Temperate Forest
description
Transcript of Temperate Forest

NORA DESIMONE
Temperate Forest

Temperate Forest
Subgroups: Temperate coniferous
forests Temperate broadleaf
and mixed forests Deciduous forests

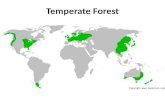
Where is this biome located?
United States CanadaEuropeChina JapanRussia

Climate
Four different seasons Summer is warm and wet
4-6 months Fertile Vegetation
Winter is cold Temperatures usually don’t drop below -2 °C Not as cold as higher elevations
No dry season Second rainiest biome 75-150 cm a year
Average temperature is 50°

Plants
Trees Deciduous
lose leaves during winter Maples, oaks, chestnuts, beeches, elms
Temperate Deciduous Forest 5 layers Stratum, small tree, shrub, Herb, Ground
Coniferous Leaves are needles Also called evergreens
Pines, firs, cedars Broad-leaved evergreens
New Zealand, Australia, South America Flat, leathery leaves, waxy
Olive, holly, tea, eucalyptus

Plants
Other trees: Sycamore Oak Aspen Walnut tree Lime tree Chestnut tree Birch Elm Tulip tree

Animals
Squirrels Brown bears Badgers Hedgehogs Deer Bobcats woodpeckers Birds Ant Bat Bison Coyote Fox Tit (bird) Tiger

Animals Plants
SeasonsCold winters
Heavy fur coats Hibernation
Squirrels, chipmunks, jays store nuts and seeds
migration Hot summersPredators
Decidious forests have leaves not pine needles Lose leaves and grow them back
In the summer: broad green leaves capture sunlight and perform photosynthesis
Cool temperatures in the fall: leaves turn yellow, orange, red
Winter: lose leaves, seal up the spots where the leaves attach to the branch
Adaptations

Food web

Human Impacts on biome
Deforestation Timber Paper Good land for farming Etc.
Killing animals Affecting food chains
PollutionAcid rain

Bibliography
"World Biomes: Temperate Forest." Kids Do Ecology. 2004 Kids Do Ecology, n.d. Web. 13 Feb 2014.http://kids.nceas.ucsb.edu/biomes/temperateforest.html
"List of Temperate Forest Animals." Skyenimals. Skyenimals. Web. 13 Feb 2014.http://www.skyenimals.com/browse_habitat.cgi?habitat=temperate_forest "Temperate Forest Biome." Eniscuola. Eni S.p.A. Headquarters,. Web. 13 Feb 2014.http://www.eniscuola.net/en/ecosystems/contenuti/temperate-forest/left/temperate-forest-biome/plants-of-the-temperate-forest/ "Temperate Forests." GRID-Arendal. GRID-Arendal, n.d. Web. 13 Feb 2014. http://www.grida.no/graphicslib/detail/temperate-forests_1753# "Impacts." Temperate Broadleaf Forest. N.p.. Web. 13 Feb 2014.http://leavesittous.weebly.com/human-impacts.html
Mobley, George F.. "Brown Bear." National Geographic. National Geographic Society, n.d. Web. 13 Feb 2014.
http://animals.nationalgeographic.com/animals/mammals/brown-bear/
"Temperate Forests." Glossopedia. GLOBIO, n.d. Web. 13 Feb 2014. http://test.glossopedia.org/temperate-forest/