Organisational Design: Aligning Your Organisational Structure with Business Goals
Apple Inc. Organisational Structure
-
Upload
shona-baroi -
Category
Documents
-
view
6.249 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Apple Inc. Organisational Structure
-
ANALYSIS OF ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR, STRUCTURE & EFFECTIVENESS: APPLE INC. (GROUP 10)
[You can add an abstract or other key statement here. An abstract is
-
1
Contents
About Organization __________________________________________________________ 2
Organizational Culture at Apple ________________________________________________ 4
Organizational Structure ______________________________________________________ 6
Organizational Process ______________________________________________________ 13
Analysis as Q&A ___________________________________________________________ 19
Exhibits Only ______________________________________________________________ 20
Other Sources ______________________________________________________________ 23
-
2
ABOUT ORGANIZATION
Apple Inc. Formerly Apple computer Inc. is an American multinational corporation with
headquarters based out of Cupertino California. The company was founded on April 1st 1976.
And incorporated as apple computer Inc. on Jan 3rd 1977. The name was changed to Apple Inc.
on Jan 09, 2007. The same day Steve jobs introduced iPhone, reflected its shifted focus towards
consumer electronics.
Apple is worlds second largest information technology company by revenue and the worlds
third largest mobile phone maker. It has been awarded the most admired company by fortune
magazine in United States in 2008 and in the world from 2008 to 2012. On Sep 30, 2013 Apple
over took Coca-Cola to become the most valuable brand in the Omnicon groups best global
brands report. However the company has received criticism for its contractors labour practices
and for Apples own environmental and business practices.
History:
Initially it was established to sell Apple 1 personnel computer kit. A computer single-handedly
designed by Wozniak. During the first five years revenues doubled every four months with an
average growth rate of 700%. The Apple II also invented by Wozniak was introduced on April
1977. Apple II was chosen to be the desktop platform for Killer App. Of the business world,
VisiCalc, A spread sheet program. By the end of 1970s Apple had a staff of computer designers
and a production line. The company introduced Apple III in May 1980 in attempt to compete
with IBM and Microsoft. On December 12 1980, Apple went public at $22 per share generating
more capital than any IPO and instantly creating about three hundred millionaires than any
company in history. In 19982, Jobs took over Jef Ruskins low cost computer project which
was launched in 1984. It was a first personnel computer to be launched without any
programming language at all.
In 1985, a power struggle developed between Jobs and CEO John Sculley who had been hired
two years earlier. The Apple board of directors instructed Sculley to limit Jobs ability to launch
expensive forays into untested products. Rather than submit to Sculleys direction, Jobs
attempted to oust from him from his leadership role. Jobs after a conflict with Apples board of
directors sided with Sculley founded NeXT Inc., the same year.
-
3
The Macintosh portable was introduced in 1989 by Apple. After that Apple introduced power
book in 1991. The same year Apple introduced system7, which remained the architectural basis
for Mac OS until 2012. The magazine MacAddict named the period between 1989 and 1991 as
the first golden age of the Macintosh. In attempt to avoid competing with various consumer
outlets such as Walmart. Apple introduced many products leaving consumer confused during
this time Apple experimented with a number of other failed consumer targeted products making
consumers to not understand the difference between models. Apple relied on high profit
margins and never developed a clear response. Instead, they sued Microsoft for using GUI
similar to the Apple lisa The law suit was finally dismissed and at the same time a series of
major product flops and missed deadlines sullied Apples reputation, which made Sculley to be
replaced as CEO by Michael Spindler. In1996, Michael Spindler was replaced by Gil Amelio,
who chose to purchase NeXT and its NeXT STEP operating system bringing Steve Jobs back
to Apple as an adviser. Amelio was ousted by board of directors after three year record low
stock price and crippling financial losses in 1997. Jobs become interim CEO and begun
restructuring the companys product line. In the period from 1998 to 2005, Apple purchased
several companies to create a portfolio of professional and consumer oriented digital product
software. In 2003, Apples iTunes store was introduced and the service quickly became the
market leader in online music services. Between 2003 and 2006 the price of Apples stock
increased more than ten folds in January 2006, Apples market cap surpassed that of Dell. Apple
achieved widespread success with its iPhone, iPod touch and iPad products, which introduced
innovations in mobile phones portable music players and personnel computers respectively.
Delivering his key note speech at the Mac world expo on January 09, 2007 Jobs announced
that Apple computer Inc. would from that point on be known as Apple Inc. because computers
were no longer the main focus of the company, which shifted its emphasis to mobile electronic
devices. The following day Apple share prices hit $97.8 and all time high at that point. After
introducing iPad on January 27, 2010 and fourth generation iPhone Apple share hit an all-time
high in October 2010. On January 7, 2011 Jobs announced medical leave of absence to allow
him to focus on his health COO Tim Cook to assume Jobs day to day operations at Apple.
