The Human Body: The Excretory System Textbook Chapter 34 Review Topic 1.
-
Upload
sophia-small -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
2
Transcript of The Human Body: The Excretory System Textbook Chapter 34 Review Topic 1.

The Human Body:The Excretory System
Textbook Chapter 34
Review Topic 1

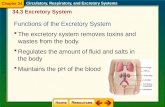
Function
• Removes toxins and wastes which build up in the body as a result of metabolism
• Regulates the amount of fluid and salts in the body and maintains pH of the blood
• Helps regulate homeostasis

Parts
• Lungs• Excretes carbon dioxide
• Skin• Excretes water and salts contained in sweat
• Kidneys• Major excretory organ in the body

Kidneys
• Bean-shaped
• Filters out wastes, water and salts from the blood
• Two regions• Renal cortex ~ outer region• Renal medulla ~ inner region

• Contains microscopic tubules and blood vessels
• Renal pelvis ~ center of kidney where these filters are found

• Nephron filtration
• Each kidney has 1 million filtering units called nephrons
• Blood enters each Nephron through a long tube surrounded by capillaries called a glomerulus
• Surrounded by the Bowman’s capsule


• Renal artery transports nutrients and wastes to the kidney
• Branches into smaller blood vessels forming the glomerulus
• Blood vessel walls are thin and under high pressure

• Urea ~ nitrogenous waste product containing water and substances dissolved in water
• Pushed through capillary walls into the Bowman’s capsule
• Red blood cells and proteins are too large and remain in the blood stream

• Reabsorption/formation of urine
• Filtrate collects in the Bowman’s capsule and flows through renal tubules (loop of Henle and collecting tubule)
• Most water and useful substances (ex. glucose, minerals) are reabsorbed back into blood stream (reabsorption)


• Excess fluids and toxic substances are collected to form urine
• Leaves the kidneys through ducts called ureters
• Urine is stored in the urinary bladder
• Exits the body through the urethra


• Each kidney filters 180 L of blood a day in adults to produce 1.5 L of urine
• Process requires large amounts of energy
• Use 20-25% of your body’s oxygen intake for their internal energy requirements!
• Controls pH balance by absorbing or filtering out acids or bases to regulate pH of the blood

• Urinary System BrainPop

Kidney Disorders• Infections
• Start as bladder infections which spread to kidney
• Fever, chills, mid-/lower-back pain
• Can be caused by blockages
• If untreated, kidneys can scar causing a loss in function
• Can be treated with antibiotics

• Nephritis• Inflammation (painful swelling) of the
glomeruli
• Cause by blockages
• Blood in urine, swelling of body tissues, protein in urine
• Can improve on its own but may require a special diet or prescription drugs to treat the infection

• Kidney Stones• Crystallized solid (calcium compound) which
forms in the kidney
• Small stones can be passed out in urine
• Larger stones are broken up using ultrasonic sound waves or removed using surgery


• Diabetes/High Blood Pressure• Causes reduced kidney function or kidney
failure
• Illegal/Prescription Drugs• Can cause kidney damage

Treatments
• Dialysis• An artificial
kidney machine
filters out wastes
and toxins from
a patient’s blood

• Two types• Blood is passed through the machine
temporarily to be filtered and cleaned, then returned (3-4 hours/3 days week)
• Membrane lining the abdomen acts as an artificial kidney by injecting it with a special fluid through a small tube attached to the patients body to collect draining wastes (30-40 min/daily)