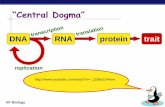
DNA replication Central dogma of molecular biology.
-
Upload
lewis-conley -
Category
Documents
-
view
235 -
download
3
Transcript of DNA replication Central dogma of molecular biology.

DNA replication
Central dogma of molecular
biology


1.the basic principle of DNA
replication
(1) Semiconservative
replication


a. concept
b. evidence
c. conclusion


(2) Semidiscontinuous replication
* The synthesis direction of
DNA polymerase
* leading strand & lagging
strand


* Okazaki fragment
(3) RNA primer
* the synthesis
* the function


(4) fidelity
2. Enzymes & proteins cooperate
in the DNA replication

(1) E.coli DNA polymerase I
(Kornberg enzyme,DNA-Directed
DNA polymerase,DDDP,pol I )

* The principle materials for pol I
# four dNTP
# Mg 2+
# RNA primer or DNA single
strand possessed 3’-OH
# DNA template

* Multiple function of pol I
Klenow fragment-------
(large fragment)
DNA polymerase activity,
3’-5’ exonuclease activitysmall fragment-------
5’-3’ exonuclease activity

5’ 3’ 3’ 5’ exonuclease exonuclease DNA polymerase activity activity activity
Small fragment large fragment (Klenow fragment)
pol I
Proofreading



* the principle materials for pol II
& pol III
# four dNTP
# Mg 2+
# RNA primer or DNA single
strand possessed 3’-OH
# DNA template

* the characteristics of pol II & pol III
pol II---mostly concerned with
proofreading & DNA repair
pol III---- indispensable for DNA
replication,the highest rate
of chain elongation and
processive



(2) DNA polymerase in eukaryocyte polymerase : gap filling & synthesis of lagging
strand
: DNA proofreading & repair
: DNA repair
: mitochondria DNA synthesis
: processive,leading strand synthesis,
need the assistance of PCNA

(3) helicase & gyrase
a. helicase
* function
* require
b. single strand binding protein
(SSB) ,helix disabling
protein,HDP


* function
c. topoisomerase I
* function
d. topoisomerase II, gyrase
* function

(4) Primosome
(5) DNA ligase
* function
* require
* process



* characteristics
* usage
3.procedure of DNA replication
(1) the initiation of the
replication

* the origin of replication ----
The special structure
(ori C)
* the process of initiation
formation of replication fork
( replication bubbles)



* how to deal with synthesis
direct ?
(3) the termination of the
replication
(2) the elongation of the
replication







*Removes primers---- pol I
small fragment
* fills the gap with dNTP----- pol I
large fragment
(Klenow fragment)
* ligation----DNAligase



4. Summarize of DNA replication
a.identification of the origin of
replication
b.unwinding (denature)of ds DNA to
provide ssDNA
c. formation of replication fork
d.initiation of DNA synthesis & elongation

e. formation of replication bubbles with
ligation of the newly synthesized DNA
segment
f. Reconstitution of chromatin DNA




5.Telomere & telomerase
(1) telomere
*concept
*structure
* function

(2) The function & molecular
components of telomerase
* function
* components (RNP)
* mechanism



• Telomerase & carcinoma
5.DNA damage & repair
(1) the basic of repair
(2)the causes of DNA damage
*remove purine by heat &
acid


• ionizing radiation
• ultraviolet ray
• chemical agents
(3) The type of DNA damage


(4)Mechanism of DNA repair
* photo repair
* excision repair
significant (correct large defects)
* base excision repair
a.process







• Characteristics
• summarize
a. the enzyme uracil DNA
glycosylase removes the uracil
created by spontaneous
deamination of cytosine

b. an endonuclease cuts the
backbone near the defect
c. an endonuclease removes a
few bases
d. the defect is filled in by the
action of a repair polymerase
( pol I )

e. The strand is rejoined
by ligase