Thyroid Gland · Thyroid Gland It is the largest endocrine glands. First by “Thomas Wharton”....
Transcript of Thyroid Gland · Thyroid Gland It is the largest endocrine glands. First by “Thomas Wharton”....

www.nepeducation.com
Thyroid Gland It is the largest endocrine glands. First by “Thomas Wharton”.
Origin: -
It is endodermal in origin.
Structure & Location:-
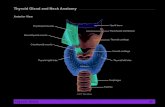
It is a bow tie shaped structure found in the neck. The two lobes of the gland and the isthmus of tissue joining them, lie just below the larynx or, voice box, just anterior to the upper portion of the trachea or,windpipe. Its weight is about 15
Anatomy: -
It is made up of a large number of follicles
about 3 million follicles, diameter of an average
ceased follicle being about 200
Thyroid Gland It is the largest endocrine glands. First of all described
It is endodermal in origin.
It is a bow tie shaped structure found in the neck. The two lobes of the gland and the isthmus of tissue joining them, lie just below the larynx or, voice box, just anterior to the upper portion of the trachea or,windpipe. Its weight is about 15-20 gm in adult human beings.
It is made up of a large number of follicles
about 3 million follicles, diameter of an average
follicle being about 200 µm. Follicles are
described
It is a bow tie shaped structure found in the neck. The two lobes of the gland and the isthmus of tissue joining them, lie just below the larynx or, voice box, just anterior to the upper portion of the trachea or,

www.nepeducation.com
held together by loose connective tissue. Each follicle is a hollow sphere whose wall consists of a single layer of cuboidal epithelium. They become columnar in shape when the gland is activated by TSH from the anterior pituitary gland.
Hormones of Thyroid Gland:
which is a polypeptide of tyrosine amino acid. Iodine atoms get attached with these tyrosine to form monofacilitates organification.(Formation of organ)
DIT molecules coupled either with MIT or DIT to form Triiodothyronine (T3) or, Tetra-cells now extrude thyroglobulin containing Tfollicle.
When necessary, follicular cells engulfs it and digest the thyroglobulin by protease enzyme and T4 & T
Its C cells secrete calcitonin.
Chemical Structure: -
I
I
HO
THYROXINE
HO O
I
Triiodothyronine (T )
together by loose connective tissue. Each follicle is a hollow sphere whose wall consists of a single layer of cuboidal epithelium. They become columnar in shape when the gland is activated by TSH from the anterior
d: -
The follicular cells synthesize thyroglobulin which is a polypeptide of tyrosine amino acid. Iodine atoms get attached with these tyrosine to form mono-iodothyronine and di-iodothyronine. TSH
(Formation of organ)
DIT molecules coupled either with MIT or DIT to form Tri--iodothyronine (T4) respectively. The follicular
cells now extrude thyroglobulin containing T4 & T3 into the space of the
ecessary, follicular cells engulfs it and digest the thyroglobulin & T3 released into blood in the ratio of 19:1.
calcitonin.
O
I
I
THYROXINE (T4)
O
I
I
CH 2 CHCOOH
NH2
Triiodothyronine (T )3
together by loose connective tissue. Each follicle is a hollow sphere whose wall consists of a single layer of cuboidal epithelium. They become columnar in shape when the gland is activated by TSH from the anterior
The follicular cells synthesize thyroglobulin which is a polypeptide of tyrosine amino acid. Iodine atoms get attached
iodothyronine. TSH
) respectively. The follicular into the space of the
ecessary, follicular cells engulfs it and digest the thyroglobulin released into blood in the ratio of 19:1.
CH 2 CHCOOH
NH2

www.nepeducation.com
T3 is active form of T4: -
In liver, kidney & brain, an enzyme deiodrinase is present. It removes one iodine from T4 molecules to form Treleased into blood but brain doesn’t.
Function of Thyroxine or T4 or T
· Metamorphosis: - T3 causes growth of CNS in the foetus and post natal life.
· Oxidative metabolism: in O2 uptake of all tissues.
· Carbohydrate metabolism: glycogenolysis by enhancement of adrenaline.
· Lipid metabolism: - Increases lipolysis.· Protein metabolism: - · It controls BMR & heat production of the body. [160 KJ· It also controls the working of
decreased urine output and vice
Calcitonin (CT): -
It is secreted by parafollicular cells or, C cells or, clear cells. The name calcitonin coined by Copp (Douglas Harold Copp) of Canada in 1962.
CT is a single chain polypeptide hormone containing 32 amino acids. Its effects are opposite of those of parathyroid hormone.
Function: -
It regulates concentration of release from bones. It is triggered by lower concentration
In liver, kidney & brain, an enzyme deiodrinase is present. It removes molecules to form T3. T3 formed by liver and kidney is
released into blood but brain doesn’t.
or T3: -
causes growth of CNS in the foetus and post natal
Oxidative metabolism: - Excepting brain & testis T3 stimulates increase uptake of all tissues.
Carbohydrate metabolism: - It increases gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis by enhancement of adrenaline.
Increases lipolysis. Increases metabolism of Protein.
It controls BMR & heat production of the body. [160 KJh*囊mIt also controls the working of kidneys. Its deficiency results in decreased urine output and vice-versa.
It is secreted by parafollicular cells or, C cells or, clear cells. The name calcitonin coined by Copp (Douglas Harold Copp) of Canada in 1962.
ngle chain polypeptide hormone containing 32 amino acids. Its effects are opposite of those of parathyroid hormone.
It regulates concentration of Ca嫩嫩 in the blood by decreasing their release from bones. It is triggered by lower concentration of Ca嫩嫩
In liver, kidney & brain, an enzyme deiodrinase is present. It removes formed by liver and kidney is
causes growth of CNS in the foetus and post natal
stimulates increase
uconeogenesis and
m*挠] kidneys. Its deficiency results in
It is secreted by parafollicular cells or, C cells or, clear cells. The name calcitonin coined by Copp (Douglas Harold Copp) of Canada in 1962.
ngle chain polypeptide hormone containing 32 amino acids.
in the blood by decreasing their 嫩 in blood.

