How is RNA Transcribed from DNA AP Biology Fall 2010.
-
Upload
paige-vaughan -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of How is RNA Transcribed from DNA AP Biology Fall 2010.

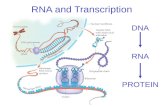
How is RNA Transcribed from DNA
AP BiologyFall 2010

It takes three classes of RNA to synthesize proteins ◦ Messenger RNA (mRNA)◦ Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)◦ Transfer RNA (tRNA)

Messenger RNA (mRNA)◦ Carries the “blueprint” to the ribosome
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)◦ Combines with proteins to form ribosomes upon
which polypeptides are assembled Transfer RNA (tRNA)
◦ Brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome and pairs up with an mRNA code for that amino acid

RNA differs from DNA◦ RNA uses ribose sugar,
not deoxyribose◦ RNA bases are A, G, C,
and U (uracil)

Transcription differs from DNA replication in three ways:1. Only one region of one DNA strand is used as a
template2. RNA polymerase is used instead of DNA
polymerase3. The result of transcription is a single-stranded
RNA


Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter region (a base sequence at the start of a gene)
Then moves along to the end of a gene ◦ Copies from 3 prime to 5 prime end of DNA
molecule◦ Builds from 5 prime to 3 prime end of RNA
molecule After free ribonucleotides are
complementary bonded to the template, an RNA transcript is created


Transcription ends when RNA polymerase reaches “the end” signal
RNA transcript is then released

Newly formed mRNA is an unfinished molecule, not yet ready for use
mRNA transcripts are modified before leaving the nucleus

The 5’ end is capped with a modified guanine that serves as a “start” signal for translation ◦ The cap will also help bind
the mRNA to a ribosome A “poly-A tail” of about
100-200 molecules of adenine ribonucleotides is added to the 3’ end

Noncoding portions (introns) are snipped out, and actual coding regions (exons) are spliced together to produce the mature transcript ◦ Both are transcribed before transcript reaches
cytoplasm Alternative splicing of exons mixes up
different parts of the same gene◦ Resulting in different proteins that increases the
cell’s capacity to make diverse proteins One gene can specify two or more proteins
that differ slightly in form and function