Neuron Structure and Function Relationship between Stimuli Input Nervous System Organization
The Nervous System. Key Concepts Muscle Motor Neuro n Interneuron Skin receptors Sensory Neuron...
-
Upload
shonda-bond -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of The Nervous System. Key Concepts Muscle Motor Neuro n Interneuron Skin receptors Sensory Neuron...

The The Nervous Nervous SystemSystem

Key ConceptsKey Concepts
Muscle
MotorNeuron Interneuron
Skin receptors
SensoryNeuron
Brain
Know the function and Know the function and divisions of the nervous divisions of the nervous system (CNS & PNS)system (CNS & PNS)
Describe the structure of a Describe the structure of a neuronneuron
Identify and know the Identify and know the function of the three types function of the three types of neurons and the of neurons and the describe neurotransmissiondescribe neurotransmission
Know the main parts of the Know the main parts of the brain and explain their brain and explain their functionsfunctions
Identify the lobes of the Identify the lobes of the cerebral cortexcerebral cortex

Funtion of the Nervous Funtion of the Nervous SystemSystem
Receive Receive information information externally and externally and internallyinternally
Respond to stimuliRespond to stimuli Maintain stable Maintain stable
internal conditions.internal conditions.

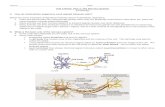
NeuronsNeurons
Neurons are the cells that Neurons are the cells that carry nerve impulses carry nerve impulses through your nervous through your nervous systemsystem
There are 3 kinds of There are 3 kinds of neuronsneurons Interneuron -connects motor Interneuron -connects motor
and sensory neurons; what and sensory neurons; what the brain is mostly made ofthe brain is mostly made of
Sensory – picks up stimuli Sensory – picks up stimuli from internal and external from internal and external sourcessources
Motor – sends message to Motor – sends message to muscle to produce an action muscle to produce an action or movementor movement

Neuron StructureNeuron Structure A neuron is made up of 3 A neuron is made up of 3
main partsmain parts Cell body – where the Cell body – where the
nucleus and organelles are nucleus and organelles are foundfound
Dendrites – extensions Dendrites – extensions that pick up nerve that pick up nerve impulses and carry to the impulses and carry to the cell bodycell body
Axon – carries the nerve Axon – carries the nerve impulse away from the cell impulse away from the cell body and to another body and to another neuronneuron
Nerve impulses travel in Nerve impulses travel in only ONE directiononly ONE direction

NeurotransmissionNeurotransmission1.1. Message travels form the Message travels form the
dendrites through the cell dendrites through the cell body and to the end of the body and to the end of the axon.axon.
2.2. The message causes The message causes chemicals, neurotransmitters, chemicals, neurotransmitters, to be released from the end of to be released from the end of the axon into the space the axon into the space between the axon of one between the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of neuron and the dendrites of anotheranother
3.3. The neurotransmitters then The neurotransmitters then travel across the synapse on travel across the synapse on the the receptors receptors on the on the dendrites of another neuron.dendrites of another neuron.
4.4. Once the neurotransmitters Once the neurotransmitters have attached to the have attached to the receptors the impulse is receptors the impulse is passed on.passed on.
5.5. The neurotransmitters are The neurotransmitters are released from the receptors.released from the receptors.

Divisions of the Nervous Divisions of the Nervous SystemSystem
Central Nervous System (CNS)Central Nervous System (CNS) BrainBrain Spinal cordSpinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) All of the nerves located OUTSIDE of All of the nerves located OUTSIDE of
the CNS (senses)the CNS (senses)

Main Parts of the BrainMain Parts of the Brain
CerebrumCerebrum CerebellumCerebellum Brain StemBrain Stem

Peripheral Nervous Peripheral Nervous SystemSystem
Consists of a Consists of a network of nerves network of nerves that branch out that branch out from the CNS.from the CNS. Somatic system – Somatic system –
control voluntary control voluntary actionsactions
Autonomic system Autonomic system – controls – controls involuntary actionsinvoluntary actions

ReflexReflex
Automatic Automatic response that response that occurs very occurs very rapidly without rapidly without conscious controlconscious control Nerve impulse Nerve impulse
goes to spinal goes to spinal cord but NOT the cord but NOT the brain; helps to brain; helps to speed up the speed up the reactionreaction