Cell as a unit of life Cell theory (4) Types of cells Types and specialized of cell...
-
Upload
ruth-conley -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
1
Transcript of Cell as a unit of life Cell theory (4) Types of cells Types and specialized of cell...

Cell as a unit of life
Cell theory (4)
Types of cellsTypes and
specialized of cell
prokaryotes eukaryotes
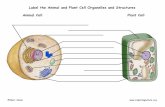
Plant
cell
Animal cell
animalplant
meristem perman
entground tissue
vascular
- Nerve
- Epithelial
- Connective
- Muscle
differences

BiocatalysisBiocatalysis
Properties and
mechanismsPropertie
s of enzyme
Mechanism of
activation energy
! Activation energy
models
Lock and key
2 hypothesis
Induce fit
cofactors
- Types of
cofactors
inhibition
reversible
irreversible
competitive Non-
competitive
Enzyme classification

Gaseous Gaseous exchange exchange
and its and its controlcontrolanimaanima
llplantplant
Organ & Organ & structurestructure
ss
alveolusalveolus
haemoglobihaemoglobinn
Gas Gas transportatiotransportatio
nn
Oxygen Oxygen dissociation dissociation
curvecurve
myoglobimyoglobinn
Foetus & Foetus & adultadult
Bohr Bohr effecteffect
breathinbreathingg
stomastoma
openopen closeclose
2 hypothesis2 hypothesis
1.1. Sugar Sugar accumulationaccumulation
2.2. K+ K+ concentrationconcentration
O2O2 CO2CO2

Mammalian heart & its control
Structure
Initiation factors affecting
Cardiac cycle
Heart beat
Cardiovascular Diseases
Hypertension
Myocardial infarction
arteriosclerosis
Cardiac output
Electrocardiogram

Homeostatic organ
Liver kidney
Role
Control of Blood glucose level
Liver structure
Formation of urea
Homeostatic function
Carbohydrate metabolism
detoxification
transamination
deamination
Ornithine/urea cycle

Nervous systemNervous system
organizationorganization
Basic unit : Basic unit : neuronneuron
Central Central nervous nervous systemsystem
componentscomponents
Peripheral Peripheral nervous nervous systemsystem
somatisomaticc
autonomiautonomicc
SymphatetiSymphateticcparasymphateparasymphatetictic
Generation of action Generation of action potential from potential from resting stageresting stage
Transmission of Transmission of impulseimpulse
synapsesynapse
structuresstructures mechanismmechanism