Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN Effects of Deregulation on Airports Dr. Richard de...
-
Upload
brittany-robinson -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
6
Transcript of Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN Effects of Deregulation on Airports Dr. Richard de...
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Effects of Deregulation on Airports
Dr. Richard de Neufville
Professor of Engineering Systems and Civil and Environmental Engineering
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Effects of Deregulation on Airports
Objective: To explore implications of airline deregulation on airports operations and management
Topics Hub-and-Spoke Operations Instability of Traffic Short Term Horizons Conclusions
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
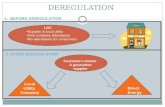
Consumer Orientationto define objectives
New Decision-Makerscompanies not governments
Faster changesmore risk
Essence of Economic Deregulation
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Consumer Orientation
When governments cannot determine profit levels (by fare levels, route protection)
Consumer desires will define criteria for efficiencyMain consumer desires:
Business Market– Speed: time saved = money– Comfort: third party pays– Frequency: schedule flexibility
Consumer Market– Cheap fares– Speed and access secondary– Package deals
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Hub - and - Spoke Operations I
One way to satisfy consumer desiresDescription
Drop direct flights between secondary points Substitute flights via hubs central to market,
system• Higher fuels costs• Passengers change at hubs (maybe not to
same airline - examples: Continental - SAS at New York/Newark; KLM - NW at Amsterdam)
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Description (cont.) Concentrate traffic to hubs
• More frequency on routes• Larger aircraft -- lower cost per seat-km.• Higher load factor - lower breakeven per
flight• Economies in crew basing, inventories
Hub - and - Spoke Operations I (cont.)
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Waves or Banks
Average Arrivals, DFW, June 2000
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0:00 1:30 3:00 4:30 6:00 7:30 9:00 10:30 12:00 13:30 15:00 16:30 18:00 19:30 21:00 22:30
15 minute intervals
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Net Effects: Lower Overall Costs, Fares for network More Frequency Lower average speed (maybe not more time
when schedule delay included)
Hub - and - Spoke operations Cost-Effective Pattern in US, Increasing in Europe, Somewhat
in Asia
Hub - and - Spoke Operations II
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Point to Point Service
Direct Flights, Thin Routes Low Frequency Low Load Factor Smaller Aircraft
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Hub and Spoke Service
Indirect, Heavy Routes via Hub Central to Market High Frequency Higher Load Factor Larger Aircraft
H
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
US Transcontinental Traffic from one coast (San Francisco, Los
Angeles…) Sent to a Midcontinental Airport (Chicago, Denver,
Dallas/Ft. Worth…) Distributed to Destinations (Boston, Philadelphia…)
Intercontinental Traffic from Europe Goes to Distribution hubs (Bangkok, Singapore…) Distributed to - Australia, Japan, Hong Kong
Hub - and - Spoke Operations III: Descriptions
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Criteria for a good Hub Centrality to Market High Capacity Reliability for Schedules --uncongested, good
weather Control by Airline -- to maintain schedules
Airports with 3/4 traffic with one airline Minneapolis -- Northwest/KLM Houston/Bush -- Continental Dallas/Fort Worth -- American Atlanta, “Cincinnati” -- Delta
Hub - and - Spoke Operations IV
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Major US East-West Hubs
An Airline dominates at each major US East-West HubHubbing Airline may have up to 80% of the traffic at
hub airport
NW
United
USAirways
American
Continental
NWUnited
Delta
Delta
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Specific markets have their own Hubs Along US East Coast, most serve US
Miami serves US-Latin America and is central to its market
Miami (American)
Charlotte (US Air)
Dulles (United)Cincinnati (Delta)
Atlanta (Delta)
Philadephia (US Air)
East Coast North-South Hubs
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Major European Hubs
Swissair
British Airways
SAS/Continental
KLM/Northwest
Lufthansa/United
Alitalia
Iberia
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Major East Asian Hubs
NWUAL
FDX
Hong Kong
Singapore
Kuala Lumpur
Bangkok
Guangdong
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Hub - and - Spoke Cargo Operations
UPS in United States• Louisville (1 billion items/day)• Regional Hub – Cologne, Germany --
Rockford, IL - Ontario, CA - Columbia SC - Dallas, TX
Fedex Memphis• Guangdong Paris
Emery Dayton
TNT Liege (Belgium)
DHL Cincinnati East Midlands (UK)
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Instability of Traffic I
Deregulation removes barriers to change immediate readjustments frequent bumps
Automobile Analogy Regulation like shock absorbers Taking shock absorbers out
• adjustment to new level• you feel every bump
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Instability of Traffic IIExamples
“Southwest effect” Providence 1 to 5 million in a few years Liverpool -- similar effect with easyjet
Memphis Fedex creates it (Likewise UPS and Louisville)
Boston -- Northwest Many ‘definitive’ choices
Hub operations appear, disappear New York/Newark -- Peoples Express Raleigh-Durham -- American
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Short Term Horizons
Because of UncertaintiesAirlines less ready to make long term
commitments only good for short term leases
Incompatibility withlong term capital investments
Therefore, need for smaller building additions more flexible space more operational solutions more aggressive management!!!
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Summary
Deregulation had and does mean:
Significant reorganizations
Strategic planning required
Greater risks than ever
...and less security!!!
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Waves or Banks (2)
Average Departures, DFW, June 2000
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
0:00 1:30 3:00 4:30 6:00 7:30 9:00 10:30 12:00 13:30 15:00 16:30 18:00 19:30 21:00 22:30
15 minute intervals
Airport Systems Planning & Design / RdN
Competition Among Airports
Airports now compete as Hubs -- many alternatives
• Amsterdam vs. Frankfurt• Bangkok vs. Singapore• US midcontinentals
Destinations - for tourist packages
Relatively new phenomenon due to: development of hubs, importance of consumer
travel
How could this affect your region?