Apple become the most valuable consumer facing brand in the world. In June 2011, Steve Jobs
surprisingly took the stage and unveiled I Cloud, which was the last product launched Jobs
attended before his death. On Aug 24, 2011 Jobs resigned his position as CEO of Apple and
was replaced by Tim Cook. Jobs became Apples chairman prior to which Apple did not have
chairman and instead had two co-lead directors. Apple launched many products in 2012 and
2013 and also acquired many companies like Embark Inc. etc. A mid October 2013
-
4
announcement revealed that Angela Ahrendts will commence as senior vice president at Apple
in mid-2014.
Organizational Culture at Apple:
Apples culture has invaded the business world and had a powerful impact. As a supremely
successful company that has risen above strife to become a market leader, competitors look to
Apple for inspiration, adopting its practices to improve their own companies. Apples culture
is loosely structured around Steve Jobs personality, one of the Co-founders of Apple. Based on
this background let us look at how work culture at Apple evolved over the years.
Initial Years (1976-80):
Apple was established on April 1, 1976, by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak and Ronald Wayne in
Steve Jobs parents garage.
Apple was incorporated January 3, 1977, without Wayne, who sold his share of the company
back to Jobs and Wozniak for $800. Multi-millionaire Mike Markkula provided essential
business expertise and funding of $250,000 during the incorporation of Apple.
Since its inception Apple and its culture was heavily influenced by Steve Jobs personality. He
was extremely passionate and fearless when it came to growing Apple. Many actions in his
career were controversial and at certain points risked the future of the company. He passed this
passion and commitment to its products and customers to others employees of Apple. This
passion and commitment can still be seen in all the Apples employees to this day. Because of
this passion and commitment and Steve Wozniaks technological expertise, Apple grew at a
very fast rate. During first five years, revenues doubled every four months, an average growth
rate of 700%.
Lisa and Macintosh (1981-85):
As Apple grew, the Steve Jobs, then CEO felt need for someone with business expertise and
someone who can guide Apple to become one of the technological giants of the current century.
To bring about this change Jobs hired John Sculley, then CEO of Pepsi co. Initially everything
went well.
Apple started working on Lisa computers having best features. Steve Jobs wanted to introduce
Lisa as low cost product. But Sculley refused because of its high cost of production. This
-
5
difference of opinion led expulsion of Steve Jobs from the Lisa project. Jobs obsession to
produce low cost computer turned his attention to Macintosh, another product on which Apples
team was working on. This led to a division within the company. Different divisions within the
company started focusing on different objectives. One was Lisa group and the other was
Macintosh group. Since competitiveness was inculcated in employees personalities, this
competitiveness led to huge infighting between two groups for resources. This infighting
resulted in removal of Steve Jobs as the CEO of Apple.
Decline (1986-97):
After Steve Jobs, John Sculley took control of Apple. But his lack of expertise on the
developing industry, his short sightedness and risk averseness led to fall in sales and revenue
of the company. During this period Apple and its employees lost their vision and mission. John
Sculley failed to inspire the employees. The competitiveness and passion which defined Apple
was lost. Apple was not producing the kind of products for which it was admired and loved.
The profits declined. Even the series of changes in the top management failed to inspire
employees and there was decline in Apples reputation and profits.
Transition and Return to Profitability (1998-current):
After series of transitions, Steve Jobs returned to Apple. The time when Steve Jobs was away
from the company, he started working on different projects. Enriched from these experiences,
Jobs started bringing the culture back to Apple. The team where given complete freedom for
creativity and enough time to successfully execute the set targets. The employees where given
sense of purpose and the bigger picture and overall mission of the company were explained to
them. Employees where challenged to come up with new ideas. To motivate them, they were
awarded higher wages, the star performers and their families were given a chance to go on
yacht with Steve Jobs where new ideas about products where discussed and the best ideas were
brought to production. The sense of purpose and award for excellence motivated employees
which led to renaissance in the company and it became one of the most renowned companies
of this century.
Ethical behaviour of Apple Inc.
Apple bases its success on Creating innovative products and services and on demonstrating
integrity in every business interaction. The four main principles of Apple that contribute to
integrity are honesty, respect, confidentiality and compliance. As many of the Apples product
-
6
components are manufactured in countries with low labor costs, the potential for misconduct
if high due to differing labor standards and less direct oversight. Apple makes each of its
suppliers to sign its Supplier Code of Conduct and performs factory audits to ensure
compliance.
Though Apple has consistently won first place as the worlds Most Admired Company, it has
aced several ethical issues in recent years. The issue requiring product quality oversight
continuously. As Apples brand hinges upon product quality, so mistakes can create serious
ethical dilemmas. Another important issue was regarding privacy which is the major concern
for Apple. The most important issue for Apple is sustainability. As we see all the Apple products
are using green technology it is constantly trying to ensure environmental friendly usage for
the customers. Apple has many lawsuits regarding the intellectual property rights of the
company against other companies. As it is totally based on innovation, these issues would be
more common. It also frequently involved in the patents cases against other companies.
Hence we can see that Apple is more concerned about its ethical standards and is constantly
upgrading itself to comply with the standards it has set for its own operation.
