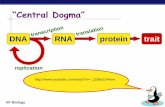
Biomolecules of the Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein.
-
Upload
jody-kennedy -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
1
Transcript of Biomolecules of the Central Dogma DNA RNA Protein.

Biomolecules of the Central Dogma
DNA RNA Protein

Nucleotide Structure

DNA vs. RNA
• Sugar (C2’)
• Single vs. Double Stranded– Stem-loop (Hairpin)
• Thymine vs. Uracil

Nucleic Acids
• Sugar phosphate backbone– 5’ Phosphate– 3’ Hydroxide
• Base Pairing Rules– Purine: A, G– Pyrimidine: C, U, T– A=T, G≡C

DNA Coiling to form Chromosomes

Protein: Primary Structure
• The sequence of amino acids
• N-terminus, C-terminus

Protein: Secondary Structure

Protein: Secondary Structure
• β pleated sheet
• β barrel– A large beta-sheet that
twists and coils to form a closed structure

Tertiary Structure
• 3D structure of a single protein molecule
• Folding is driven by chemical interactions of R groups:

Protein: Quaternary Structure
• Assembly of several protein subunits
• Stabilized by non-covalent interactions and disulfide bonds– Dimer, trimer, tetramer,
multimer– “Homo” = same subunits– “Hetero” = different subunits

Metabolism
Metabolic Direction Water Energy Examples
Anabolic “Building up”
Condensation Used Photosynthesis
Polymerization
DNA replication
Transcription & Translation
ADP + Pi ATP
Catabolic “Breaking down”
Hydrolysis Released Digestion
Glycolysis/ Krebs Cycle
Combustion
ATP ADP +Pi

Condensation Reactions(a.k.a. Dehydration Synthesis)
• Two monomers are joined together, with the loss of water.
• Synthesis of all the important biological macromolecules:– carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids

Protein Synthesis
• Polymers of amino acids linked by peptide bonds

Carbohydrate Synthesis
• Linked by glycosidic bonds– Ex) Di-, Tri-, Polysaccharides– Ex) Polymers of glucose form cellulose and
starch.

Nucleic Acid Synthesis
• DNA/RNA strands string of nucleotides joined together by phosphodiester bonds

Lipid Synthesis
• “Fats” are a subgroup of lipids called triglycerides Ester linkage

Depicting Molecules in Space

Ribbon Diagrams(a.k.a. Richardson Diagrams)
• 3D schematic representations of protein structure

Alternative Views & Representations
• A: schematic/ribbon• B: molecular/ball &
stick• C: view from top• D: space filling model