Rheumatic valvular diseases - Dr. S. Srinivasan
-
Upload
pediatricsmgmcri -
Category
Healthcare
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Rheumatic valvular diseases - Dr. S. Srinivasan

Rheumatic Valvular Heart Disease
S . SrinivasanProfessor of Paediatrics
MGMCRI, PlillayaarkuppamPuducherry
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Learning Objectives• To discuss the common etiologies of valvular
stenosis and regurgitation.• To recognize the signs and symptoms of valvular
stenosis and regurgitation• To clinically recognize, identify clinical features
of Rh. Mitral and Aortic Valvular Diseases and their attendant complications
• To offer a plan of investigative work up and interpret a few important findings
• To offer preventive and treatment modalities recommended in treating and preventing complications
• To identify & refer children with RHD for further work up, medical and surgical management
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Rheumatic fever • Inflammatory autoimmune response
triggered by Group A beta-hem. streptococcal pharyngitis
• Children & Adolescents
• Poor SE Status, overcrowding, poor sanitation, developing & underdeveloped countries
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

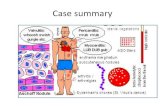
Acute rheumatic Carditis PancarditisENDOCARDITIS MV Insufficiency (65 -100%)
AV Regurgitation (20-30%) TV (10% - ass.with MR,AR or both)
MYOCARDITIS Marked Sinus tachycardia S3; changing Murmurs ; Carey-Coomb’s MDM
Pericarditis Chest pain over the left chest and axillaPericardial Rub on auscultationRarely affects cardiac functionRarely results in large effusions or constrictive pericarditis
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

PREVALENCE RHD IN INDIA ( ECHO proven)
0.67/1000 to 0.12/1000 children(Periwal et al Bikaner) 2006
0.5 per 1000 children(Misra et al. 2003 -2006)
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Genetic studies in RF
Progression to Chronic RHD Strong correlation to:HLA antigen DR class II alleles
Inflammatory protein-encoding genes MBL2 and TNFAGenes
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Chronic Rheumatic Heart Disease in Children & Young Adults
Worldwide occurrence of RHDEstimated occurrence
5-30 million Children & Young Adults
New Cases 2.5 - 3 Lakhs of RHD added every year
Deaths attributed to Chronic RHD
90 Thousands – 2.5 Lakhs / Year
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Rheumatic heart disease
Valvular Stenosis and/or Insufficiency ( Regurgitation)
( structural damage due to fibrosis, thickening, shortening and fusion of valvular cusps and apparatus )
Post Infective ( GpA-ᵦ hemolytic Strep) Autoimmune mediated Cardiac inflammation and scarring
Pancarditis -Myocarditis-Endocarditis & -Pericarditis)
Acute RF Chronic RH Disease
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

RHD• More severe in females than in males
• Mitral Insufficiency of Ac.RF resolves in 60-80% of patients who adhere to antibiotic prophylaxis
• Aortic Regurgitation in 20-30 % of ARF persists in spite of strict adherence to Secondary Rheumatic Prophylaxis
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Rheumatic ( Valvular ) Heart Disease
Permanent structural alterations to heart valve cusps and supporting structures caused by a single or more attacks of ARF.
RHD.: 40-60% of children with ARFValves involved :
-- Mitral > Aortic > TV>PV -- MR(MI) > MR+MS > MS -- MR+AR > MS+AR > AR
-- Rt. Heart Valves in RHD : Rare -- AS of Rheumatic etiology : Uncommon -- ( seen beyond Adolescent age group )
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

