EE140 Introduction to Communication Systems Lecture...
Transcript of EE140 Introduction to Communication Systems Lecture...

3/4/2018
1
EE140 Introduction to
Communication Systems
Lecture 9
Instructor: Prof. Xiliang Luo
ShanghaiTech University, Spring 20181
Architecture of a (Digital) Communication System
2
Source A/Dconverter
Sourceencoder
Channelencoder Modulator
Channel
DetectorChanneldecoder
Sourcedecoder
D/Aconverter
User
Transmitter
Receiver
Absent ifsource isdigital
Noise

3/4/2018
2
Contents
• Analog Modulation
– Amplitude modulation
– Pulse modulation
– Angle modulation (phase/frequency)
3
AM and PM• Amplitude modulation (AM) is linear
–
• Angle modulation (PM and FM) is nonlinear
4
m(t))t(dm
)t(ds of tindependen is
tfcos)t(mA)t(s cπ2
23
22
22
3
1
2
11
2
32
322
2
tfsin!
)t(tfcos
!
)t(tfsin)t(tfcosA
)t(!
j)t(!
)t(j A eRe
eA eRe)t(tfcosA)t(s
cccc
tfj
)t(jtfjc
c
c
πθ
πθ
πθπ
θθθ
θπ
π
θπ

3/4/2018
3
Narrowband FM (NBFM)• Narrowband FM (NBFM) – sinusoidal modulating
signal
• Given
– where is the peak frequency deviation, and is the modulation index
5
]d)(mKtfcos[A)t(st
fc 0
0
2 θττπ 0 and 2 0 θtfcosa)t(m mπ
tfsintfsinf
ftfsin
f
aKd)(mK)t( mm
mm
m
ft
f πβπππ
ττθ 22220
Δ
fΔ β
NBFM (Cont’d)• If (i.e. ), the narrowband FM
signal is given by
• Compared with DSB-LC (AM)
6
1)t(θ10 β
tfjtfjtfj
cmc
mmc eeAeRe
tfsintfsinAtfcosA)t(s
πππ ββ
ππβπ
222
221
2 2 2
tfjtfjtfj
cmc
mmc em
em
AeRe
tftfmAtfcosA)t(s
πππ
πππ
222
221
2cos 2cos 2

3/4/2018
4
Wideband FM• If modulation index is NOT small, the spectral
density of a general angle-modulated signal cannot be obtained by Fourier transform.
• Wideband FM
– Modulation index
7
]d)(mKtfcos[A)t(st
fc 0
0
2 θττπ
tfsinjtfj
mcmm
fc
mc eAeRe
tfsintfcosAtfsinf
KtfcosA)t(s
πβπ
πβπππ
π
22
2222
2
m
f
m f
K
f
f
πβ
2
Δ
Wideband FM• is a periodic function of time with a
fundamental frequency of . Its Fourier series representation is
– Bessel functions of the first kind
8
tfsinj me πβ 2
2
2
2222 1 where
T
T
tnfjtfsinjn
n
tnjn
tfsinj dteeT
FeFe mmmm ππβωππβ ,
)(JF nn β

3/4/2018
5
Spectra of FM Signal• Total average power in an FM signal is a constant.
9
constant mf constant fΔ
Generation of Wideband FM Signals (Cont’d)
• Indirect method: Armstrong indirect FM transmitter
– As a result of the multiplication and heterodyne operations, it is difficult in this system to maintain the correct magnitude of carrier to sidebands, and thus it could not be used for an information signal with DC content.
10

3/4/2018
6
Demodulation of Wideband FM Signals• Demodulation: to provide an output signal whose
amplitude is linearly proportional to the instantaneous frequency of the input FM signal.
• Direct method: use frequency discriminator – Frequency discriminator is the system that has a linear
frequency-to-voltage transfer characteristic. – Ideal differentiator has a linear amplitude versus frequency
characteristic and therefore is a frequency discriminator.Input:
Output:
– If , the modulating signal can then be detected by an envelope detector.
11
]d)(mktfcos[A)t(st
fc 00 2 θττπ
00
2 ]2[ θττ d)(mKtπfsin)t(mKπfA)t(sdt
d t
fcfc
cf f)t(mK π2
Demodulation of Wideband FM Signals (Cont’d)
• Examples of frequency discriminator
12

