2.0 Blood Circulation
-
Upload
jamaliah-kamisan -
Category
Documents
-
view
241 -
download
2
Transcript of 2.0 Blood Circulation
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
1/29
SCIENCE FORM THREE
2.0 BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT.
2.1 Understanding the transport system in humans
2.2 Analyzing the human blood.
2.3 Analyzing the transport system in plants
LESSON OUTLINE A LESSON PLAN OUTLINE A
LESSON OUTLINE B TEACHERS NOTES
LESSON OUTLINE C STUDENTS NOTES
TASK DESIGN TASK DESIGN ANSWER
2.1.1 Structure and function of the heart.
2.1.2 Blood Circulation System.
2.1.3 Types Of Blood Vessels.
2.1.3 Exercise
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
2/29
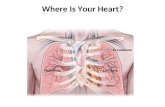
ITS ABOUT OUR
HEART
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
3/29
LOCATION FUNCTION
PROPERTIES SHAPE
Heart lies
in the
thorax behind
the chest
bone andbetween
lungs
Conical
shape
Divided
into
four
chambers
Main function
is to pump
blood
throughout
the whole
body
Heart is
the mostimportant
organ in a
human
body.
HEART
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
4/29
THE STRUCTURE OF HEART
Pulmonary Vein
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
5/29
Aorta
Carry the oxygenated blood away from
the heart (except pulmonary artery)
to all parts of the body (except the
lungs).Left Atrium/Left Auricle
Pumps blood into the left ventricle
Pulmonary Vein
Carries the oxygenated blood from
lungs to the left atriumMitral Valve/ Bicuspid Valve
Pumps one way flow of blood from leftatrium to left ventricle. Prevent the
backflow of blood.Left Ventricle
Pumps blood round the whole body
LEFT SIDE
Pulmonary Vein
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
6/29
RIGHT SIDE Vena CavaCarry the deoxygenated blood from the
upper parts and other parts of the
body (except the lungs) towards the
heart (except pulmonary veins).Right Atrium/Right Auricle
Pumps blood into the right ventricle.
Pulmonary ArteryCarries the deoxygenated blood to the
lungs.Tricuspid Valve
Pumps one way flow of blood from
right atrium to right ventricle. Prevent
the backflow of blood.Right Ventricle
Pumps blood only to the lungs.
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
7/29
From the lungs, theoxygenated bloodenters the leftatrium through thepulmonary vein.
Bicuspid valve opensand bloodenters the left
ventricle.Bicuspid valve nowcloses to prevent thebackflow of blood.
Blood enters the
aorta and istransported toall parts of thebody (except thelungs).
BLOOD CIRCULATION SYSTEM
Receive deoxygenatedblood from all partsof the body byvena cava to the right
atrium.
Tricuspid valve openand deoxygenatedblood enters to theright ventricle.
Tricuspid valve closesto prevent thebackflow of bloodinto atrium.
Blood enters thepulmonary artery and
carries thedeoxygenated bloodto the lungs.
start click
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
8/29
TYPES OF BLOOD VESSEL
ARTERY VEIN CAPILLARY
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
9/29
ARTERY
Lumen
Structure of wall Thick, muscular and elastic wall towithstand the high pressure.
Direction of blood flow Away from the heart
Blood pressure High
Rate of blood flow Rapid and irregular
Presence of valve No
Type of blood
carried
Oxygenated (except for the pulmonaryartery)
Narrow
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
10/29
VEIN
Lumen Fairly wide
Structure of wall Relatively thin wall, not as elastic and
Muscular as that of arteries.
Direction of blood flow Towards the heart
Blood pressure Low
Rate of blood flow Slow and regular
Presence of valve Yes
Type of blood
Carried
Deoxygenated (except for the pulmonaryvein).
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
11/29
CAPILLARY
Lumen Very narrow
Structure of wall Wall is only one-celled thick with gaps inbetween allowing the exchange of
materials with the surrounding tissue.