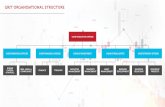
Organizational Structure
Apple has change in organizational structure and that is by time frame. In this report we try to
present what are the major changes has been done to the organizational structure of the apple
year wise. Here the main objective is try to find out the benefits and the disadvantages of the
structural changes happened with Apple Inc.
New Organizational Structure of Apple (2010-current)
Apple Inc. hired a new Vice President who will report directly to Tim Cook. Paul Deneve is
cited as having responsibility for special projects and will report directly to Tim Cook.
The organizational structure (in Exhibit 1) is CEO centric one and circular type. Where the
each and every functions of the company caters around the Chief Executive Officer role. The
left side of the structure suggests normal business function oriented departments where right
side of the structure is suggesting product oriented functions.
-
7
Advantages:
1. Responsiveness is very high.
2. Inter department decision making is possible.
3. CEO has influence to the decision making of departments functions.
4. Centrally controlled structure.
5. Reduction of the traditional hierarchy.
Disadvantages:
1. Too many department to handle for CEO.
2. Functions are not inter related mainly product oriented ones, so communication gap
between departments.
3. Transaction cost between departments.
Exhibit 1:
The main areas of Apples Management:
Marketing
The goal of this part of the firm is to identify the customers needs and preferences and to
market the products that satisfy their needs.
-
8
Design
Industrial Design is responsible for designing the all Apple products, including the Apple
Macintosh computer line.
Device Engineering
The main task of this department is to design Apples hardware as well as the Software. To do
customization, configuring according to latest trends and technology are the prime focus of the
organization.
Retail
The retail business of Apple I tunes and music stores are being marketed by this department.
Software Engineering
This department is responsible for designing the OS platform of the Apple Inc.
Changes in Organizational Structure:
In year 1977 Apple Inc. had traditional organizational structure that was created by Steven Jobs
and Stephen Wozniak. They hired first professional manager A.C. Markkula.
As the enterprise was growing and in 1983 the structure was look like as shown in Exhibit 2.
Exhibit 2:
-
9
Due to the Apple products were not competitive enough that became the reason to retire of
Markkula as the CEO (but still remained as a consultant) and hire on his post John Sculley
from PepsiCo.
In 1984 new President John Sculley simplified the organizational structure. The main change
was
1. To reduce the number of Apple product division to three. The three categories were
Macintosh, Apple II.
2. The job maintained the position of the chairman of the board of directors.
Exhibit 3:
-
10
In 1985 Sculley made change in organizational structure. The changes were:
1. The main cause was to change the three product category to one Product Operations.
2. The change should lower the operating cost of the products.
Changes consequences:
1. Steve Jobs was no longer a member, he resigned from Apple and Jean-Louis Gassee,
head of Apple France, was promoted to replace him.
2. Steve Jobs found company NeXT what will be bought by Apple later.
Exhibit 4:
The centralization concept:
-
11
1. To centralize operations and involve Apples senior management in day-to-day
decisions, Sculley created a new position of Chief Operation Officer
2. Yocam was appointed as Chief Operating Officer.
Exhibit 5:
Failure of the change in Organizational Structure:
1. Scully was forced out of his leadership position by Apple's board of directors in 1993
due to bad results.
2. Michael Spindler, broke tradition by licensing Apple technology to outside firms.
The Big Mistake:
Spindler made a horrible mistake in 1995, when Apple had unfilled order in worth of $1 billion
(underestimated demand). This was his last mistake, after that was replaced by Gil Amelio. But
Amelio was not the chairman for much time. In 1997 was replaced again by Steve Jobs. This
was because lately in 1996 Apple bought NeXT, Steve Jobs enterprise.
Apple Organic or Mechanistic structure
-
12
While mechanistic structures induce people in predictable, accountable ways with centralized
decision making organic structure encourage people to take initiatives and is found to be very
flexible. Apple cannot be clearly defined as purely organic or purely mechanistic. Industry
that apple operates is very dynamic and it had tried to keep its structure as organic as possible
and it was quite successful. Steve jobs created a flattened organizational structure which
focused on decentralization.
Mechanistic structure in Apple
Apple manufactures its Ipad and Ipod through foxconn industries,China. Apple outsource this
as they can focus on their core competency. Foxconn is found using performance appraisal
and organizational structure is pyramid style bureaucracy. Foxconn even landed up in
controversy for threatening employees using performance appraisal. So it can be noticed that
whatever functions that may require mechanistic structure have been outsourced.
Organizational structure
Apple follows a flat organizational structure and this encourages employees to contribute
effectively to company by taking part in the decision making process. With
Hardware,software and retail functions apple clearly follows a divisional structure.This
segregation was done based on the product the division is specialized in. So it can be said that
apple revolves around departments rather than people.
Advantaged this structure than offer could be
Stronger pursuit of internal organizational efficiency,motivated by the extra control
provided by the corporate office
Corporate can easily identify the division/department which is performing poorly or
which is earnng maximum returns on investment
Division would tend to adopt international best practices as the division is linked with
international counterparts.
