Management of LDL as a Risk Factor · Management of LDL as a Risk Factor • Epidemiological...
Transcript of Management of LDL as a Risk Factor · Management of LDL as a Risk Factor • Epidemiological...

Management of LDL as a Risk Factor
Raul D. Santos MD, PhD
Heart Institute-InCor
University of Sao Paulo
Brazil

Disclosure
• Consulting for: Merck, Astra Zeneca, ISIS-Genzyme, Novo-Nordisk, BMS, Pfizer, Lilly, Amgem, Aegerion, Sanofi
• Sponsored research: ISIS-Genzyme, GSK, and Roche
• Speakers Bureau: Pfizer, Merck, Astra Zeneca, Abbott, Biolab and Novartis

Management of LDL as
a Risk Factor
• Epidemiological association of
cholesterol and CVD
• Evidence for cholesterol lowering
– Safety and cost effectiveness
• Statins and diabetes onset
• Unmet needs
• The future

Source: The Lancet 2010; 375:959-961 (DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60364-9)
LDL particles

What is the importance of cholesterol for CVD ?

Blood cholesterol and vascular mortality by age, sex and blood
pressure: a meta-analysis of individual data
from 61 prospective studies with 55 000 vascular deaths
Lancet 2007; 370: 1829-39

Lancet 2007; 370: 1829–39
N=900,000

What is non-HDL cholesterol ?
HDL LDL IDL VLDL CM remnants
apoA-I apoB apoB apoB apoB 48
Cholesterol
Triglycerides
•All lipoproteins
non-HDL
non–HDL-C = Total Cholesterol − HDL-C
Courtesy Roger Blumenthal

N=302,430
Non-HDL-cholesterol, CHD and, Ischemic Stroke
CHD Ischemic Stroke
N=173,312
JAMA 2009;302:1993-2000
4X more
potent
for CHD
vs. Stroke
FUP 2.79 million /persons years

Intervention studies with statins
What’s the evidence?

Lancet 2010.; 376:1670-81

Impact of 40 mg/dl reduction on LDL-C upon
major cardiovascular events and mortality
CTT 2010
Relative Risk (95% CI)
All cause mortality 0.90 (0.87-0.93), p<0.0001**
CHD mortality 0.80 (0.74—0.87); p<0.0001**
Other cardiac deaths 0.89 (0.81—0.98); p=0.002**
Stroke deaths 0.96 (0.84—1.09); p=0.5
Major vascular events 0.78 (0·76—0·80); p<0.0001
Non-fatal MI 0.73 (0.70 − 0.77); p<0.0001
Myocardial revascularization 0.75 (0.72 − 0.78); p<0.0001
Ischemic stroke 0.79 (0.74 − 0.85); p<0.0001
Cancer incidence 1.00 (0.96 − 1.04); p=0.9
Hemorrhagic stroke 1.12 (0.93 − 1.35); p=0.2
Adapted from The Lancet 2010.; 376:1670-81 **- CI 99%

Re
du
cti
on
in
CH
D E
ve
nts
%
Risk Reduction (%) in CHD Events p/ 39 mg/dl LDL-C Lowering
According to Treatment Length
2nd year >6th year
3rd to 5th years
Adapted from Law MR et al BMJ 2003;326:1423
1st year
-11
-33
-36
-22

+ Importance of reducing
non-HDL-C
Evaluated studies
• 14 with statins (n=100,827) • 7 with fibrates (n=21.647) • 6 with niacin (n=4.445) • 1 with resins (n=3.806) • 1 with diet (n=458) • 1 with ileal bypass (n=838)
TOTAL – 132,021 patient AVERAGE FOLLOW-UP – 4.5 Y
1% non-HDL-C = 1% CHD risk
J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;53:316-322

The ideal cholesterol level?
Is really lower the better?

LDL-C of MI Subjects in The USA: Primary Prevention 2000-2006
LDL
>130 mg/dL 27.9%
100-129 mg/dL 30.6%
< 100 mg/dL 41.5%
Sachedeva A et al. Am Heart J 2009;157:111-7
N=48,093
<70 mg/dL = 12.5%

Re
lative
ris
k o
f C
HD
de
ath
Total Plasma Cholesterol (mg/dl)
0.5
1.0
2.0
MRFIT
272
0.5
116 156 194 233
0.25
Shanghai 0.125
Low Cholesterol – A China Business?
Chen et al. BMJ. 1991;303:276-82. Kannel et al. Am Heart J. 1986 112:825-36.

CTT: Effects on Major Atherosclerotic Events
Pro
po
rtio
nal
red
uct
ion
in
ath
ero
scle
roti
c ev
ent
rate
(9
5%
CI)
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
30% Statin vs control
(21 trials)
Mean LDL cholesterol difference
between treatment groups (mg/dL)
More vs Less (5 trials)
0 20 40 10 30
Lancet 2010.; 376:1670-81

What is the cost effectiveness of LDL-C lowering?
Who will benefit the most?

Baseline LDL-C and risk reduction
Lancet 2010.; 376:1670-81

Cardiovascular events per 40 mg/dL reduction in LDL-C in 5 years: CTT
Primary
Prevention
Secondary Prevention
Relative risk reduction
20% 20%
Absolute risk reduction
2% 5%
Events avoided per 1,000 (CI 95%)
25 (19-31) 48 (39-57)
NNT 50 20
Mean LDL-C 148 (118-190) mg/dL
Adapted from CTT Lancet 2005;366:1267-78

Does cholesterol lowering cause cancer?

Alsheikh-Ali et al. JACC 2008;52:1141-7

LDL-C Reduction and Cancer Incidence
Lancet 2010.; 376:1670-81

Do Statins Increase the Risk
of Type 2 Diabetes?

