slide 3 surgery thyroid
-
Upload
eman-nazzal -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of slide 3 surgery thyroid
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
1/53
Thyroid diseases
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
2/53
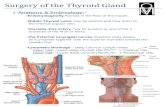
Thyroid Anatomy
1. Endocrine gland2. Normally extends from ~ C-5
through ~ T-1
3. Highly vascular
4. Weights ~20 - 30 grams
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
3/53
Thyroid, Detailed Anatomy, continued
5. Pyramidal lobea. present in ~ 33% of population.
b. Extends upward from isthmus
c. anterior to thyroid cartilage
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
4/53
The Thyroid Gland
Located in theanterior region of
the neck This gland has an
accessory(pyramidal) lobe
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
5/53
Thyroid, General Information, continued
8. Isthmus crosses trachealcartilages 2-4
9. Base located ~4-5th tracheal cartilage
10. Thyroxin function: regulates basic
metabolism in all cells
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
6/53
Thyroid Gland, Anterior and Posterior Views
Thyroid Gland: anterior view (left); and posteriorview (right)
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
7/53
Thyroid, Detailed Anatomy, continued
c. Lobes:1. Attached to cricoid cartilage
by ligaments
2. Medial surface adapted to
larynx and trachea
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
8/53
Thyroid, Detailed Anatomy, cont
d. Isthmus
1. 1.25 cm x 1.25 cm
2. Crosses @
tracheal rings ~2-4
3. Occasionallyabsent
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
9/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
10/53
Histology
Functional unit of thyroid gland is thethyroid follicle
cuboidal epithelial cells surrounding
colloid filled lumen
active follicles are smaller
responsible for thyroid hormone
synthesis Parafollicular C Cells (Clear cells)
secrete calcitonin
respond to serum ionized calcium levels
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
11/53
Embryology
Thyroid gland is derived frominvagination of endoderm of firstbranchial pouch near lingual bud
Grows inferiorly around the hyoid toanterior trachea
remnant is thyroglossal duct
Aberrent thyroid tissue can belocated anywhere along thyroglossalduct
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
12/53
Embryology
Parafollicular Cells are of differentorigin than thyroid follicular cells
these cells originate from
ultimobranchial apparatus near inferiorportion of pharyngeal pouch
ultimobranchial organ seen in lower
vertebrates as a separate organ
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
13/53
Physiology
Primary function of the thyroid glandis the secretion of thyroid hormones
T4 is primary released hormone
T3 at least 10 times more active
T4 is converted to T3 peripherally
Production of thyroid hormones isregulated in normal gland by thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH) from theanterior pituitary gland
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
14/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
15/53
Physiology
Thyroid Hormone Secretion:
TSH joins follicular cell receptor, then:
cAMP mediates:
active transport of iodide
synthresis of thyroglobulin (TG) by ER
Thyroperoxidase (TPO) mediates:
conversion of iodide to iodine coupling of iodine to tyrosine and TG
(colloid)
Lysosymes release T4/T3
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
16/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
17/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
18/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
19/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
20/53
Ultrasound
Used to establish the size & shape ofthe gland .
May indicate if nodules are single ormultiple.
It will distinguish between cystic &solid lesions. (intrathyroid lesion)
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
21/53
Radioisotpe scan
Single or multiple nodules .
Over functioning (hot nodules) ornon-functioning (cold nodules)
20% of cold nodules are malignant
Hot nodules .rarely malignant
Hot n Cold n
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
22/53
FNA
Should be performed in the investigation of all
thyroid nodules.
Distinguish between a solid lesion & a cyst
If the lesion is solid.cells are sent for
cytological examination If the lesion is a cyst .then the fluid can be
removed
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
23/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
24/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
25/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
26/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
27/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
28/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
29/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
30/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
31/53
Hypothyroidism - Primary
Autoimmune Diseases are the mostcommon cause of hypothyroidism
Hashimotos Thyroiditis
Graves disease (usuallyhyperthyroidism)
Iatrogenic causes are the next most
common causes Surgery, radioiodine ablation,
inadequate replacement, Li,
Amiodarone, iodide
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
32/53
Hypothyroidism - Congenital
Cretinism
severe hypothyroidism in the newborn
PE: protuberant abdomen, face, flat
nose, yellow skin, constipation,lethargy, feeding difficulties, hoarse, MR
Endemic: goiter present. Maternal IgG
or maternal antithyroid medications Sporadic: thyroid agenesis (Di George
syndrome most common)
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
33/53
Treatment
thyroxine
to render the patient euthyroid normal dose 75-150 ug
TSH cheacked every 12-18 months
liothyronine(T3) is an alternative
elderly patient with ischemic heart disease
starting at 25ug & dose every fortnight
(to avoid tachyarrhythmias & cardiac failure)
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
34/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
35/53
Common Signs and Symptoms
of Hyperthyroidism
Nervousness
Irritability
Difficulty Sleeping
Bulging Eyes
Unblinking Stare
Goiter
Rapid Heartbeat
Increased Sweating
Heat Intolerance
Unexplained Weight Loss
Scant Menstrual Periods
Frequent Bowel
Movements
Warm, Moist Palms
Fine Tremor of Fingers
May Include:
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
36/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
37/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
38/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
39/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
40/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
41/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
42/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
43/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
44/53
Thyroiditis - Continued Acute Suppurative Thyroiditis
Bacterial infection, usually S. aureus orS. pneumo. Usually preceded bytrauma
Tx: IV abx, I and D if abscess Painful Thyroiditis (de Quervains)
Unknown virus
Painful thyroid following URI Hyperthyroidism followed by
hypothyroidism - lasts 2 month
Tx: beta blockers/thyroxine, supportive
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
45/53
Thyroiditis, Continued
Postpartum Thyroiditis
Silent thyroiditis of pregnancy andfirst few postpartum months
Associated with Graves disease andother autoimmune diseases
Tx: beta blockers/synthroid as needed
Usually self limiting, but high titers ofantibodies heralds long term disease
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
46/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
47/53
Hashimotos Disease, Cont.
Histology: Askanazy changes-predominant lymphocytes withgerminal centers. Scant follicles
Tx:
Hypothyroid patients: synthroid
Hyperthyroid: antithyroid medications
Surgery reserved for failure ofsuppression or suspicion of lymphoma
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
48/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
49/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
50/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
51/53
Thyroid Diseases
Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Uncommon
Can run in families
Good cure rate
Intermediate
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
52/53
-
7/29/2019 slide 3 surgery thyroid
53/53