Disadvantages this structure can offer
Huge Bureaucratic costs due to extensive duplication of activities within the
organization
Divisions competing eachother for human resources in external and internal labor
market
-
13
Transfer pricing issues determination of the same and coordination problems that
can emerge because of that
Employee Motivation:
Apples culture is greatly influenced by its founder Steve Jobs. He inculcated passion for the
products into his employees. The employees are given complete freedom to use their
imagination. They are given complete freedom in terms of product development to product
delivery. The employees are encouraged to work in cross functional teams. Micro-management
is discouraged. Opinions respected, ideas listened to, bug bears acted onto. To keep daily stock
of activities, regular meetings are arranged but none of the employees are forced to attend these
meetings. Because of the work environment and sense of purpose and chance to work on big
things, employees are ready to work for long hours even though they are forced to.
Secrecy:
Because Apple is a hardware company they knew that letting details out about new products
would kill sales of existing products, so they built culture of secrecy early on. Employees at
Apple aren't allowed to tell even their co-workers about what they are working on.Everything
is on a need to know basis reducing redundancy of data and as such limited confusions.
This extends even into meetings. If you are in a meeting and you aren't on the disclosure list
for something you'll be asked to leave. Generally people don't bring up stuff in meetings they
aren't allowed to discuss with the group. In labs, every project is kept under black cloths, just
in case someone gets into a section they weren't supposed to be in. Plus the labs are all sectioned
off and you have to sign into your part of the lab (and, of course, key cards only work if you
are supposed to have access to that lab).
Organizational Process
1. Product Design
The success of the Apples products predominantly depends on the design of the product and
application. In order to narrow down a specific design for a product of specific category or an
application, the company follows several methods to finalize it. They are as follows
i) 10 to 3 to 1
-
14
In this method, the designers are allowed to come up with up to 10 ideas, where the seven are
selected to make the other three look better compared to them. After this, the selected three
designs are taken to next level. The designers are allowed to work on them and the final strong
decision on design is arrived by boiling down the options from 3 to 1.
ii) Paired Design Meetings
This method like the above mentioned is a bottom to top approach process, where the flow of
ideas happen from the bottom level of the management such as employees to the top level of
management such as C-suite persons. There are two meetings held by the company every week.
One being the Idea Meeting and the other being the Production Meeting. The aim of the
former one is to help people come up with innovative ideas through brain storming whereas
the later one involves the designers and engineers to nail down the work to make the idea
finalized in the former meeting work.
iii) Pony Meetings
This process in contrast to the earlier mentioned methods involves top down management
involvement. In this session, the senior manager clearly states the problem definition in terms
of a required application or a product. During these meetings, the production engineers are
expected to chalk out a road map that shows the building up of the requirement and present it
to top management. Once these plans are approved by the people from C-suite, the plan is put
into action. This method has several advantages. Through this method, the workers at the
bottom will get hold of an idea of the vision that top management team trying to achieve. On
the other hand, the top management can have a check on designers work before approving
them.
2. Staffing
i) Recruitment
Throughout all these years right from beginning, Apple has maintained positive recruitment
policy. And, the company achieved these by offering internship, on-the-job training and career
opportunities. The company emphasized importance of computer knowledge in people in every
one of its recruitment drive. The company had several business groups within itself, which
have been given the privilege of recruiting people for specific domain. For instance, the
software developers group hired interns to work on OS X server, Technical publications,
Graphics and Imaging. Moreover, the company also recruited people based on feedback
-
15
collected from consumers. Apple always recruits its product marketing manager based on the
feedback collected from consumers. Very often Apple insists on task primacy and individual
responsibility. As a result, during its communication to employees, the company stresses on the
employees to take a better offer if it came along their way. Through this the company gives the
employees freedom to choose their career. On the other hand, Apple is unapologetic about the
layoffs it makes. From this, we can see that Apple believed in Employability security rather
than Employment security.
ii) Responsibilities:
Apple employees are required to perform different responsibilities from time to time like:
Overseeing multiple projects with strict timelines, allocating resources, driving business,
functional, financial, and reporting requirements. Cross-functional project schedules include
development on the iTunes Store, back-end financial systems, and other Apple groups.
Collaborate with IS&T, Treasury, legal, Tax, finance, operations and other organizations both
within and outside of Apple to develop solutions for partnerships and promotions and other
new business.
iii) Accountability:
An employee is accountable for any undertaking taken up by him. He is strictly under
observation of the governing bodies within the organization at all times. All the regulations and
guidelines of the organization and must be followed religiously and thereby operate within the
boundaries of professional ethics. Sharing complete knowledge of the overall activity as a part
of his job, a project manager must act as a guide to the concerned departments.
iv) Probationary Period:
Any candidate joining Apple has to sign a 12 month probationary period agreement which
includes training and performance management to determine the satisfactory work capabilities.