EtiologyPathophysiologyHistory & Physical ExamNatural HistoryInvestigative EvaluationComplications Treatment Prevention
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Mitral Regurgitation
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Most commonly observed Murmurs of ARF
Aortic Regurgitation
High-pitched, blowing, decrescendo, early diastolic murmur of Aortic Regurgitation ,heard best along the right upper and mid-left sternal border after deep expiration while the patient is leaning forward.
Apical high-pitched, blowing-quality murmur pansystolic murmur radiating to the left axilla
MV insufficiency
◦ Apical diastolic murmur (also known as a Carey-Coombs murmur) in active carditis and accompanies severe mitral insufficiency
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Mild (physiological) MR: 80% of normal individuals
Mitral Regurgitation
Definition Backflow of blood from the LV to the LA during systole
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Chronic Mitral RegurgitationAge Group
Etiologies
YOUNG Rheumatic MVP Her. Connective Tissue Disorders Ac. Collagen Vascular Disorders
Elderly Rheumatic heart disease Myxomatous degeneration (MVP)
Ischemic MR Infective Endocarditis
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Mitral RegurgitationPathophysiology
Volume OverloadCompensatory Mechanisms
LA enlargementLVH Increased contractility
Progressively increasing VO in Chronic MR
Progressive LA dilation Pulm.Arterial Hypertension RV Dysfunction Progressive LV volume
overload LV dilation Progressive heart failureMGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Mitral Regurgitation Physical Exam findingsSymptoms Exertion Dyspnea (exercise Intolerance)
- Worsening with severity Palpitation ( more marked in combined MS &MR)
Signs Pulse : NV/HV/LV; Irregularly irregular in AF
Precardial prominence, LV type of APEX AuscultationHeart Sounds soft S1; Loud S2 in PAH;
S3 (CHF/LA overload)Murmurs Holosystolic murmur at
the apex radiating to the axilla;-Flow Middiastolic murmur

Rheumatic Mitral Regurgitation: Natural History
Compensatory phase
10-15 years
Asymptomatic severe MR
5%/year mortality rate
Severe Symptomatic MR
Sharp Rise in mortality rate
MR with EF <60%Cause of Mortality
Progressive CHF, Complications of MR like Arrhythmias, Embolism
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Mitral Regurgitation : imaging studies
Chest X-Ray
LA enlargement, Central Pulmonary Artery enlargement
ECG To look for : LA enlargement, Atrial Arrhythmias like Atrial flutter, fibrillation and LVH
ECHO To estimate LA, LV size and functionTo assess valve structure
TEE inconclusive transthoracic ECHO
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Mitral Regurgitation-Medical Management
1. Hydralazine & other Vasodilators
2. -blockers, CCB, digoxin : To control Heart Rate in atrial fibrillation with MR
3. Anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation and flutter
4. Diuretics for fluid overloadMGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Management of MR• Serial Echocardiography: – Mild: 2-3 years– Moderate: 1-2 years– Severe: 6-12 months
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

IE prophylaxis Dental procedures Prosthetic valves
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

MR: Surgical Indications
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

MR: Important Indications for MV Replacement
Symptomatic Severe MR• Any cardiac related Symptoms at rest
or exercise with (repair if feasible)
Asymptomatic MR EF <60%New onset Atrial Fibrillation
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Mitral Stenosis
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Mitral Stenosis
• Recurrent episodes: Progressive Valvular Damage • Residual and progressive valve deformity• 10-40% of older children 2-10 years after
previous ARF with MR• Fusion of the valve apparatus (at the level of the
valve commissures, cusps, chordal attachments, or any combination of these ) resulting in stenosis or a combination of stenosis and insufficiency
99% of MS in adults: Rheumatic etiology
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Mitral Stenosis
DefinitionLV inflow Obstruction: Impaired LV diastolic filling
Normal MV Area : 4-6 cm2
Basic Facts Onset of Symptoms
MV Area < 2 cm2 With Increasing
Transmitral gradientsPredominant Cause
Rheumatic HD
Prevalence and incidence
Decreasing due to a reduction of RHD
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Etiology of Mitral Stenosis
Rheumatic heart disease
77-99% of all cases
Mitral annular calcification
2.7%
Infective endocarditis
3.3%
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Mitral StenosisPathophysiology
Cause Physical Symptoms & Signs
impaired LA emptying resulting in Increasing PV Pressue in capillaries
Progressive Dyspnea (70%) due to pulmonary congestion
Palpitations(worsening with exercise,
fever, tachycardia, and pregnancy)
Increasing Transmitral Pressures
Haempotysis, Progressive Dyspnea , PND, Pedal Oedema, Increased JVP, Hepatomegaly LA enlargement; LA
DilatationPulmonary venous HTNRupture of bronchial vessels PAH RHF-CHF
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Natural History of MS
• Disease of plateaus: –Mild MS: 1 - 10 years after initial ARF–Moderate: 5 -10 years later– Severe: Beyond 10 years
Mortality
Pulmonary OedemaInfections-BE,LRI, andThromboembolismPulmonary EmbolismMGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Physical Exam Findings of MS
JVP prominent "a" wave
Signs of right-sided heart failure
in advanced disease
Mitral facies Severe MS & Cachexia with GRetdn
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

