Reproductive cloning Biotechnology/Cloning. Reproductive cloning.
REPRODUCTIVE CLONING
description
Transcript of REPRODUCTIVE CLONING

REPRODUCTIVE CLONING
Definition = making an exact genetic copy of an organism.
Occurs naturally with identical twins
Lab methods - artificial twinning- Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer

Artificial Twinning
• Similar to how identical twins form
• Early stage embryo (blastocyst) is pulled apart
artificial twinning process

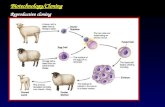
Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer
• Somatic cell = any body cell (not sex cells)
• Oocyte = egg
• Enucleated = nucleus is removed; click link and select “Enucleation Video” on right-hand side

Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer cont.
• In SCNT, any somatic cell is fused with an enucleated donor oocyte.
• “Fertilized egg” is given a shock and transferred into a surrogate female.
• Result is genetically identical to the somatic cell donor. (Animation)


Why Clone?
• Preserving endangered or recreating extinct animals.
• Restoring the life of a lost pet.

Why Clone?
• Making exact copies of livestock or crops that have prized traits.

What animals have been cloned?ANIMALS THAT HAVE CLONED BY SCNT• Tadpole• Carp• Sheep• Pig (xenotransplantation = using animal organs in humans)• Gaur• Cattle• Cat• Mule• Deer• Horse (Champion the Wonder Clone)• Rat• Fruit Flies• Dog
ANIMALS THAT HAVE BEEN CLONED BY ARTIFICIAL TWINNING• Rhesus Monkey


What animals have been cloned?ANIMALS THAT HAVE BEEN CLONED BY ARTIFICIAL TWINNING• Rhesus Monkey

Any Problems With Cloning?• Video
1. High Failure Rate
- Success rate ranges from 0.1 – 3%
- Dolly was result of 277 attempts!

Any Problems With Cloning?
2. Large Organ Syndrome • Kidney, brain, immune system malformation

Any Problems With Cloning?3. Abnormal gene
expression
• Same genes, but body isn’t using them the same as the original.

Any Problems With Cloning?4. Telomere is too short
• Shorten as we age
• Dolly started with shorter than normal telomeres
• Developed arthritis at an early age

Cloning Misconceptions
• Myth #1 – Instant Clone

Cloning Misconceptions• Myth #2 – Carbon Copies
• Nature vs Nurture
• In females, X-inactivation- each cell can’t have multiple copies of the X chromosome
- each cell randomly chooses which X chromosome to inactivate
- female clones are not phenotypic clones

Should we clone humans?