(Colorimetric/ ab65390 Cholesterol Assay Kit HDL and LDL ...
Extracellular cholesterol and cholesterol-filled macrophages (foam cells) accumulate in...
-
date post
22-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
261 -
download
0
Transcript of Extracellular cholesterol and cholesterol-filled macrophages (foam cells) accumulate in...
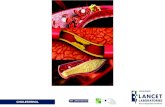
Extracellular cholesterol and cholesterol-filled macrophages (foam cells) accumulate in subendothelial space. Subsequent structural modifications of LDL particles render them more atherogenic. Oxidation of subendothelial LDL attracts monocytes, which enter subendothelium and change into macrophages. Macrophages may take up oxidized LDL to form foam cells.
Fibrous plaque larger than fatty streak and occupies more of the arterial lumen. Thickened cap synthesized by modified smooth muscle cells. Central core consists of extracellular cholesterol. Foam cells surrounding core derived primarily from smooth muscle cells. Fatty streaks may continue to form at periphery of plaque.
Total or partial occlusion of coronary artery due to plaque rupture and thrombosis can cause angina or frank myocardial infarction.
Plaques likely to rupture termed unstable. Rupture usually occurs in lipid-rich and foam cell-rich peripheral margins and may result in thrombosis and arterial occlusion.