• Loud S1• Opening S1 snap: Apex when leaflets are
still mobile Due to the abrupt halt in leaflet motion in
early diastole, after rapid initial rapid opening, due to fusion at the leaflet tips
Shorter the S2 -OS interval, severer the MS
Heart Sounds in MS
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Low-pitched Diastolic Rumble Most Prominent at the Apex Best heard in the Left lateral position Bell of the stethExpiration Mild Exercise when in doubt
Heart Murmur in Mitral Stenosis
MidDiastolic Murmur
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Evaluation of MSCXR LA enlargement
Pulmonary congestionSigns of PAH
ECG LA enlargementAtrial Fibrillation
ECHO: GOLD STANDARD To Assess
MV Leaflet mobilityGradientMV AreaNature of damage
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Complications of Chronic RHD (Established Valvular disease )
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16
1. heart failure from valve insufficiency (acute rheumatic carditis)
2. Atrial Arrhythmias ( rare in children)
3. Pulmonary Edema4. Recurrent Pulmonary Emboli5. Infective Endocarditis6. Intracardiac Thrombus Formation 7. Systemic Emboli.

Management of MSSerial echocardiography
-blockers, CCBs, Digoxin which control heart rate and hence prolong diastole for improved diastolic fillingDuiretics for fluid overload
Mild: 3-5 YearsModerate:1-2 YearsSevere: Yearly
Medications
Medical therapy does not prevent progression as MS is a mechanical problem and MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Management of MS• Identify patient early who might benefit
from percutaneous mitral balloon valvotomy
REMEMBER to Implement :
IE Prophylaxis & Secondary RHD Prophylaxis
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Simplified Indications for Mitral valve replacement
• ANY SYMPTOMATIC Patient with NYHA Class III or IV Symptoms
• Asymptomatic moderate or Severe MS with a pliable valve suitable for PMBV
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Aortic Regurgitation
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Etiology of Aortic Regurgitation
• Physical Findings:Wide pulse pressureDiastolic murmurFlorid pulmonary edema
AcuteARF( 20-30% in children )EndocarditisAortic Dissection
Chronic ARBicuspid aortic valveRheumatic Infective endocarditisCollagen Vascular Disorders
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Pathophysiology of AR• Combined pressure & volume
overload
• Compensatory Mechanisms• LV dilation, LVH• Progressive dilation• Heart Failure
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Natural History of AR• Asymptomatic until 4th or 5th decade• Rate of Progression: 4-6% per year• Progressive Symptoms include:
- Dyspnea: exertional, orthopnea, and paroxsymal nocturnal dyspnea
- Nocturnal angina: due to slowing of heart rate and reduction of diastolic blood pressure
- Palpitations: due to increased force of contraction
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Physical Exam findings of AR• Wide pulse pressure: most sensitive• Hyperdynamic and displaced apical
impulse• Auscultation- –Diastolic blowing murmur at the left
sternal border– Austin flint murmur (apex): Regurgitant jet
impinges on anterior MVL causing it to vibrate – Systolic ejection murmur: due to increased
flow across the aortic valve MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Evaluation of AR
CXR enlarged cardiac silhouette and aortic root enlargement
ECHO Evaluation of the AV and aortic root with measurements of LV dimensions and function (cornerstone for decision making and follow up evaluation)
AortographyMGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Management of AR• General: IE prophylaxis in dental
procedures with a prosthetic AV or history of endocarditis.
• Medical: Vasodilators (ACEI’s), Nifedipine improve stroke volume and reduce regurgitation only if pt symptomatic or HTN.
• Serial Echocardiograms: to monitor progression.
• Surgical Treatment: Definitive TxMGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

Simplified Indications for Surgical Treatment of AR
• ANY Symptoms at rest or exercise• Asymptomatic treatment if:–EF drops below 50% or LV becomes
dilated
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16

THANK YOU
MGMCRI- 8th&9th Semesters MBBS-UG PEDIATRICS Theory Lecture 12 th Feb 16