3/4/2018
7
Demodulation of Wideband FM Signals (Cont’d)
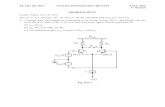
• Indirect method: use phase-locked loop (PLL)
– Phase comparator detects the timing difference between the two periodic signals (with the same fundamental frequency) and produces an output voltage that is proportional to this difference.
– Loop filter controls the dynamic response of the PLL. We have
– Voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) generates a constant-amplitude periodic waveform whose instantaneous frequency is proportional to the input voltage, i.e., .
13
Phasecomparator)(tsi
Loopfilter
Voltage-controlledoscillator (VCO)
)(tso
)(tsc
)(ts f
)t(h)t(s)t(s co
)t(sKf)t(s ofcf π2
Demodulation of Wideband FM Signals (Cont’d)
• Indirect method: output of PLL
– Assume and the phase comparator output is then
– If is small and we have .14
)]t(tfcos[A)t(s ici νπ 21 )],t(tfsin[A)t(s fcf νπ 22
)]t()t(sin[AA
)]t(tfsin[A)]t(tfcos[A)t(s
if
LPfcicc
νν
νπνπ
21
21
2
1
2 2
)t()t( if νν )]t()t([k)t(s ifcc νν
Phasecomparator)(tsi
Loopfilter
Voltage-controlledoscillator (VCO)
)(tso
)(tsc
)(ts f

3/4/2018
8
Demodulation of Wideband FM Signals (Cont’d)
• Indirect method: output of PLL
15
)t(h)]t()t(sin[kk)t(h)t(sk)t(sk)t(dt
difcfcfoff ννν
Phasecomparator)(tsi
Loopfilter
Voltage-controlledoscillator (VCO)
)(tso
)(tsc
)(ts f
0 )t(kk)t(kk)t(dt
dicffcff ννν
1
)t(h
x)xsin(No PLL loop
Demodulation of Wideband FM Signals (Cont’d)
• Indirect method: output of PLL (with loop)
– Output voltage is proportional to the instantaneous frequency (referred to the carrier) of the input wideband FM signal.
– The PLL demodulates the input wideband FM signal!
16
ττνν d)(sk)t()t(t
offi 0
)t(dt
d
k)t(s i
fo ν
1

3/4/2018
9
Signal-to-noise Ratio (SNR) in FM Reception
• Input signal and input noise of the FM detector
• Output signal of the FM detector
• For convenience, assume• Output noise of the FM detector
– Unmodulated carrier with additive bandpass noise
where and
17
2 2 200
/AS]d)(fktfcos[A)t(s i
t
fc θττπ
)t(fk)t(dt
d)t()t(s fcco ωθωω
)t(fkS)t(fk)t(s fofo22
)]t(tcos[)t(r
tsin)t(ntcos)t(ntcosA)t(ntcosA
c
cscccc
γω
ωωωω
)t(n)t(n)t(nNtfsin)t(ntfcos)t(n)t(n scicscc222 22 ππ
22 )]t(n[)]t(nA[)t(r sc .)t(nA
)t(ntan)t(
c
s 1
γ
SNR in FM Reception (cont’d)• Output noise of the FM detector
– Assume the noise is small, i.e. , we have
– Output noise: .
18
A)t(n&)t(n sc
A
)t(n
A
)t(ntan
)t(nA
)t(ntan)t( ss
c
s
11γ
)t(ndt
d
A)t(
dt
d)t(n so
1 γ

3/4/2018
10
Power Spectral Density / Mean Power of Noise
• Input noise of the FM detector
Bandwidth:
• Quadrature noise component
Bandwidth:
19
Hzwatts)(Sn 2ηω
π
η
πω
2
2 2 2 WW
)(S)t(nN ni mnW ω 2
0 2W2W
)(snS
)t(ns
ηωωω LPcncnn )ω(S)ω(S)(Ss
π
η
πω
2
2
2 22 WW
)(S)t(nsns
mnW ω 2
Power Spectral Density / Mean Power of Noise
• Output noise of the FM detector
– where is the frequency response of the time differentiator (recall
• The discriminator output is limited by a low-pass filter (LPF) with a cutoff frequency of , the bandwidth of output noise is .
20
)t(no
2
2
2
22
2
1
A)(S
A)(H)(S
A)(S
sso nnn
ηωω
ωωωω
ωω j)(H
)(Fj)t(fdt
dFT ωω
mω
mω
2
3
0
22
2
3
2
1
Ad
Ad)(S)t(nN m
noo
mm
mo π
ωηωω
π
ηωω
π
ωω
ω

3/4/2018
11
SNR in FM Reception (cont’d)• Signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) in FM reception
– For wideband FM, the output signal-to-noise ratio increases as the square of the bandwidth, which is proportional to .
21
W
A
N
SSNR
i
ii
2
η
π
3
222
3
m
f
o
oo
)t(fKA
N
SSNR
ωη
π
fK
SNR in PM Reception• Input signal of the PM detector
• Output signal of the PM detector
• For convenience, assume • Input noise of the PM detector
• Output noise of the PM detector
– Assume the noise is small,
22
2 20 AS])t(fKtcos[A)t(s ipc θω
)t(fkt)t()t(s pco 0θωθ
)t(fkS)t(fk)t(s popo22
)t(n
π
η
πωηω
2
2 2 2 2 WW
)(S)t(nNHzwatts)(S nin
)t(no
)t(nA)t(ntan)t()t(n cso 1γ
.A
)t(n)t( sγ
222
22
22
1
AA)t(nN
A)(S
A)(S mm
oonn so π
ωη
π
ωηηωω