Apple monitors its new project manager`s performance closely since a large portion of
responsibility is rested on his shoulders. Unsatisfactory performance of the candidate may lead
to the termination of the job during the probationary period.
v) Compensation and material benefits
-
16
Post recruitment, various benefits are enjoyed by the employees of Apple. The benefits depend
on the location and employment status. The common benefits enjoyed include insurance
coverage, flexible spending account, and an employee stock purchase program and a 401K
investment and savings plan. Product discounts, on-site fitness centres, and opportunity to work
on big projects with some of the experienced players were added bonuses.
In 1995, Apple initiated the Apple Fellows program to reward an employee, who had made
extraordinary contributions to personal computing while at the program. Each Apple Fellow
acted as a leader and a visionary, guiding the company in the area of their expertise. Apple also
offered FlexBenefits program, where the employees can chose among the pool of benefits
offered according to their need.
In October 2008, Apple tried to setup a program called Apple University, with Mr. Joepodolny
as head in 2010. Through this program the company tried to replicate the successful concept of
Pixar University initiated by Steve Jobs.
vi) Recognition:
In the company, a group of 100 people are selected and labelled as Apple Elite. This group
comprised of talented members from various domain. The idea behind the group formation is
that the companys then CEO Steve Jobs organizes a meeting with these people and shares the
vision of Apple and communicates where the company was heading at that point of time.
Moreover, it was stated that only in these meetings, the draft of companys idea on every new
product is communicated.
Customer Satisfaction, Product/Services Concept
1. Customer Management and Satisfaction:
Walking past an Apple store on the eve of every new product launch, one undoubtedly notices
the line-up of devoted Apple fanatics impatiently waiting to get their hands on Apples newest
delivery. Apple has always been triumphant in cultivating a cult of Apple fanatics who have
repeatedly proved to be the most brand loyal consumers present in the market. Recent Bernstein
research study shows that an incredible 90% of iPhone users indicated an intention to purchase
another iPhone as their next phone, many as soon as the new iPhone comes out.
-
17
Although revolutionary product conceptualization, out-of-the-world design, and chic, clever
marketing are largely accredited for Apples incredible sales and marketplace dominance over
the last half a decade, its unique customer management system has also provided the foundation
of its aforementioned features to nurture. Apple has been consistently ranked at the top for
customer service in the personal computers category of the American Consumer Satisfaction
Index (ASCI), has consistently scored highest in Vocalabs phone support satisfaction surveys.
It also achieved the highest customer satisfaction scores in numerous Consumer Reports.
Apples customer management has depths beyond being just its obvious function as customer
support. It is more devoted to consistently deliver a customer experience that not only meets,
but even exceeds expectations.
Apples Customer Management can be explained from 5 different perspectives as follows:
i) Apple Stores, the Perfect Customer Experience:
Apple products are sold through Apples own chain of retail stores. Apple does not leave
primary customer interaction to random employees of big multiband stores who treat each
product indifferently or based on prejudice. Apple Stores are a microenvironment within them,
devoted and dedicated to provide primary customers an experience of a lifetime, presenting
every detail of Apple products in entirety, each time they visit an Apple Store.
ii) Provide customers with an environment to hang-out:
Along with being the most valuable brand in the world, Apple Stores are also the most
profitable marketplaces in the world. However a key fact that has been noticed here is that, the
majority of customers that enter an Apple store dont actually make any purchases. Instead,
teenagers, students, young professionals, and parents often visit Apple Stores to hang out and
play around with Apples cool new products. Apple too, rather than pressurizing their staff to
persuade the customers into sales, insists them to greet the customers by smiling and
encouraging the customers to experience the products. Over the years Apple has been
successful in turning shopping for computers and phones into an extremely enjoyable customer
experience and it has resulted in creating a brand image that competitors can only be envy of.
iii) Tight Quality Control, best strategy to minimize customer service problems:
-
18
For any company that aspires to be a market leader in customer satisfaction, customer service
has to form the heart of its business model. Its because no matter how good the technicians
are, how amicable the sales staff are and how efficient the outsourcing partners are, poor quality
products can never produce brand loyalty and customer retention. It is here that Apple has taken
quality control to a whole new level. Apple exercises tight control over every aspect of their
business model. Whether be it the impeccable veil of secrecy over its upcoming products or
their strict proprietary control over the iOS, Apple has never left any slack on their security
measures. This manifested in an unprecedented level of control over the user experience and
allowed them to stand a class apart from all competitors when it comes to the level of customer
satisfaction. In their App store, Apple checks and sends every piece of software through
stringent quality control tests before it can be installed onto an iOS device. Apples decision not
to allow flash support on their devices shows its level of quality control. Flash, required by
most video websites has the notoriety of random crashes, which was unacceptable for Apple.
iv) Customer Management, a Long Term Investment:
Although most companies take customer management as an expense and try their best to
minimize it, Apple welcomes it as a long term investment in fostering customer loyalty and
building brand image. Apple refused to move its North American phone support offshore,
despite the huge cost benefits associated with the move. Also Apple maintains a hassle-free
approach of replacing broken devices instead of repairing, as done by the competition. Studies
show that these decisions have consistently resulted in placing Apple at number one position
in customer service satisfaction. Apple believes that these decisions though seem costly in the
short term, produce much greater dividends in the long run and we all have seen that it has
been starkly correct.
iv) Pin-point Targeted Business Focus:
Although Apple is worlds richest technology company, it makes only a handful of products.
