Properties of Sound Making Waves. Sound Waves ■Sound is created by vibrations.
SOUND # Vibrations & Waves & Sound When things vibrate, they move the air and create sound waves...
-
Upload
chris-grundy -
Category
Documents
-
view
233 -
download
1
Transcript of SOUND # Vibrations & Waves & Sound When things vibrate, they move the air and create sound waves...

SOUND

#
Vibrations & Waves & Sound
• When things vibrate, they move the air and create sound waves
• Music, talking, sirens, etc.

#
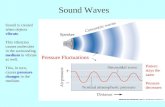
Sound waves begin as vibrations. As an object vibrates forward it pushes air
molecules together forming a compression and as it moves backward the air molecules are less dense creating a rarefraction.
As the vibrations continue they create a series of compressions and rarefractions in waves.
Sound waves are longitudinal: the air molecules virbate parallel (in the same direction) as the wave moves.
Sound Waves

#
Sound waves that can be heard by human ears are audible waves and have frequencies ranging from 20 Hz to 20 000 Hz. Sound waves below 20 Hz are called infrasonic;
elephants can hear infrasonic waves. Sound waves above 20 000 Hz are called
ultrasonic; dogs can hear ultrasonic waves.
Characteristics of Sound Waves

#
Sound Waves
Molecules in the air vibrate about some average position creating the compressions and rarefactions. We call the frequency of sound the pitch.

#
Sound Waves

#
Pitch is the highness or lowness of sound; as frequency increases, pitch increases; as frequency decreases, pitch decreases.
Pitch and frequency are conversely proportional. Pitch cannot be measured but frequency can be measured (in Hertz)
Intensity-the rate at which energy is transferred from one air molecule to the next
Intensity decreases with distance-this is why the intensity of an echo is less than the intensity of the original sound
Characteristics of Sound Waves (cont’d.)

#
Speed of sound depends on: Type of medium: sound travels faster in solids because
the molecules are closer together, making it easier to “bump” each other.
Temperature (of gases): As temperature increases molecules are moving faster, colliding more often, therefore sound travels faster in high temperatures in gases. Temperature makes little difference in solids and liquids.
Characteristics of Sound Waves (cont’d.)

#
Sound
Now consider your ear
Eardrum vibrates
Nerves tell brain “sound!”

#
Speed of Sound• Depends on the material of the vibrating
medium• Sound can vibrate water, wood (speaker
enclosures, pianos), metal, plastic, etc.• Faster in warm air, slower in cold• Water 4 times faster, steel 15 times
faster

#
Wave Reflection
• When a sound wave reflects from a surface we generate an echo
• Wave reflection from surfaces depends on the characteristics of the surface
• Smooth hard surfaces reflect best• Rough soft surfaces reflect poorly• Energy not reflected is absorbed or
transmitted through the material

#
Wave Refraction• If there is a change in the characteristics
of a medium, waves are bent• This occurs because different parts of the
wave front travel at different speeds• Think of a marching around a curved track
• The inside people have to move more slowly than the outside people to keep the lines straight

#
Wave Refraction

#
Natural Frequencies
• Objects have “natural” frequencies based on their size and structure
• Guitar strings are an example

#
Forced Vibrations
• Can externally impose a vibration on an object
• Guitars and violins and pianos• Set the wood into motion at the frequency
of the string• This provides a larger surface to interact
with the air• Harp vs. Piano

#
Resonance
• When the forced vibration matches a natural frequency we get a “resonance” condition
• Think about a swing on a playground
• You go high when you pump the swing at its natural vibration frequency

#
What is Resonance?
Many objects have a natural frequency – vibrates in a regular pattern.
Resonance occurs whenever a sound wave has the same frequency as the natural frequency of an object. The sound will cause the object with the same natural frequency to vibrate.

#
What is sound intensity?
Sound intensity is the energy that the sound wave possesses. The greater the intensity of sound the farther the sound will travel and the louder the sound will appear.
Loudness is very closely related to intensity. Loudness is the human perception of the sound intensity. The unit for loudness is decibels.

#
How is frequency related to pitch?
The pitch of a sound wave is directly related to frequency. A high-pitched sound has a high frequency (a screaming girl). A low-pitched sound has a low frequency (a fog-horn).

#
What is the Doppler Effect?
The Doppler Effect is the apparent change in frequency detected when the sound is moving relative to the hearer.
Video-Excellent example of Doppler Effect with car horn (26 seconds)
Video-A Motorcycle does the Doppler Effect (27 seconds)



![17.2 Sound Waves: In Halliday and Resnick: Longitudinal waves are sound waves! Chapter 17: [Sound] Waves-(II) Sound waves propagate in gases. Can they.](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/56649eb25503460f94bb9375/172-sound-waves-in-halliday-and-resnick-longitudinal-waves-are-sound-waves.jpg)