www.nepeducation.com
Disorder of Thyroid Gland: -
1. Hypothyroidism: -
The phenomenon of undersecretion by the thyroid gland is called hypothyroidism.
(i) Cretinism: -
It is caused by less secretion of thyroxine in infants.
· Reduced metabolic rate and · Slow heart beat.· Low Blood Pressure.· Body temperature is decreased.· Pigeon chest.· Body growth and mental development retarded.· Sexual development is retarded.
(ii) Myxedema: - Deficiency of thyroxine in late life gives rise to a condition
known as myxedema.
The phenomenon of undersecretion by the thyroid gland is called hypothyroidism.
It is caused by less secretion of thyroxine in infants.
Reduced metabolic rate and oxidation. Slow heart beat. Low Blood Pressure. Body temperature is decreased. Pigeon chest. Body growth and mental development retarded.Sexual development is retarded.
Deficiency of thyroxine in late life gives rise to a condition dema.
The phenomenon of undersecretion by the thyroid gland is
Body growth and mental development retarded.
Deficiency of thyroxine in late life gives rise to a condition

www.nepeducation.com
· Reduction of metabolic rate accompanied by decreased
oxygen consumption.· Heart beat and body temperature is decreased.· This causes the face and eyelids to become puffy due to
accumulation of fat and water in the sub
[Note: -
A protein, hyalmonic acid and chondroitin sulfate together form a complex which attracts water. This complex stays usually in the skin and subattraction by it produces local retention of water. Fat is deposited due to
· Weight gain.· Loss of hair.· Blood pressure is decreased due to low heart beat.
Reduction of metabolic rate accompanied by decreased oxygen consumption. Heart beat and body temperature is decreased.This causes the face and eyelids to become puffy due to accumulation of fat and water in the sub-cutaneous tissue.
A protein, hyalmonic acid and chondroitin sulfate together form a complex which attracts water. This complex stays usually in the skin and sub-cutaneous tissue and water attraction by it produces local retention of water. Fat is
ited due to low metabolic rate.]
Weight gain. Loss of hair. Blood pressure is decreased due to low heart beat.
Reduction of metabolic rate accompanied by decreased
Heart beat and body temperature is decreased. This causes the face and eyelids to become puffy due to
cutaneous tissue.
A protein, hyalmonic acid and chondroitin sulfate together form a complex which attracts water. This complex
cutaneous tissue and water attraction by it produces local retention of water. Fat is
Blood pressure is decreased due to low heart beat.

www.nepeducation.com
(iii) Goiter: -
Due to deficiency of iodine, thyroxine can’t be secreted. So, pituitary gland se
Due to deficiency of iodine, thyroxine can’t be secreted. So, pituitary gland secretes more and more TSH which enlarges the
Due to deficiency of iodine, thyroxine can’t be secreted. So, cretes more and more TSH which enlarges the

www.nepeducation.com
thyroid gland and leads to goiter. It can band myxedema.
2. Hyperthyroidism: -
The phenomenon of oversecretion by the thyroid gland is called hyperthyroidism or thyrotoxicosis..
Grave’s disease or Exophthalmic goiter:
· Bulging of eye-balls. · The enlarged thyroid is overactive and secretes excessive amount of
thyroxine. · High metabolic rate. · Rapid heart rate. · Rise in body temperature.
thyroid gland and leads to goiter. It can be followed by cretinism
The phenomenon of oversecretion by the thyroid gland is called hyperthyroidism or thyrotoxicosis..
disease or Exophthalmic goiter: -
It is caused by hyperthyroidism.
The enlarged thyroid is overactive and secretes excessive amount of
Rise in body temperature.
e followed by cretinism
The phenomenon of oversecretion by the thyroid gland is called
It is caused by hyperthyroidism.
The enlarged thyroid is overactive and secretes excessive amount of


![New {Anatomy/ Lec 6}————Thyroid gland / part 2Edited by : Rua’a … · 2020. 5. 9. · * Thyroid gland has to migrate from site of origin [ between future parts of tongue]](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/605360ddde603a02de4f5d5e/new-anatomy-lec-6aaaathyroid-gland-part-2edited-by-ruaaa-2020.jpg)