Such has been its reputation that almost every tech enthusiast, be it an Apple fanatic or not, can
recite every Apple product produced till now. Steve Jobs believed that the goal of customer
management is to be able to answer the question, What is our business? Jobs understood
that this question had to be asked from the customers perspective. Apple believes in delivering
more than just the physical form of its products, Apple delivers cool, elegant, reliable products
that stands out from the crowd, and thus makes the users stand out from the crowd. By taking
-
19
utmost care and diligence in catering this experience to customers, Apple has been able to build
an incomparable customer loyalty and user satisfaction.
2. Products/Services Concept:
Apple bases its marketplace advantage on two key Product/ Services Concepts which are:
"category-killer innovation" and its expertise in making complexity simple".
i) Apple Concept: Category-Killer Innovation
"Category-killer innovation" is when a company produces a product that fundamentally
changes both the rules of the game and the customer's value proposition in a product category.
It requires that Think different" attitude. Apple examples of "category-killer innovation"
include the iPod, iPhone, iPad and iCloud. Each one of these products have brought futuristic
technologies at the times when they were released. The iPod with its compactness and huge
memory and sound quality, the iPhone 1 with its fluid interface and the latest iPhone 5s with
its fingerprint sensor are some examples of this very fact. Unlike other companies who believe
in taking baby steps by just tweaking one product with minor changes to release a newer one,
Apple takes its time, and delivers complete innovative products.
ii) Apple Concept: Make Complexity Simple
A company make complexity simple" when it moves technology out of the way and
technology includes not just hardware and software but also obtuse jargon and confusing
terminology. In Steve Jobs words, "the best technology is invisible - things work like magic".
Apple achieves simplicity by focusing on the few most important concepts or features that add
the most value - rather than include every feature you can imagine. Apple never included
Bluetooth in its iPhones, nor did it allow music transfer without iTunes, still these have hardly
had any impact of customer acceptance. Simplicity is about clean, uncluttered design and the
iOS, both in its mobile and Mac versions represent the epitome of simplicity.
3) Apple Success
-
20
Reliance on these key fundamental uniqueness have differentiated Apple in the marketplace
and enabled it to establish a leadership position in mobile technology. All these culminated in
placing Apple at the helm of the most valuable companies in the world.
Analysis as Q&A
Why Apple to be considered as a learning organization in terms of Organizational
behavior?
1. The most important reason is Steve Jobss contribution towards Apples organizational
design change.
2. The employees are satisfied in working at Apple Inc. as mentioned by famous employee
opinion website Glassdoor.com.
3. Main motto of the organization is learning as collective activity not an individual one.
Supportive environment is always available.
4. The direction in which the organization is growing is to REFLECT, PLAN &
GENERATE.
5. If the above one achieve then INTEGRATE, INTERPRET & ACT.
Why Apple was forced to change its organizational structure?
1. To produce innovative product for long term reputation and making product that
customer wish for.
2. To survive with financial failure and make organizational structure strong.
3. Competitive market share increase with competing IBM and MICROSOFT.
4. To revise corporate strategy.
How Organizational change makes Apple Inc. successful?
1. Apple implements Peter. M. Senges fifth discipline to increase their sales
2. They involved in research and development with senior resources with several years.
3. Systems Thinking, Personal Mastery, Mental Models, Building Shared Vision, and
Team Learning have been implemented as core values of Apple Inc.
Exhibits Only: (Source cited)
Chronologically Apple:
-
21
The founding of Apple1976-1980
Apple I: The Byte Shop ordered fifty units for $500 per unit
Apple II: The first West Coast Computer Faire (April 1977)
Apple III: Compete against IBM and Microsoft (May 1980)
o The years of innovation 1981-1989
Lisa: First Personal Computer with a Graphical User Interface (GUI) (1983)
Machintosh: The first User-friendlyPC, using GUI with the metaphor of desktop
and Mouse. (1984)
Machintosh Portable: Compete against IBM and Microsoft (May 1980)
o Decline and resurrection 1990-1997
Microsoft rolled out Windows 3.0, Apple was in trouble.
April 10, 2012 [APPLES ORGANIZATIONAL LEARNING ]
Apple Guys | 5
o Steve Jobs turnaround 1997-2011
Jobs understood the rapidity of change in the computer industry and therefore change
the Apples leadership, alliance, licensing, market, and product range. Increase
innovation withG3 Power Mac, this systems could also be used as network servers
Buzusers G3 PowerBooks (1998) & iMac boom! This fact sent Apples stock to 52
weeks high!
(1998)
o Website renovation & Power Mac G4, 2000
The whole idea of being the best started to emerge in the website as well as the products.
o New iBook & iMovie, 2000
The new iBooks started to show that there is a major shift in designing products.
o Music revolution; iPod first generation, 2001
The revolution in the music industry happened by introducing this particular product.
o Director MX for Mac OS X, 2002
Continues improvement in the software industry and Apples simple, easy to use
software owned the market.