Direction of blood flow From the artery to the vein
Blood pressure Very low
Rate of blood flow Very slow
Presence of valve No
Type of blood
Carried
Oxygenated blood to the tissues
Deoxygenated blood from the tissues.
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
12/29
Exercise
1. Label the diagram below
Left Ventricle
Semi lunar Valve
Bicuspid valve
Right Atrium
Tricuspid Valve
Right Ventricle
Septum
Left Atrium
Septum Vena Cava
Aorta
Vena Cava
Aorta
Left Ventricle
Semi Lunar Valve
Right Atrium
Tricuspid Valve Bicuspid valve Left Atrium
Right Ventricle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Click to know the answer
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
13/29
2. Choose (T) for TRUE statement and (F) FALSE statement in the box
provided.
a). The heart lies in the thorax behind the chest
bone and between the lungs. T F
b). The heart is divided into six chambers. T F
c). Pulse rate is caused by heart beat.
d). Pulmonary artery carries oxygenated blood
from right ventricle to the lung.
e). The valve prevent the backflow of blood.
f). The tricuspid valve found between the right
atrium and the right ventricle. .
g). The right ventricle is thicker than the left
ventricle.
T F
T F
T F
T F
T F
CHECK ANSWER
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
14/29
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
15/29
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
16/29
2. Choose (T) for TRUE statement and (F) FALSE statement in the box
provided.
a). The heart lies in the thorax behind the chest
bone and between the lungs. T F
b). The heart is divided into six chambers. T F
c). Pulse rate is caused by heart beat.
d). Pulmonary artery carries oxygenated blood
from right ventricle to the lung.
e). The valve prevent the backflow of blood.
f). The tricuspid valve found between the right
atrium and the right ventricle. .
g). The right ventricle is thicker than the left
ventricle.
T F
T F
T F
T F
T F
*Click to know the answer
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
17/29
HUMAN BLOOD
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
18/29
Blood is the fluid of life.Blood is the fluid of life.
Blood carries oxygen, which it picks up in the lungs andBlood carries oxygen, which it picks up in the lungs and
distributes it to all body parts and transporting carbon dioxidedistributes it to all body parts and transporting carbon dioxidefrom body tissue to the lungs.from body tissue to the lungs.
Poor blood circulation can cause insufficient supplyPoor blood circulation can cause insufficient supply
of nutrients and oxygen to the cells in our body leading toof nutrients and oxygen to the cells in our body leading to
deterioration of body functions and health.deterioration of body functions and health.
Blood is the fluid of growth.Blood is the fluid of growth.
Blood supplied food and water .Blood supplied food and water .Blood also contains all of the food substances and chemicals needed by the cell.Blood also contains all of the food substances and chemicals needed by the cell.Blood transporting nourishment from digestion and hormones from glands throughoutBlood transporting nourishment from digestion and hormones from glands throughoutthe body.the body.
Blood is the fluid of health.Blood is the fluid of health.
Blood is warm and works like liquid in the central heating system.Blood is warm and works like liquid in the central heating system.
Blood absorbs warmth from busy parts such as the heart and muscles and spreads itBlood absorbs warmth from busy parts such as the heart and muscles and spreads it
out to the cooler parts like the skin.out to the cooler parts like the skin.Blood also transporting disease fighting substances to the tissue and waste to theBlood also transporting disease fighting substances to the tissue and waste to thekidneys.kidneys.
A FEW FACTS OF HUMAN BLOODA FEW FACTS OF HUMAN BLOOD
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
19/29
Plasma -55%
blood cell -45%
THE HUMAN BLOOD
Blood is alive because it contains living cells. An average adult
has about five liters of blood living inside of their body.
