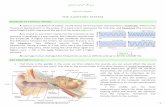
S 319 < Auditory system >
-
Upload
madaline-leon -
Category
Documents
-
view
27 -
download
5
description
Transcript of S 319 < Auditory system >

S 319 < Auditory system >
• Focus:
- Anatomy and function of the ear
- Sound transfer function of ear:
When sound is conducted into the ear, how sound is affected by that process

•
Outer earMiddle earInner ear

Four major divisions of auditory system - Anatomy
1. The outer ear - pinna - ear canal - eardrum
2. The middle ear - three ossicle bones;
(malleus, incus, stapes) - two major muscles (stapedial muscle, tensor tympani) - Eustachian tube
3. The inner ear - cochlea (hearing) - vestibular system (balance)
4. The central auditory system

Four major divisions of auditory system – Function(CD, Figure 3.4.1)

I. Outer ear (CD, Figure 3.4.2)
• Three parts of outer ear
1) Pinna
2) Ear canal
3) Ear drum
• Major function of outer ear 1) protection
2) amplification
3) sound localization

I. Outer ear: (1) Pinna (Binaural cue to sound source
location)
t Left
t Right
* Different distances from source to each ear => different arrival times (Interaural time-difference) and different sound level (interaural level-difference)
Rightear
Left ear
Sound

I. Outer ear: (1) Pinna (Spectral cue to sound source location)
Ou
ter
ear
gain
-15°
0°
+15°
The spectral feature of sound is changed depending on the sound elevation=> Head Related Transfer Function (HRTF)

I. Outer ear (1) Pinna: Cases of abnormal pinna
• Anotia • Microtia (Grade I)
• Microtia (Grade II) • Microtia (Grade III)

I. Outer ear: (2) Ear canal (CD, Figure 3.4.4)
• Three parts of outer ear
1) Pinna
2) Ear canal
3) Ear drum
• Major function of outer ear 1) protection
2) amplification
3) sound localization

I. Outer ear: (2) Transfer function of ear canal
From Gelfand (1998)

I. Outer ear: (3) ear drum (CD, Figure 3.4.5)
•
.
Major function of outer ear : As a boundary between outer and middle ear: Vibrates in response to sound
Three-dimensional finite element method (FEM) analysis of the middle ear http://www.wadalab.mech.tohoku.ac.jp/FEM_mid-e.html#fig1

II. Middle ear • Three main parts of middle ear
(1) Three Ossicle bones: - Malleus(1), Incus(3), Stapes(6) Function) Impedance matching
(2) Two muscles - Stapedial muscle(5) - Tensor tympani(9) Function) Protection (3) Eustachian tube(8) Function) Equalizer of air pressure

II. Middle ear (3) Eustachian Tube
• Comparison of Eustachian tubes In adults and children : shorter, smaller, less steep eustachian tube in children => Hard to be drained away from middle ear

II. Middle ear (CD, Figure 3.4.7)
• Middle ear cavity • Function of ossicles
- 99.9% sound is reflected due to high impedance of fluid in the cochlea (0.1% sound is only passed = - 30 dB sound loss from air - fluid impedance mismatch)
- Middle ear bones overcome the loss of sound by increasing sound pressure (+34dB)
=> Impedance matching

II. Middle ear (CD, Figure 3.4.9)
• Three mechanisms for impedance matching
1) Area ratio of the ear drum to the stapes footplate (20:1)
=> 20 log (20/1) = +26dB SPL
* Basic concept: p = f/a
2) Lever action of the ossicles (1.3:1)
=> 20 log(1.3/1) = +2 dB SPL
3) Buckling of ear drum
( x 2 pressure increase
=> 20 log(2/1) = +6dB SPL

II. Middle ear - Impedance matching
In total, 20 x 1.3 x 2 increase in pressure by middle ear and ear drum ( + 34 dB SPL). It works for mismatched impedance It works for mismatched impedance (99.9% sound loss = apx - 30 dB)(99.9% sound loss = apx - 30 dB)
Three-dimensional finite element method (FEM) analysis of the middle earhttp://www.wadalab.mech.tohoku.ac.jp/FEM_mid-e.html#fig6

III. Inner ear (CD, Figure 3.4.11)
• • Twp parts of inner ear 1) Cochlea (Hearing)
- Scala vestibuli
- Scala media - Scala tympani 2) Vestibular system (balance)
• Major function of inner ear 1) Hearing (It transmits sound to neural impulse and gives resonant frequency) 2) Balance

III. Inner ear – Cochlea
perilymph
perilymph
endolymph

III. Inner ear – Resonance of Basilar membrane
Figure 15.32

III. Inner ear – Cochlea
Figure 15.28

III. Inner ear – Inner hair cells (IHC) & Outer hair cells (OHC)
Inner hair cells: produce sensation of hearing
Outer hair cells: modify BM response and act as amplification system

III. Inner ear – Sound transduction

IV. Central auditory system (CD, Figure 3.4.14)
•

IV. Central auditory system
- Auditory pathway to brain
Tonotopy!

Outer ear:Outer ear:Acoustic energy, in the form of sound waves, passes pinna, ear canal. Sound waves hit the ear drum, causing it to vibrate like a drum. Middle ear:Middle ear: It sets three ossicle bones (malleus, incus, stapes) into motion, changing acoustic energy to mechanical energy. These middle ear bones mechanically amplify sound and compensate mismatched impedance. Inner ear and Central auditory nervous system:Inner ear and Central auditory nervous system:When the stapes moves in and out of the oval window of the cochlea, it creates a fluid motion, hydrodynamic energy. It causes membranes in the Organ of Corti to shear against the hair cells.This creates an electrochemical signal which is sent via the auditory nerve to the brain.
Overall, how sound travels through the ear...how sound travels through the ear...

QUESTIONS?