Technical drawing
-
Upload
meheng1001 -
Category
Education
-
view
660 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Technical drawing

www.topcadservices.com
PRESENT article
CAD Technical Drawing for engineers and
technicians.
1.Technical drawing for engineers and
technicians.
In a few words, Technical Drawing is a discipline
for visual communication, which can also show
us how something functions and how it’s
constructed and designed. Internationally
knows as drafting. A Technical Drawing is an
excellent way for engineering communication.
Most designers, architects, engineers,
technicians use this discipline for work and
communicating between them.
There are many standards, symbols, units and
ways of presentations. People who make these
drawings are known as drafting technicians.
Depending on the discipline (architecture,

engineering, design), there are lots of methods
of drawing and sketches.
Explaining for technical drawing.
Let we explain what is technical drawing by
example of two PARTS(they are mechanical
parts but excellent examples for explanation).
First one is a holder and is a symmetrical part
and second is a tail pipe and is not symmetrical
part. We can explain them by presentation of:
-Three views(2D drawing);
-Axonometric view in 3D presentation.
No matter how complex are technical drawings
of the parts are symmetrical and not
symmetrical pieces.
System of lines are used for drawing a technical
drawing
Lines used for the preparation of the technical
drawing are following:
Thick lines are used for drawing the outline;
Thin line is used for hatch, dimensioning and

placement of symbols;
Center line is used for showing symmetry.
Dashed line is used for drawing invisible parts
in the respective views and drawings.
On the images below we can clearly see the
lines, type and weight too.
The first example is a three-view model of an
object, in this case, a part holder, which is a
mechanical engineering drawing. We can see
that the object is symmetric, that’s why we use
the three-view in 2D presentation. A standard
technical drawing of an object is in 2D which
shows the three views (upper or bottom,
frontal and side view), and in some cases if

necessary, an extra detail is shown.
Axonometric view is the 3d presentation. On
the images below we can clearly see the 2D and
3D presentation.
The three views. On the upper left we can see
the frontal view, bottom left is the top view and
on the right side the side view is shown with a
cross section.
At not symmetrical parts we use the six-view in
2D presentation. Technical drawing of an object
is in 2D which shows the six views (top view,
bottom view, frontal view, left side view, right
side view, back view), and in some cases if

necessary, an extra detail is shown.
Axonometric view is the 3d presentation also.
On the images below we can clearly see the 2D
and 3D presentation.
2.Section views.
Section views. There are several types of
section views: cross-section view, half section
view, quarter section view partial selection

view and etc. We use some of them depending
on the drawing.
Cross section view is used to show the holes,
lines, details that can not be seen in all of the
three views. On the drawing, there is one
section view that shows us the big hole where a
circle profile will pass through.
A partial cross section is shown in the frontal
view, on the lower right, that helps us see the
small hole where probably ll entered some
screw. Therefore, we are using partial cross-
section to show some elements that can not be
seen even if we make a cross-section view.(Also
we can see the section view on the images up).
3.Dimensions-Elevations
Dimensions are used to show us the length,
width, the bending of a line and etc.
Dimensions also tell us the intensity of an
angle, diameter of a circle and other
geometrical features. Difference is made by the

shape of the head of the dimension or knows as
elevation – kota. So there are many types like:
architectural, engineering, designers, geological
and e.t.c
Information on measures subjects enrolled in
numerical form, the drawing and thus its
transmission becomes independent of the
accuracy of the drawing. Parts drawings that
contain information on measures objects are
called elevations. Elevation consists of the
following elements:
-Number of elevation;
-Arrow;
-Measuring lines and;
-Auxiliary measurement lines.

Number of elevation dictate items action. They
are entered with the technical writing above
surveyors around the middle. So that they can
be read from the bottom to up and from the
left to right. One should avoid drawing
measures with other measures, and auxiliary
measuring lines narrower wheel closer and
further from the edge of broader subjects,
including the spacing between parallel
surveyors must be steady and sufficient for
registration numbers. Dimensions number, not
cross any other line. Size of the witness
numbers depends on the nominal line width,
but at least 2.5 mm.

Arrows determine for where to where is some
measure. They must not exceed the auxiliary
measuring lines or edges. Typically drawing a
line in the auxiliary measurement or edges, and
exceptionally, if there is not enough space for
them they are drawn from outside. In the case
of repeated dimensioning, when there is not
enough space inside, the arrows are replaced
by a dot. Dimensions arrows depend on the
nominal width of the line.
Measuring lines is a line parallel with the
length of which indicates surveyors measure
can not be replaced by another line. The
spacing between parallel surveyors must be
steady and sufficient for registration numbers.
The distance should not be too small between
surveyors and edges.
Auxiliary measuring lines drawn to measure
objects outside the drawing objects. When is it
appropriate solution can be replaced by an
edge case. Can be crossed with all other types

of lines except surveyors. For slightly inclined
edges, if this improves the vividness can be
drawn and skewed.
Dimensioning can be performed in series,
parallel and combined.
In series dimensioning the leader is drawing
mutually parallel, starting from a certain area.
See example in the image below.

Parallel dimensioning consists of entering a
series of individual wheel to continue to one
another. See example in the image below.
Combined dimensioning is a combination of
the previous two methods and is most
commonly used. See example in the image.

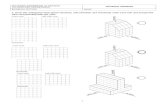
Level dimensioning in section view and in floor
plan is made with symbols shown at the image.
They show the height in cross section and in
floor plan. See example in the images below.

Make comparison about the dimension style. In
first two images below are mechanical, next
two images are architectural-construction.


3.PARTS
A standard technical drawing of an object is in
2D which shows the three views (upper or
bottom, frontal and side view), and in some
cases if necessary, an extra detail is shown.
Axonometric view is the 3d presentation. On
the images below we can clearly see the 2D and
3D presentation.
At not symmetrical parts we use the six-view in
2D presentation. Technical drawing of an object
is in 2D which shows the six views (top view,
bottom view, frontal view, left side view, right
side view, back view), and in some cases if

necessary, an extra detail is shown.
Axonometric view is the 3d presentation also.
On the images below we can clearly see the 2D
and 3D presentation.
4.ASSEMBLY
Assembly, the act of combining components in
manufacturing.
Assembly is also technical draw. Represents
combination of parts combination of pieces
interlinked.
For assembly is necessary to connect at least

two parts that will work mutually.
On the images below we can clearly see some
assembles.

VISIT US CLICK HERE TOPCADSERVICES
Read more:
http://www.topcadservices.com/2012/tehnical
-drawing/#ixzz2rq6T20y6