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
20/29
THE HUMAN BLOOD
White blood cellRed blood cell
PlasmaPlatelet
BLOOD VESSEL
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
21/29
Plasma
a) Pale yellowish liquid which constitutes about
55% by volume of whole blood.
b) Made up of 90% of water.
c) The other 10% of plasma are substancessuch as hormones, dissolved mineral salts,food substances like glucose, excretoryproducts like urea and soluble proteins likeprothrombin and fibrinogen.
d) Transports hormones, digested foodsubstances, heat and excretory productssuch as carbon dioxide (function)
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
22/29
Red blood cell
a) has no nucleus, hence they are circular andbiconvace in shape
b) contains haemoglobin
c) has a small diameter of less than 0.01 mm,hence this enable them to squeeze through
capillaries
d) has a life span of about three to four monthse) is produced by the bone narrow
f) transport oxygen
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
23/29
White blood cellsa) colorless and contains a nucleus
b) larger than the red blood cell but much fewer innumber
c) irregular in shape
d) able to move and change its shape
e) protects the body by destroying bacteria and byreleasing antibodies
Platelet
a) fragments of cytoplasm from certain bone marrow cells.
b) a life span of about four days
c) plays a part in blood clotting
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
24/29
Blood GroupEverybodys blood is not the same.
Blood group Antigen
(Special proteins on the
surface of red bloodcells)
Antibody
A A Anti-b
B B Anti-a
AB A and B None
O None Anti-a and Anti-b
Blood group Can donate to Can receive from
A A and AB A and O
B B and AB B and O
AB
(Universalacceptors)
AB A,B,AB and O
O
(Universal Donor)
A,B,AB and O O
Blood Donor
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
25/29
Component ofblood
Structure Production Life Span Function
PlasmaYellow fluid
-90% of water
-10% of othersubstance
_ _
Transportshormones,digested foodsubstances,heat andexcretoryproducts e.g.CO2
Red Blood Cells Circular andbiconcave inshape, lacksnucleus
By the bonemarrow
About 3-4months
Transportsoxygen
White BloodCells Irregular in
shape, containsa nucleus
By the bonemarrow Ranging from 2
days 6 months
Protects thebody by
destroyingbacteria & byreleasingantibodies
Platelets Smallfragments,lacks nucleus
By the bonemarrow
About 4 days Plays a part inblood clotting
HUMAN BLOOD
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
26/29
1. Which of the following is false? White blood cells Red blood cells
A. Irregular in shape Biconcave in shape
B. Does not contain hemoglobin Contains hemoglobin
C. Large in size Small in size
D. Does not contain nucleus Contains nucleus
2. A person with blood group O can donate blood to a person withblood group
A. A only
B. B onlyC. A and AB
D. A, B and AB
X Can produce antibodies
Y Are fragment of the cytoplasmfrom certain bone marrow cells
3. X and Y are two substances present in blood.
Which of the following may represent X and Y?
X Y
A. Red blood cells White blood cells
B. White blood cells Platelets
C. Platelets Plasma
D. Plasma Platelets
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
27/29
4. People of which blood group are called universal donors?
A. O
B. A
C. BD. AB
5. Which of these pairs is incorrect blood component and
characteristics?
Component CharacteristicsA. White blood cell Has nucleus
B. Red blood cell Is produced by the bone narrow
C. Platelet Produces antibodies
D. Plasma Makes up about 55% of the
whole blood
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
28/29
Part BAnswer the following question
I. Choose a word from the list on the right and match the statement on the left.
1. Transport oxygen. PLASMA
2. Consists of blood cells,plasma and platelet.
RED BLOOD CELL
3. Life span about four days. WHITE BLOOD CELL
4. Irregular in shape andcontains a nucleus.
PLATELETS
5. Yellow fluid containing
90% water and 10% othersubstances.
BLOOD COMPONENTS
II. Name and state the function of each cell below.
Diagram Name Function
Red blood cells
White blood cells
Platelets
Transport oxygen
Protect the body by
destroying bacteria
and releasing antibodies.
Plays a part in
blood clotting.
-
8/4/2019 2.0 Blood Circulation
29/29
Group members
BUSHRA BT SHARIFSMK BANDAR TUN RAZAK
JAMALIAH BT KAMISANSMK BANDAR TUN RAZAK
ROSLINA BT HASIMSMK BANDAR TUN RAZAK
SITI NORA BT SULAIMANSMK CHANIS
HUZAINI BT HIRAZAKISMK SELANCAR