The new iPod (second generation) & iTunes, 2003
Another revolution in the music industry with introduction of iTunes, it was so
important that the music became the #3 navigation element in Apples website.
-
22
o Cellphone revolution; iPhone, 2007
Another evolution by Apple, this time in the cellphone industry, Apple has changed the
functionality of smartphones to something other couldnt compete at the time and still
struggling to keep up with it.
o Tablet revolution; iPad, 2010
Another revolution in the tablet industry, this time Apple had owned and ruled the tablet
business and sold enormous number of iPads worldwide.
April 10, 2012 [APPLES ORGANIZATIONAL LEARNING ]
Apple Guys | 6
Apples core business has been in a constant evolution and change since the day it
started as a personal computer company, Apple focused on the PC industry from 1976
till the late 90s which Jobs returned to Apple, in that time the internet was the biggest
hit in the computer industries and Apple just like the others was trying to get involved
in it as much as it could but in that time Apple was in a serious trouble.
Steve Jobs was fired mainly because he argue that Apple should be more of a software
company instead of PC and hardware but the board of directors were denying his
argument and finally they have fired him. However it became obvious in the 90s that
they were wrong and company was going to the drain, so they hired him back and this
time Jobs turn the company to the most valuable computer business of all times by
changing the companys core business from old PC making to current more exciting
products such as iPod and iTunes. Apple has been considered to be software, hardware
and consumer electronic company ever since. So todays Apple core businesses can be
categorized as below:
Personal Computer (iMac) and notebook (MacBook)
Consumer electronics (iPod, iPhone, iPad, Apple TV)
Online music market (iTunes store)
Mobile advertising market (iAd)
Digital video editing market (Final Cut Pro)
Software Production (Mac OS X, iOS, iLife, iWork)
Real Estate (323 apple stores by November 2010)
Source of the history: http://mile.mmu.edu.my/orion/nimafotovati/files/2012/05/
-
23
Other Sources:
Apples Financial Performance:
-
24
Chloe Albanesius, Apple Promises Free Bumpers, Cases for iPhone 4 Buyers, PC Mag, July
16, 2010, http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2366596,00.asp(accessed June 6, 2011).
Paul Andrews, Apple-Microsoft Lawsuit Fizzles To A Close -- `Nothing Left' To Fight
About, The Seattle Times, June 2,
1993, http://community.seattletimes.nwsource.com/archive/?date=19930602&slug=1704430
(accessed June 8, 2011).
Julia Angwin, Apple, Google Take Heat, The Wall Street Journal, May 11,
2011,http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703730804576315121174761088.html
(accessed June 6, 2011).
Apple and the Environment,
Apple, http://www.apple.com/environment/#recycling(accessed June 8, 2011).
Apple chronology, CNNMoney, January 6,
1998, http://money.cnn.com/1998/01/06/technology/apple_chrono/ (accessed June 6, 2011).
Apple, Cisco agree both can use iPhone name, Reuters, February 22,
2007,http://www.reuters.com/article/2007/02/22/us-apple-cisco-
idUSWEN460920070222 (accessed June 8, 2011).
Apple History, http://www.apple-history.com/ (accessed June 6, 2011).
-
25
Apple Inc., Business Conduct: The way we do business worldwide,
2010,http://files.shareholder.com/downloads/AAPL/1283312876x0x443008/5f38b1e6-2f9c-
4518-b691-13a29ac90501/business_conduct_policy.pdf (accessed June 7, 2011).
Apple Inc., Policy on Reporting Questionable Accounting or Auditing Matters, November 16,
2010, http://files.shareholder.com/downloads/AAPL/1281913948x0x443017/68a6df9d-b0ef-
4870-ba8e-accc695b39e2/reporting_accounting_auditing_matters.pdf (accessed June 6,
2011).
Apple, Inc., Apple Supplier Responsibility 2011 Progress Report, February 2011.
Apple Introduces iTunesWorlds Best and Easiest to Use Jukebox Software, Apple,
January 9, 2001, http://www.apple.com/pr/library/2001/jan/09itunes.html(accessed June 6,
2011).
Apple Recycling Program, Apple, http://www.apple.com/recycling/ (accessed June 8,
2011).
John Brownlee, What Its Like To Work At Apple, Cult of Mac, July 7,
2010,http://www.cultofmac.com/what-its-like-to-work-at-apple (accessed June 6, 2011).
Building the Digital Age, BBC
News, http://newsvote.bbc.co.uk/mpapps/pagetools/print/news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/709
1190.stm (accessed June 6, 2011).
Amanda Cantrell, Apples remarkable comeback Story, CNNMoney, March 29,
2006, http://money.cnn.com/2006/03/29/technology/apple_anniversary/?cnn=ye(accessed
June 6, 2011).
Alan Deutschman, The once and future Steve Jobs, Salon, October 11,
2000,http://www.salon.com/technology/books/2000/10/11/jobs_excerpt/ (accessed June 6,
2011).
