Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
-
Upload
huong-diem-nguyen -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
0
Transcript of Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
1/43
Fundamentals of Organization
Structure
Fundamentals of Organization
Structure
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
2/43
Think of some words that might describe
Structure
and some words that might describeCulture
Define Structure - The way in which people work together ?
Define Culture - The way in which people work together ?
So what is the difference ?
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
3/43
Structure Vs Culture
Structure Culture
Firm Soft
Clear Intangible
Distribution of
Authority that helps
define how people
work together
Norms and Values
that help define
how people work
together
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
4/43
Organization Structure
Three key components
Vertical aspect of organizing
- Formal Reporting Relationships including the number oflevels and the span of control.
- Grouping of Individuals into departments and ofdepartments into the total organization
Horizontal aspect of organizing
- Design of Systems to ensure effective communication,coordination and integration of efforts
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
5/43
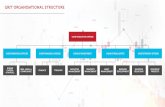
A Sample Organization Chart
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
6/43
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
7/43
Formal Organisational Structures
Grouping of activities
Responsibilities of individuals
Reporting relationships
Levels of authority
Span of control - (Flatter Structures)
Systems of communication
Degree of delegation of authority
But also
Underlying activities and processes
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
8/43
Information-Processing Perspective
on Structure
Provide Vertical and horizontal information flow
Traditional organization vs. Learning organization
- Traditional organization design emphasizes vertical
communication and control.
- Learning organization which emphasizes communication andcollaboration
Centralized vs. Decentralized decision making
- Centralized authority focused on top level decision-making
- Decentralized authority focused on shared tasks anddecisions
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
9/43
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
10/43
Efficiency versus
Learning Outcomes
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
11/43
Effect of Structure on People
- (R. Stewart - The reality of management)
People modify the working of the formalorganisation, but their behaviour is also
influenced by it. The method of workorganisation can determine how people relateto one another, which may affect both theirproductivity and morale. Managers, therefore,
need to be conscious of the ways in whichmethods of work organisation, may influencepeoples attitude and action.
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
12/43
Vertical Information Sharing
Vertical linkages coordinate activities between the top and
the bottom of the organization
Hierarchical referralare the vertical lines which identify
the chain of command
Rules and Plans- Rules enabling employees to be coordinated
- Plans provides standing information for employees.
Vertical information systems is a strategy for increasing
vertical information capacity. It includes reports,
computer-based communication and written
information
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
13/43
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
14/43
Horizontal Information Linkages
Horizontal linkage refers to the amount of communication
and coordinate activities across organizational departments.
Information Systems enable information exchange
throughout the organization
Direct Contactis a higher level of horizontal linkage (i.e.
liaison role)
Task Forces is a temporary committee composed of
representative from each department involved.
Full-Time Integratorresponsible for coordination.
Teams is the strongest horizontal linkage.
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
15/43
Ladder of Mechanisms for
Horizontal Linkages
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
16/43
OrganizationDesign Alternatives
Three keys indicators of organization design Required work activities
Reporting relationships
Departmental grouping options
- Functional grouping
- Divisional grouping
- Multi-focused grouping
- Horizontal grouping
- Virtual network grouping
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
17/43
Departmental Grouping Options
Functional
Grouping
Divisional
Grouping
Multifocused
Grouping
HorizontalGrouping
Virtual NetworkGrouping
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
18/43
Functional Structure
Allows economies of scales
within functional
departments
Enables in-depth knowledgeand skill development
Enables organizations to
accomplish functional goals
Is best with only one or a
few products
Slow response time to
environmental changes
May cause decisions to pile
on top, hierarchy overload Leads to poor horizontal
coordination
Results in less
innovation
Involves restricted
view of goals
Strengths Weaknesses
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
19/43
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
20/43
Divisional Structure
Suited to fast change inunstable environment
Leads to customersatisfaction
Involves high coordination Allows units to adapt to
differences Best in large organizations
with several products Decentralizes decision
making
Eliminates economies of
scale in functional
departments
Leads to poor coordination Eliminates in-depth
competence and technical
specialization
Makes integration and
standardization across
product lines difficult
Strengths Weaknesses
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
21/43
Functional vs. Divisional Structure -Example
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
22/43
Geographic Structure
Organizing to meet needs of users/customers by geography
It is particular common in large nonprofit organizations
Many multinational corporations are organized by country
Focuses managers and employees on specific geographic
regions
Strengths and weaknesses similar to divisional organization
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
23/43
Sample Geographic Structure
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
24/43
Matrix Structure
Conditions for Matrix:
- Condition 1: Share resources across the organization
- Condition 2: Two or more critical outputs required:
products and technical knowledge
- Condition 3: Environment is complex and uncertain
Two variations of matrix structure
-functional matrix
- product matrix
A dual-authority structure can help to ensure a
balance between vertical and horizontal aspects oforganizations.
