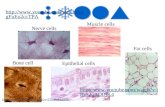
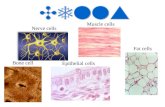
The Muscular System. Muscle tissue overview All muscle cells are elongated, thus, all muscle cells,...
-
Upload
shannon-ward -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
4
Transcript of The Muscular System. Muscle tissue overview All muscle cells are elongated, thus, all muscle cells,...
- Slide 1
- The Muscular System
- Slide 2
- Muscle tissue overview All muscle cells are elongated, thus, all muscle cells, regardless of type, are called muscle fibers The ability of muscle to shorten or contract depends on 2 types of myofilaments Prefix: -myo/mys: muscle -Sarco: flesh
- Slide 3
- Muscle Types skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle attached to bone;walls of heart; Muscle type: Body location: walls of hollow organs; single, very long multi- cylindrical, multi- nucleatestriations nucleate, striations; branching chains, uninucleate striations uninucleate, striations; Single, spindles, uninucleateno uninucleate, no striations striations; Cell Shape: Regulation of Contraction: voluntary voluntary, nervous system controls; involuntary involuntary, ner- vous system controls, hormones; involuntary involuntary, ner- vous system controls, hormones, chemicals, stretch; Contraction Speed/Rhythmic : Slow to fast/no; Slow/yes; Very slow/some
- Slide 4
- Skeletal Muscle Key words: Skeletal, Striated, Voluntary
- Slide 5
- Skeletal Muscle Skeletal muscle fibers: are packed into the organs called skeletal muscles that attach to the bodys skeleton Skeletal muscle fibers are cigar-shaped, multinucleate cells, and are the largest of the muscle fiber types It is also known as striated muscle because its fibers appear to be striped It is also known as voluntary muscle because it is the only muscle type subject to conscious control Skeletal muscle tissue can contract rapidly and with great force, but it tires easily and must rest after short periods of activity
- Slide 6
- Connective tissue wrapping Each muscle fiber is enclosed in a delicate connective tissue sheath called an endomysium A bundle of muscle fibers called a fascicle are surrounded by a connective tissue called the perimysium A bundle of fascicles are surrounded by a connective tissue called the epimysium
- Slide 7
- Tendons The epimysia blend into the strong, cordlike tendons Tendon connects muscle to bone Tendons provide durability and conserve space
- Slide 8
- Cardiac Muscles Key words: Cardiac, striated, uninucleate, involuntary, heart
- Slide 9
- Cardiac Muscle Is found only in the heart Cardiac muscle is like skeletal muscle in that it is striated and like smooth muscle in that it is involuntary and cannot be consciously controlled by most of us Cardiac muscle fibers are branching cells joined by special junctions called intercalated disks
- Slide 10
- Cardiac Muscle The cardiac muscle is cushioned by small amounts of soft connective tissue and arranged in spiral or figure 8 bundles Cardiac muscle usually contracts at a fairly steady rate set by the hearts pacemaker, but can also be stimulated by the nervous system
- Slide 11
- Smooth Muscle Key words: smooth, visceral, involuntary, uninucleate, non-striated
- Slide 12
- Smooth Muscle Smooth muscle has no striations and is involuntary Found in the walls of hollow visceral organs such as the stomach, urinary bladder etc.
- Slide 13
- Smooth Muscle Smooth muscle cells are arranged in 2 layers: -One layer runs circularly -The other running longitudinally The two layers alternately contract and relax, and this changes the size and shape of the organ, resulting in the movement of food, wastes, etc.
- Slide 14
- 4 Muscle Functions stabilizing joints producing movement maintaining posture generating heat walking; swimming; move eyes; Smile Frown move fluid; move food. help reinforce bones that do not articulate well with the skeleton; Ex.: shoulder allow you to stand up straight against the force of gravity. ATP used to cause muscles to contract; ATP energy is lost as heat; This helps maintain body temperature.