The evangelists evangelist, Creating Customer
Evangelists, http://www.creatingcustomerevangelists.com/resources/evangelists/guy_kawasa
ki.asp(accessed June 6, 2011).
Facilities Report: 2010 Environmental
Update, http://images.apple.com/environment/reports/docs/Apple_Facilities_Report_2010.pd
f (accessed June 7, 2011).
Former Apple evangelist on companys history, CNET News, March 29,
2006,http://news.cnet.com/1606-2_3-6055676.html (accessed June 6, 2011).
Governance: Investor Relations, Apple, http://investor.apple.com/governance.cfm(accessed
June 6, 2011).
-
26
Rob Hassett, IMPACT OF APPLE VS. FRANKLIN DECISION,
1983,http://www.internetlegal.com/impactof.htm (accessed June 8, 2011).
Miguel Helft, Will Apples Culture Hurt the iPhone?, The New York Times, October 17,
2010, http://www.nytimes.com/2010/10/18/technology/18apple.html(accessed June 6, 2011).
Steve Jobs, A Greener Apple,
Apple, http://www.apple.com/hotnews/agreenerapple/ (accessed June 8, 2011).
Jobs at Apple, Apple, http://www.apple.com/jobs/us/benefits.html (accessed June 6, 2011).
Ashby Jones, So Whats Up With this Apple/Google Lawsuit? The Wall Street Journal,
March 30, 2010, http://blogs.wsj.com/law/2010/03/03/so-whats-up-with-this-applegoogle-
lawsuit/ (accessed June 8, 2011).
Yukari Iwatani Kane and Ethan Smith, Apple Readies iCloud Service, The Wall Street
Journal, June 1, 2011, B1.
Yukari Iwatani Kane and Ian Sherr, Apple: Samsung Copied Design, The Wall Street
Journal, April 19,
2011, http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703916004576271210109389154.htm
l (accessed June 6, 2011).
Dawn Kawamoto, Ben Heskett, and Mike Ricciuti, Microsoft to invest $150 million in
Apple, CNET, August 6, 1997, http://news.cnet.com/MS-to-invest-150-million-in-
Apple/2100-1001_3-202143.html (accessed June 8, 2011).
Mary Ellen Lloyd, Kodak Sues Apple, RIM Over Patents, The Wall Street Journal, January
14,
2010, http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748704281204575002891721364642.htm
l (accessed June 8, 2011).
Kieren McCarthy Apple threatens iTunes.co.uk owner, The Register, December 6,
2004, http://www.theregister.co.uk/2004/12/06/apple_itunescouk_domain_dispute/ (accessed
June 8, 2011).
Scott Martin, How Apple rewrote the rules of retailing, USA Today, May 19, 2011, 1B.
Nilofer Merchant, Apples Startup Culture, Bloomberg Businessweek, June 24,
2010, http://www.businessweek.com/innovate/content/jun2010/id20100610_525759.htm (acc
essed June 6, 2011).
Millward Brown Optimor, BrandZ Top 100
2011, http://www.millwardbrown.com/libraries/optimor_brandz_files/2011_brandz_top100_c
hart.sflb.ashx (accessed June 6, 2011).
Claire Milne, Nominet UK Dispute Resolution Service Decision of Independent Expert,
March 10, 2005, http://www.nominet.org.uk/digitalAssets/766_itunes.pdf(accessed June 8,
2011).
-
27
Overview of the Open Source Movement, The University of Texas at Austin Graduate
School of Library and Information Science,
2000,http://www.ischool.utexas.edu/~l38613dw/readings/OpenSourceOverview.html(accesse
d June 6, 2011).
Marguerite Reardon and Tom Krazit, Cisco sues Apple over use of iPhone trademark,
CNET News, January 10, 2007, http://news.cnet.com/Cisco-sues-Apple-over-use-of-iPhone-
trademark/2100-1047_3-6149285.html (accessed June 8, 2011).
Steven Russolillo, Kodak Obtains Favorable Ruling In Apple Patent Lawsuit, The Wall
Street Journal, May 13, 2011, http://online.wsj.com/article/BT-CO-20110513-
711367.html (accessed June 8, 2011).
Martyn Williams, Timeline: iTunes Store at 10 Billion, ComputerWorld, February 24,
2010, http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/9162018/Timeline_iTunes_Store_at_10_billio
n (accessed June 6, 2011).
Worlds Most Admired Companies: Apple,
CNNMoney, http://money.cnn.com/magazines/fortune/mostadmired/2011/snapshots/670.html
(accessed June 6, 2011).
Suzanne Vranica, Public Relations Learned the Hard Way, The Wall Street Journal,
December 29,
2010, http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204685004576046302759708050.htm
l (accessed June 6, 2011
http://www.forbes.com/sites/stevedenning/2012/06/25/apples-employees-have-a-hell-of-a-
ride/
http://blogs.fasthosts.co.uk/business-strategy-2/5-customer-management-strategies-that-set-
apple-apart/
http://www.bumpsforboomers.com/think-different-product-concepts-drive-apples-success