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
25/43
Matrix Structure
Achieves coordination tomeet dual demands
Flexible sharing of humanresources across products
Suited to complex decisionsand unstable environment
Promote functional andproduct skill development
Best in medium-sizedorganizations with multipleproducts
Dual authority causeconfusion
Need good interpersonalskills and extensive training
Time consuming
Need commonunderstanding amongparticipants
Requires great effort tomaintain power balance
Strengths Weaknesses
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
26/43
Sample Matrix Organization
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
27/43
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
28/43
Matrix structure of ULYSSES
http://ec.europa.eu/research/transport/projects/items/ulysses_en.htm
To ensure the optimal use of the results beyond the participants, the partnership is an
open structure allowing other partners to join the meetings/activities depending on the
interests represented by new projects.
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
29/43
Horizontal Structure
Organization around core processes.
Key characteristics:
- Structure is created around cross-functional processes- Self-directed teams are the basis of organization design
and performance
- Process owners are responsible for entire process- People on the team are given authority for decisions
- Can increase organizations flexibility
- Customers drive the horizontal corporation.
- The culture promotes openness, trust and
collaboration.
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
30/43
Horizontal Structure
Promote flexibility and rapid
response to changes
Focus on the production
and delivery of value
Each employee has a
broader view of
organization goals
Promotes a focus on
teamwork and collaboration Improves quality of life for
employees
Determining core processes
is difficult and time
consuming
Requires many changes
Traditional managers may
baulk when they have to
give up power and authority
Requires significant training
of employees Can limit in-depth skill
development
Strengths Weaknesses
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
31/43
Sample Horizontal Structure
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
32/43
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
33/43
Virtual Networks and Outsourcing
It extends the concept of horizontal coordination andcollaboration beyond the boundaries of the organization
Most common strategy is outsourcing
- Contract out certain tasks/functions
Virtual or modular structures subcontract most of its majorfunctions to separate companies
The virtual network organization serves as a central hub withcontracted experts
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
34/43
Virtual Network Structure
Enables organizations to
obtain talent and resources
worldwide
Gives a company immediate
scale and reach without
huge investments
Enables the organization to
be highly flexible and
responsive to changingneeds
Reduces administrative cost
Managers do not have
hands-on control over many
activities and employees
Requires a great deal of
time to manage
relationships
Risk of organizational failure
Employee loyalty and
corporate culture might beweak
Strengths Weaknesses
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
35/43
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
36/43
Hybrid Structure
Organizations often use a hybrid structure that combines
characteristics of various structure approaches tailored to
specific needs
One common type is the combination of the functional and
divisional structures.
Often used in rapidly changing environments
Greater flexibility
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
37/43
Application of Structural Design
Each type of structure is applied in different situations and isintended to meet different needs.
Structural alignmentaligns structure with organizational goal
Symptoms of StructuralDeficiency:
Decision making is delayed or lacking quality
Organization does not respond innovatively to a changingenvironment
Employee performance declines, goals are not being meet
Too much conflict
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
38/43
Application of Structural Design
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
39/43
Summary and Interpretation
Structure must provide a framework, linking organization
into whole
Provide vertical and horizontal linkages
Variety of alternatives for grouping
Virtual network extends horizontal coordination
Matrix structure attempts to achieve balance between the
vertical and horizontal dimensions of structure.
Managers must find right balance
The purpose of the organization chart is to encourage and
direct activities
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
40/43
AQUARIUS Advertising Agency
Analyze Aquarius with respect to the fivecontextual variables. How would you describethe environment, goals, culture, size, and
technology for Aquarius? Design a new organization structure that takes
into consideration the contextual variables inthe case and the information flows.
Would a matrix structure be feasible forAquarius? Why or why not?
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
41/43
The Learning Organisation
Collective
Policy Operations
Ideas ActionIndividual
Ideas, thoughts, plans Actions, doing, behaviour
Reproduced from J. Burgoynes article Feeding minds to grow the business People management 21 Sep. 1995
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
42/43
The Learning Organisation
Collective
Policy Operations
Ideas ActionIndividual
Ideas, thoughts, plans Actions, doing, behaviour
Reproduced from J. Burgoynes article Feeding minds to grow the business People management 21 Sep. 1995
Is it this way round ?
Ideas produce action which
eventually becomes
operations which thenbecomes policy which
generates ideas etc?
-
8/3/2019 Lecture 2 Organisational Structure Final
43/43
The Learning Organisation
Collective
Policy Operations
Ideas
ActionIndividual
Ideas, thoughts, plans Actions, doing, behaviour
Reproduced from J. Burgoynes article Feeding minds to grow the business People management 21 Sep. 1995
Or is it this way round ?
Ideas produce policy which
determines operations which
drive actions which generateideas etc.