Source: The Lancet 2010; 375:735-742 (DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61965-6)
Statins and The Risk of
Diabetes: Meta-analysis
Relative increment 9% NNH= 255

Meta-analysis of New-Onset Diabetes and First Major
Cardiovascular Events in 5 Large Trials Comparing
Intensive-Dose to Moderate-Dose Statin Therapy
Preiss, D. et al. JAMA 2011;305:2556-2564
NNH=498/ year NNT= 155/year

Risk of new-onset T2DM: baseline fasting glucose > 100 mg/dl, fasting triglycerides>150 mg/dl, BMI >30 kg/m2, and a history of hypertension
Waters DD et al. JACC 2011; 57:1535-45

Do Statins Increase The
Risk of Hemorhagic Stroke?

Randomized Trials Observational Studies
Hackman et al. Circulation 2011 17 Nov e-pub
N=248,391

Do Statins Cause Cognitive
Changes?

FDA: Statins can cause cognitive
changes that are generally reversible
• 333 cases in post-marketing surveys
• HPS- memory loss objectively measured
by TICS questionnaire • 23.4% vs. 24.2 % simvastatin vs. placebo p=0.4
• Dementia
– 0.3% vs. 0.3%
• Other phsyquiatric changes
– 0.7% vs. 0.7%
Lancet 2002;360: 7–22

Statins and severe muscle
damage

Severe muscle disease with
statins: CTT • N=170,000 in 26 trials
• Defined ad CK levels > 10 x ULN
• Simvastatin 80 mg vs. 20-40 mg
– 4/10,000 vs 1/10,000
• Not seen with high dose atorvastatin
• Not associated with LDL-C lowering
Lancet 2010.; 376:1670-81

What are the unmet needs?

% Rates of CHD Patients Attaining LDL-C <70 mg/dL according to gender:LTAP-2
n=2993
Santos RD et al. Am Heart J 2009;158:860-6
637/2053
242/940 242/940
Total
879/2993
Success Faillure
Gender
Women
242/940
Men
637/2053
P=0.0033

% Non-HDL-C Success Rate by Risk Group
Risk group and success determined according to NCEP ATP III guidelines.
6224/9955
1370/1959
3070/5930
1784/2066
Risk Groups
P<0.001 among risk groups.
Santos RD et al. Atherosclerosis 2012; 224:150-3

What is the future?
Present in some cases…

Antisense oligonucleotides: mechanism of action
• Adapted from: Crooke ST, ed. Antisense drug technology: principles, strategies and applications. 2nd ed. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 2007:601
Antisense drug
(oligonucleotide)
Transcription
No disease-associated
protein produced
No
translation
DNA mRNA
Disease-associated
protein produced
Transcription Translation
Traditional
drug

Raal FJ, Santos RD et al. Lancet. 2010;375:998-1006

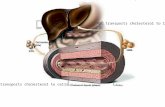
Lomitapide: Mode of Action
41
Decreases Secretion into Bloodstream
Apo B-100
MTP
Apo B-48
MT
P
Intestinal Cell
Liver Cell
VLDL
Chylomicron
n
Diet Source
cholesterol
triglyceride
Liver Source
cholesterol
triglyceride

Lomitapide Efficacy in Phase 3 (Completer Population, N=23)
Study Week
Efficacy Phase Safety Phase
Mean
% C
han
ge in
LD
L-C
fro
m B
L (9
5%
CI)
50%
Reduction
44%
Reduction
p<0.001
p<0.001
LDL-C (mg/dL):
352 ± 116 Baseline
199 ± 123 Week 56
168 ± 96 Week 26
Mean Dose: 40 mg
Mean Dose: 45 mg
Adapted from Cuchel M et al. Lancet 2013; 381:40-46

Impact of an PCSK9 mAb
on LDL Receptor Expression
For illustration purposes only

LAPLACE-TIMI 57: Mean Change in LDL-C from Baseline While
Receiving Statin Therapy to Week 12 With AMG 145
Intervention Baseline
LDL-C (mg/dL)
% Change
LDL-C
Attained
LDL-C (mg/dL)
Placebo 124
AMG 145 70 mg Q2W 120 -42%* 73
AMG 145 105 mg Q2W 128 -60%* 54
AMG 145 140 mg Q2W 120 -66%* 45
AMG 280 280 mg Q4W 124 -42%* 69
AMG 145 350 mg Q4W 124 -50%* 60
AMG 145 420 mg Q4W 120 -50%* 58
n = 631
* p < 0.0001 for % change in LDL-C vs placebo Giugliano et al. Lancet 2012; 380: 2007-17

Changes in Apo B, nonHDL-C, and Lp(a) from Baseline
to Week 12 with Alirocumab
% C
han
ge f
rom
Baselin
e t
o W
eek 1
2
1LS mean (SE)
2median (Q1-Q3)
* p < 00001
† p = 0.0022 McKenney et al. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012;59 2344-2353
10
0
-10
-20
-30
-40
-50
-60
-70
Apo B nonHDL-C Lp(a)
-2% -2%
-34%*
-56%*
-63%*
-0%
-13%†
-26%* -29%* -27%*
-48%*
-56%*

Conclusions 1
• There is a clear association between cholesterol levels and the risk of CHD death
• Cholesterol lowering reduces the risk of cardiovascular events and mortality
• The absolute benefit depends on the risk
• Cholesterol reduction does not increase the risk of cancer, hemorrhagic stroke or cognitive dysfunction

Conclusions 2
• Statin use is associated with an increase in the risk of type 2 diabetes – Absolute risk is small
– Greater in those at higher risk of becoming diabetics at baseline
• There is plenty of room for improvement in prevention of subjects at high risk of CVD