3/4/2018
12
SNR in PM Reception (cont’d)• Signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) in PM reception
• For sinusoidal modulating signal, i.e. , we have
23
W
A
N
SSNR
i
ii
2
η
π
m
p
o
oo
)t(fkA
N
SSNR
ωη
π
222
mmm
p
o
o A)(AakA
N
S
ωη
βπ
ωη
θπ
ωη
π
2
2
2
2222222
Δ
i
i
o
o
N
Sn
N
S 2β
tωcosa)t(m m
SNR in PM Reception (cont’d)• Compared to the AM signal with 100% modulation,
we have
– Conclusion: the output SNR can be made much higher in PM than in DSB-LC (AM) by increasing the modulation index .
– Assumption: (1) ; (2) .– Expense: an increase in also increases the signal
bandwidth.
24
AMo
o
AMi
c
PMo
o
N
S
N
S
N
S
22 ββ
β
A)t(n&)t(n sc 1ββ

3/4/2018
13
Comparison of CW Modulation Systems
25
Contents
• Sampling
– periodic sampling
– frequency domain representation of sampling
– Reconstruction of a bandlimited signal from samples
– change the sampling rate using discrete-time processing
• Quantization
26

3/4/2018
14
Periodic Sampling
27
• :sample period• 1/ :sample rate• Ω 2 / :sample rate
Mathematical Model for Ideal Sampling
28
[ ] ( ) | ( )c t nT cx n x t x nT
( )n
t nT
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( )
s cn
cn
x t x t t nT
x nT t nT

3/4/2018
15
Frequency Domain Representation• Fourier transform
• Nyquist sampling theorem: for a band-limited signal– 2 , no aliasing– o.w., aliasing
29
*
/
s c
n
X f X f S f
X f n T
Aliasing
30
0 0~ 2k
0 2 4 6 8 10-1
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Time
Am
plit
ude
cos(0.1n), continuous time
cos(2.1n), continuous time
cos(0.1n), discrete time
cos(2.1n), discrete time
0 2 4 6 8 10-1
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Time
Am
plit
ude
cos(0.1n), continuous time
cos(1.9n), continuous time
cos(0.1n), discrete time
cos(1.9n), discrete time
[ ] cosx n A n
0 0~ 2k

3/4/2018
16
Symmetry
31
0 2 4 6 8 10-1
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Time
Am
plit
ude
cos(0.1n), continuous time
cos(1.9n), continuous time
cos(0.1n), discrete time
cos(1.9n), discrete time
0 0~ 2k
Anyreal ∗ conjugatesymmetric
[ ] cosx n A n
0 00.1 ~ 0.1
0 00.1 ~ 2 1.9
Reconstruct Bandlimited Signal From Samples
• Impulse-train modulated signal
• Pass through LPF with impulse response to reconstruct
32
Ideal reconstruction
filter
Convert from sequence to
impulse train
sn
x t x n t nT
r rn
x t x n h t nT

3/4/2018
17
Ideal Reconstruction Filter• Ideal LPC with cut of frequency: / or 2/
33
sin /
/r
t Th t
t T
Reconstructed Signal
34
sin /
/rn
t nT Tx t x n
t nT T
j Tr rX j X e H j
Sinc function is 1 at t=0
Sinc function is 0 at nT

3/4/2018
18
Example• Reconstruct the sinusoidal signal from samples
35
0 2 4 6 8 10-1
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
Time
Am
plit
ude
cos(0.1n), continuous time
cos(1.9n), continuous time
cos(0.1n), discrete time
cos(1.9n), discrete time
[ ] cos 0.1x n n
Exercise• Sampling the signal cos 4000
– 1/6000
36

3/4/2018
19
Exercise• Sampling the signal cos 4000
– 1/1500
37
Thanks for your kind attention!
Questions?
38




![Homework 5, Fall 2004bwrcs.eecs.berkeley.edu/Classes/ee140/Fall 2004/hw/hw5... · 2004. 11. 1. · Author: dasobel [ AGAVE ] Created Date: 10/28/2004 11:56:42 AM](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/5ff9301af7033723f0432f6f/homework-5-fall-2004hwhw5-2004-11-1-author-dasobel-agave-created.jpg)