grade neoplasm
For mucinous ovarian neoplasms always rule out a metastasis from other GI primary
Thank You
AcknowledgementRobert Soslow, MD