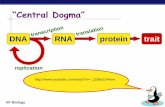
DNA and the CENTRAL DOGMA
-
Upload
jayson-hodges -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
description
Transcript of DNA and the CENTRAL DOGMA

DNA and the CENTRAL DOGMA
Everything you never wanted to know, but still need to understand… and then some more bonus stuff to really make
you happy

Transformation of Bacteria
1928 Fredrick Griffith
a) Mouse dies b) Mouse lives c) Mouse lives d) Mouse dies. Living S cells are found in blood sample from dead mouse

Phages are viruses that infect bacteria (bacteriophage)

1. Mix phages with bacteria
2. Blend to mix
3. Centrifuge and measure radioactivity

What makes up DNA subunits?
• 5-carbon sugar
• Phosphate
• Nitrogenous base


• A and G are Purines (double rings)
• C and T are pyrimidines (single rings)
“Attorney Generals are pure”

DNA REPLICATION
2 complimentary strands. A=T C≡G
Helicase breaks H bonds and unzips
DNA polymerase attaches nucleotides to each template strand
Each “daughter” DNA consists of one parental and one new strand

Conservative – parental helix remains intact; an all new copy is made
SemiConservative – two strands separate and each functions as a template
Dispersive – each strand contains pieces of old and new DNA

Meselson-Stahl Experiment
Incorporates heavy nitrogen into DNA
Incorporates lighter nitrogen into DNA
“new” DNA synthesized would be lighter than the “old” DNA
1st replication ~20 min
2nd replication ~40 min

EUKARYOTES: many origins of replication

Incorporation of nucleotideEnzyme DNA polymerase catalyzes this reaction

5’3’ direction of one strand runs counter to the other

DNA Helicase – unzips
Topoisomerase – unwind DNA
SSBP – single strand binding proteins, hold strands open
Primase – joins RNA nucleotides to eukaryotes (primer is required for polymerase to synthesize)
DNA Polymerase – adds nucleotides
Ligase – link Okazaki fragments



New DNA

Excision repair of
DNA




FROM GENE TO PROTEINBeadle and Tatum – one gene, one polypeptide