Sensory and Motor Mechanisms – chpt 49-. I. Anatomy & physiology of Muscular system n A. 3 types...
-
Upload
bartholomew-collins -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Sensory and Motor Mechanisms – chpt 49-. I. Anatomy & physiology of Muscular system n A. 3 types...

Sensory and Motor Mechanisms – chpt 49-
Sensory and Motor Mechanisms – chpt 49-

I. Anatomy & physiology of Muscular systemI. Anatomy & physiology of Muscular system
A. 3 types of muscle tissue
– 1. skeletal muscle aka striated muscle– a. attached to bone b. responsible for movement c. looks “striped” through the microscope
– 2. smooth muscle tissue a. lines walls of blood vessels & dig sys. b. non-striated so muscle contraction is
slower & more controlled

3. cardiac muscle – heart muscle
– a. produces its own action potential (doesn’t need to be stimulated by a neuron)

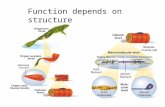
B. Anatomy of a muscleB. Anatomy of a muscle 1. muscle built of muscle cells called muscle
fibers 2. muscle fibers (myofibers) are not typical cells
– a. long, thin, multinucleate– b. cell membrane = sarcolemma
1) sarcolemma is highly invaginated with transverse tubules (t-tubules)
– c. cytoplasm = sarcoplasm– d. ER = SR – sarcoplasmic reticulum

3. muscle fiber loaded with myofibrils made of filaments
– a. actin - thin, light-stained, globular protein1) 2 strands in a double helix2) troponin & tropomyosin cover binding
sites
– b. myosin – thick, darker-stained, fibrous protein1) each filament has a protruding head at
one end2) an array of myosin filaments has
multiple heads at each end



sarcomeresarcomere

Video muscle actionVideo muscle action Contract/relax: antagonistic pairs
w/skeleton Muscles: bundle of…. Muscle fibers: single cell w/ many
nuclei consisting of…. Myofibrils: longitudinal bundles
composed of…. Myofilaments:
•Thin~ 2 strands of actin protein and a regulatory protein •Thick~ myosin protein
Sarcomere: repeating unit of muscle tissue, composed of….
Z lines~sarcomere border I band~only actin protein A band~actin & myosin protein overlap H zone~central sarcomere; only myosin

C. Micromuscular movement/contractionC. Micromuscular movement/contraction
1. Muscle cells contract only when stimulated by motor neuron
2. When not stimulated the binding sites on the actin are blocked by a protein call tropomyosin
3. A second protein – troponin- controls position of tropomyosin
4. For a muscle cell to contract the myosin binding sites on the actin must be exposed


5. Occurs in each muscle fiber after it’s been stimulated by a nerve
– a. gap between neuron & muscle fiber – neuromuscular junction – is bridged by acetylcholine – a neurotransmitter
– b. acetylcholine causes the electrical charge on muscle fiber membrane to change – change is due to ions on inside & outside of cell membrane (sarcolemma)

– 1) before stimulated – membrane resting potential
– 2) after stimulation – membrane acting potential
c. membrane becomes permeable to Na+, so Na+ moves into cell
d. Na+ in cell triggers the SR to release Ca++
e. Ca++ bonds w/ troponin which changes the shape of tropomyosin THUS uncovering the myosin binding site on the actin

Muscle contraction regulationMuscle contraction regulation

1- Myosin head hydrolyzes ATP to ADP --splits ATP (into ADP & Pi inorganic phosphate) through the addition of a water molecule
2- Myosin head binds to actin; termed a “cross bridge”
3- This causes the release of ADP and Pi myosin relaxes into its “low E” state & this allows the actin to slide
4- Binding of new ATP releases myosin head
D. Actin-myosin interactionD. Actin-myosin interaction

5. Sliding-filament model-Process of muscle contraction
– a. Sarcomere length reduced
– b. Span from 1 Z-line to the next becomes shorter
– c. Actin and myosin slide past each other (overlap increases)